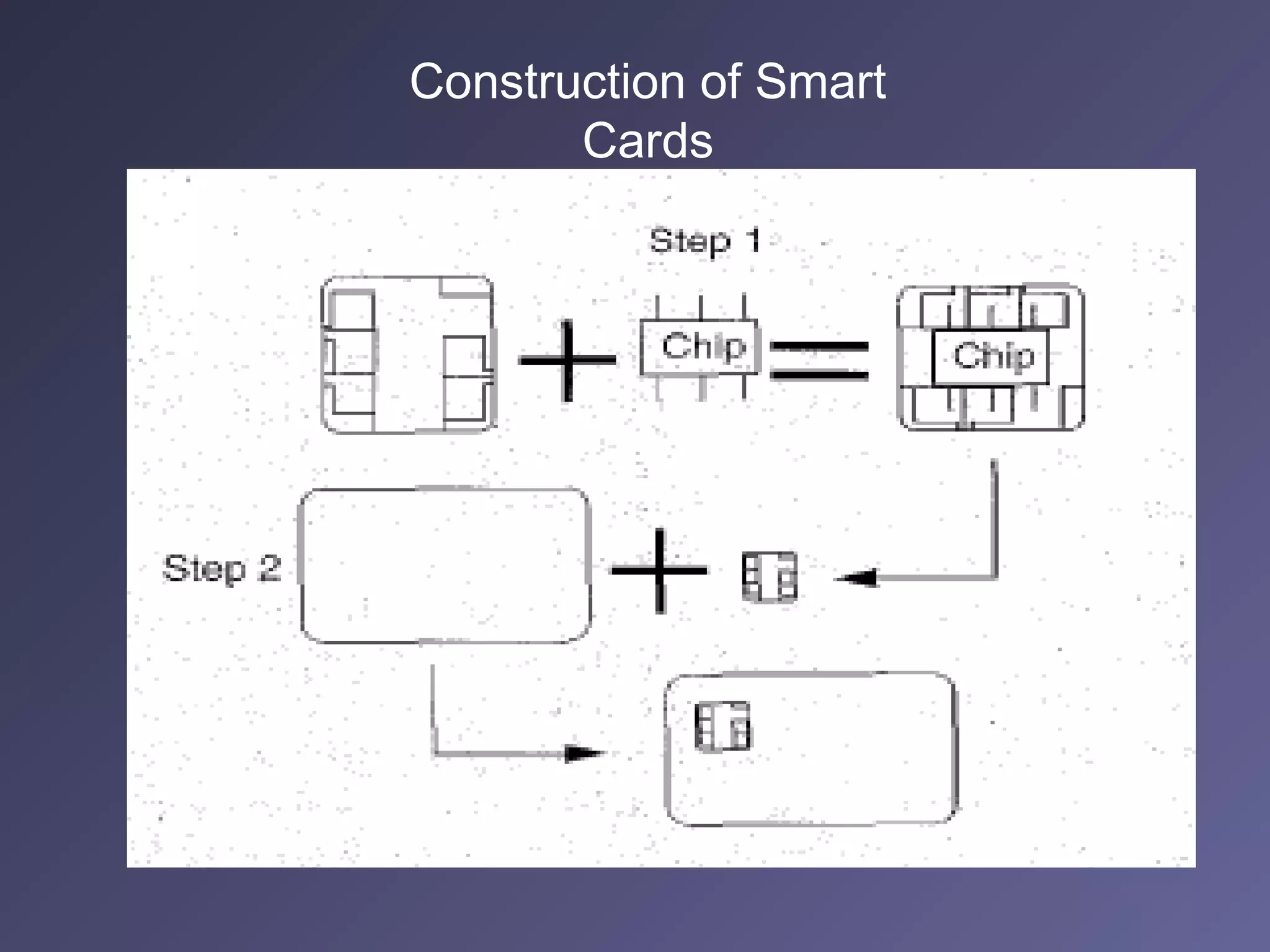
