RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology enables the electronic identification and tracking of objects using radio signals, consisting of tags, readers, and a computer system. It offers advantages such as non-line-of-sight scanning, automation, and increased data storage compared to barcodes, with applications in various fields including healthcare, libraries, and airports. The document discusses different types of RFID tags, their operation, and specific uses in real-time tracking and inventory management.

![ Introduction
Components in RFID technology
Electronic Product Code [EPC]
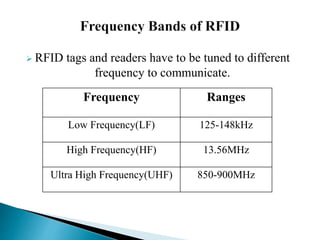
Frequency Bands of RFID
Working of RFID System
Advantages of RFID technology
Applications Of RFID
Conclusion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rfid-161103153545/85/RFID-2-320.jpg)
![ RFID [Radio Frequency Identification] is a
technology to electronically record the presence of an
object using radio signals.
This technology is used for automatically identifying
a person, a package or an item.
RFID is not a replacement for the bar coding, but a
complement for distant reading of codes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rfid-161103153545/85/RFID-3-320.jpg)


![An Electronic Product Code (EPC) is one common
type of data stored in a tag.
When written into the tag by an RFID printer, the tag
contains a 96-bit string of data.
The first 8 bits are a header which identifies the
version of the protocol.
Electronic Product Code [EPC]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rfid-161103153545/85/RFID-7-320.jpg)
![ The next 28 bits identify the organization that
manages the data for this tag.
The next 24 bits identifies the kind of product.
The last 36 bits are a unique serial number for a
particular tag.
The last 2 fields are set by the organization that issued
the tag
EPC [Contd…]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rfid-161103153545/85/RFID-8-320.jpg)

![2. Passive Tag
Have no internal power supply
Electrical current induced in antenna by the
incoming signal provides power for integrated
circuit in tag to power up and transmit response
Very Small i.e.Thinner than a sheet of paper,
Limited Range, Unlimited Life
TAG TYPES [Contd..]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rfid-161103153545/85/RFID-10-320.jpg)
![3. Semi Passive Tag
Similar to passive tags, with the
addition of a small battery
Battery powers the integrated circuit
Bigger, Longer Range, Limited Life
TAG TYPES [Contd…]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rfid-161103153545/85/RFID-11-320.jpg)


![An RFID reader transmits radio signal to the tag.
The reader broadcast the RF signal through antenna.
The tag receives the signal and get charged up if it
is a passive tag and then responses to the reader.
While it is a active tag it will respond after
receiving the signal from the reader.
The RFID tag receives the message and then
responds with its identification and other
information.
Working of RFID System[contd..]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rfid-161103153545/85/RFID-15-320.jpg)
![ The information may be serial number, or
product-related information such as a stock
number, lot or batch number, production date, or
other specific information
Then the antenna reads the data and sends to
reader.
The reader sends the information to computer for
processing the information
Working of RFID [contd…]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rfid-161103153545/85/RFID-16-320.jpg)










