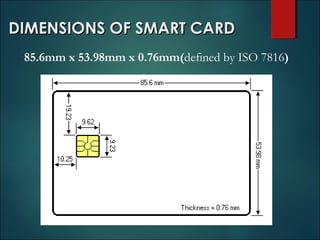
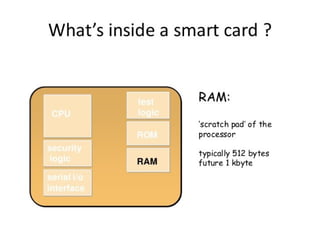
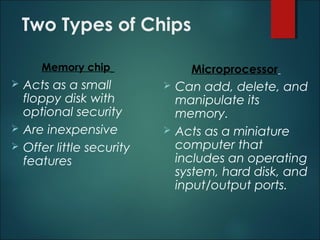
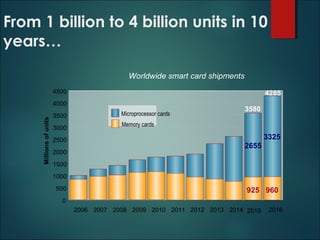
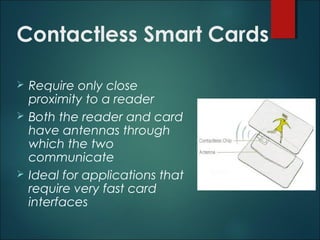
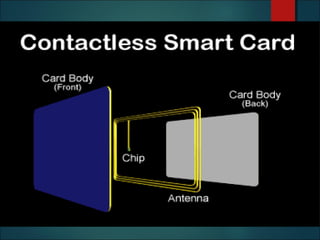
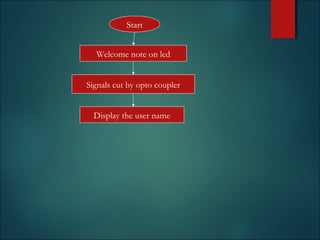
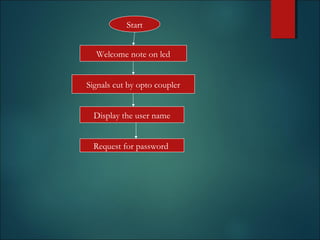
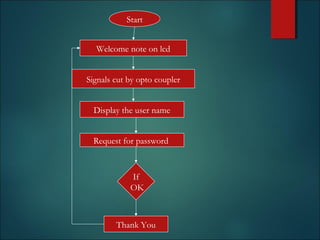
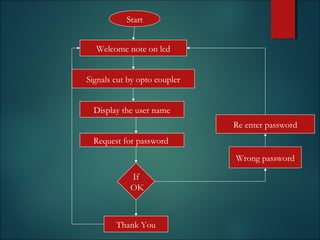
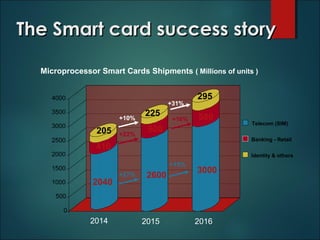
This document discusses smart cards, their history, and applications. It provides an overview of smart cards including their dimensions and components. Smart cards first emerged in the 1970s and are now used widely for applications such as payment, transportation ticketing, healthcare, and identification. The document outlines the growth of smart card usage and shipments between 2006-2016. It describes the two main types of smart card chips and discusses contact and contactless smart cards. Examples of smart card applications include banking, mobile phones, transportation, and loyalty programs. Advantages include flexibility, security, and portability, while disadvantages include potential security issues. The document predicts continued growth in smart card usage through 2020.