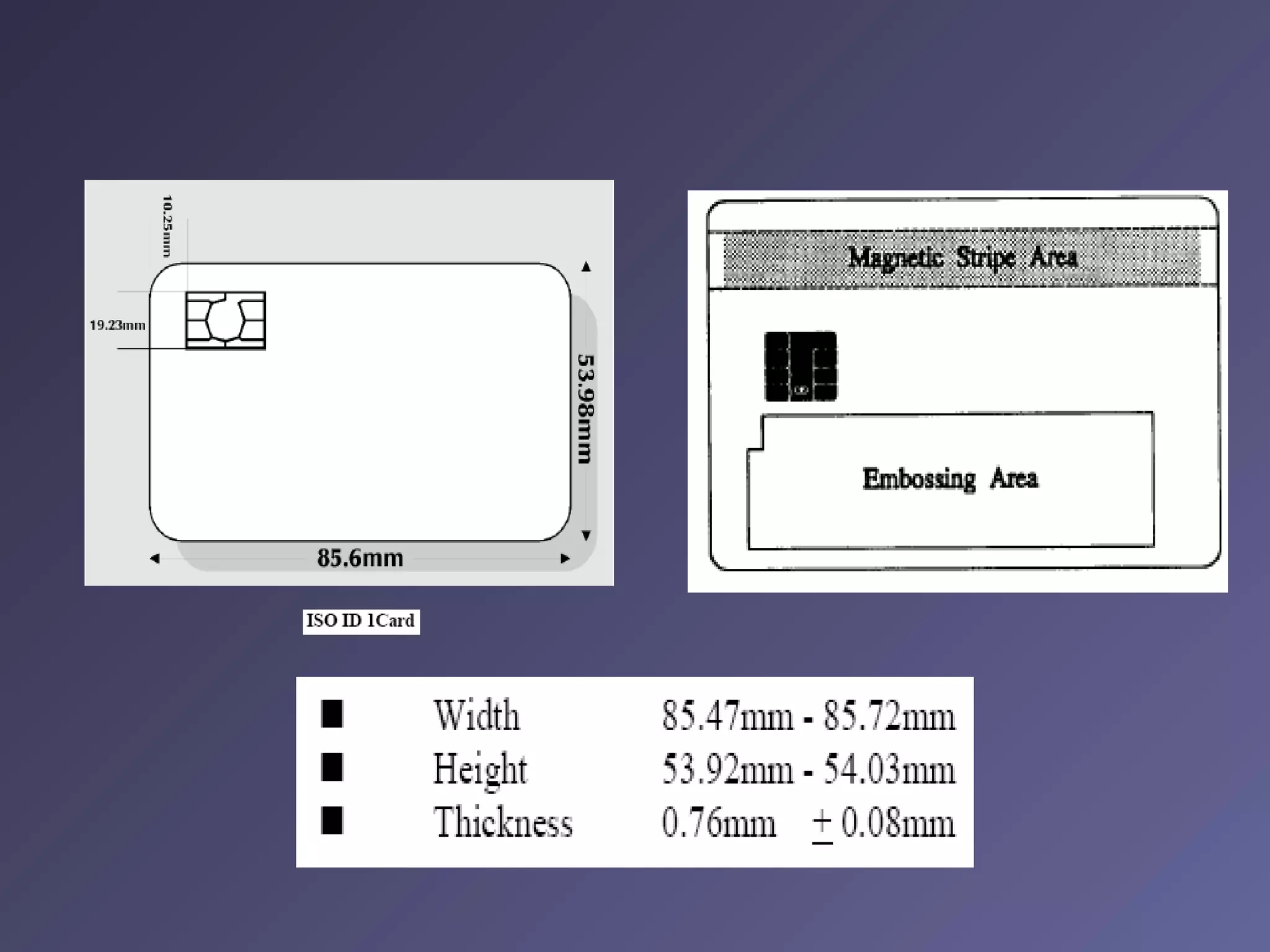
