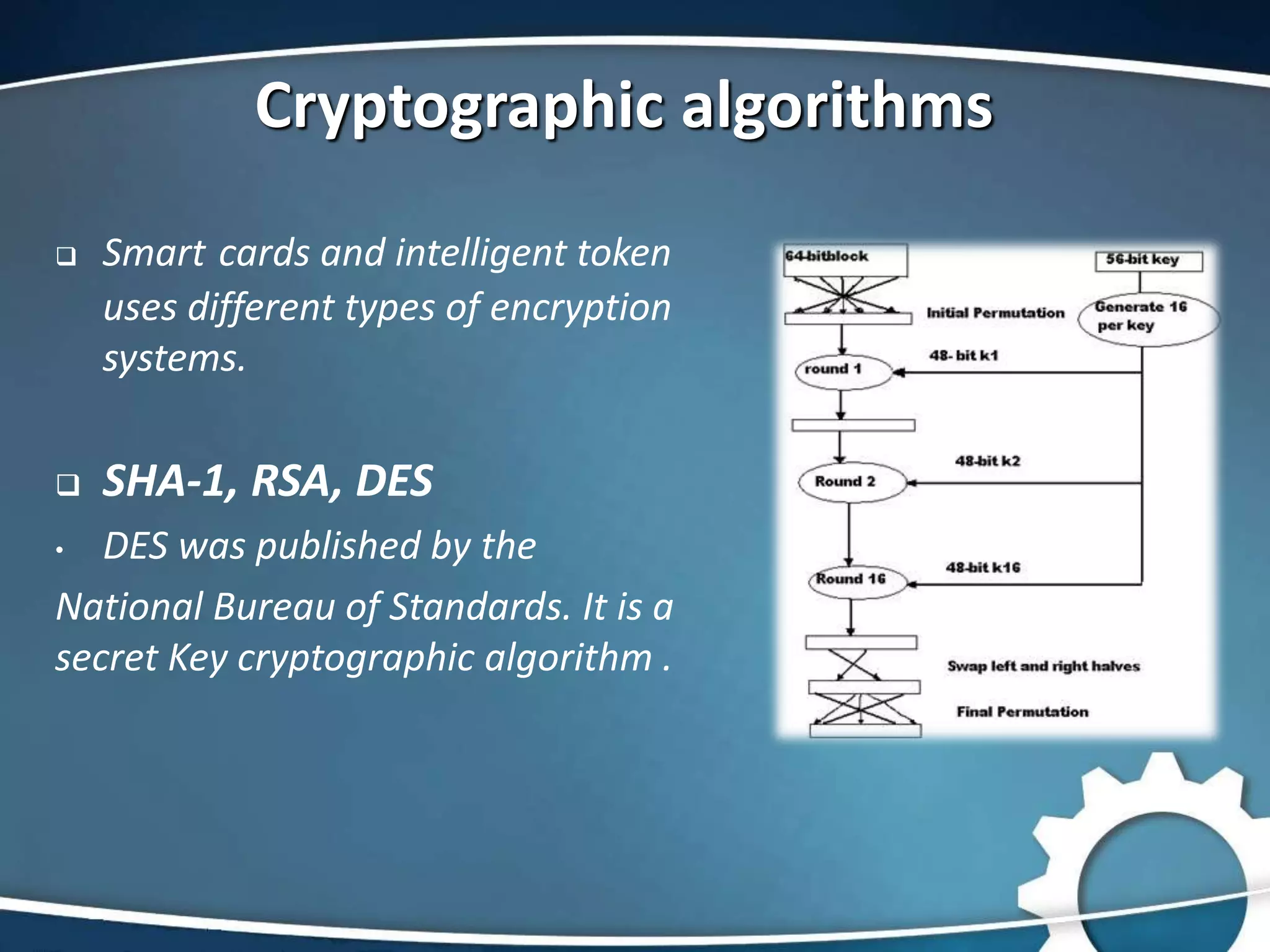
Smart cards are small, secure devices containing microprocessors or memory chips that provide cryptographic services and data protection. Their applications span across various sectors including government, e-commerce, and healthcare. Despite their advantages in security and convenience, smart cards face challenges such as potential liability issues if lost or stolen and the risk of hacking.