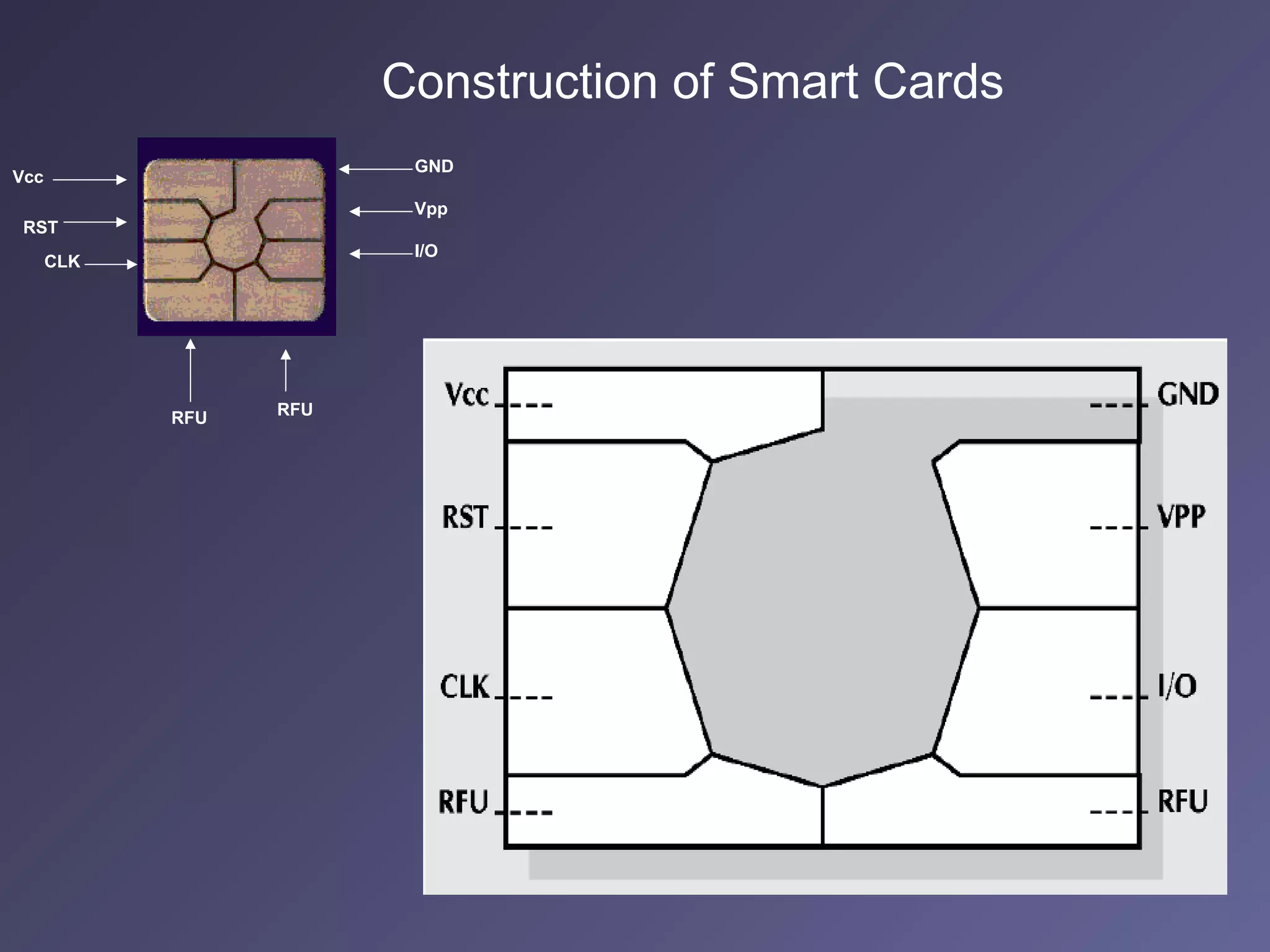
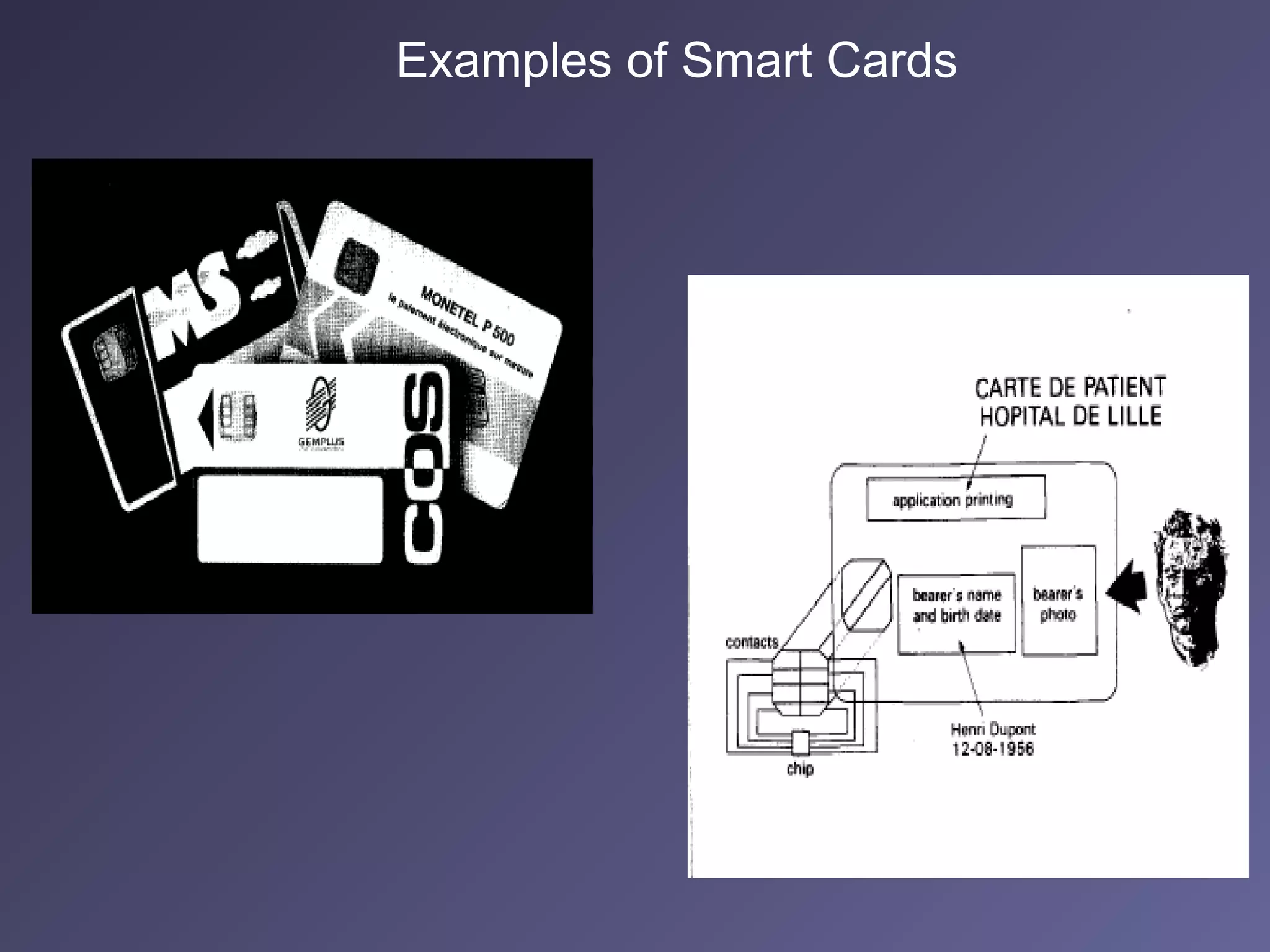
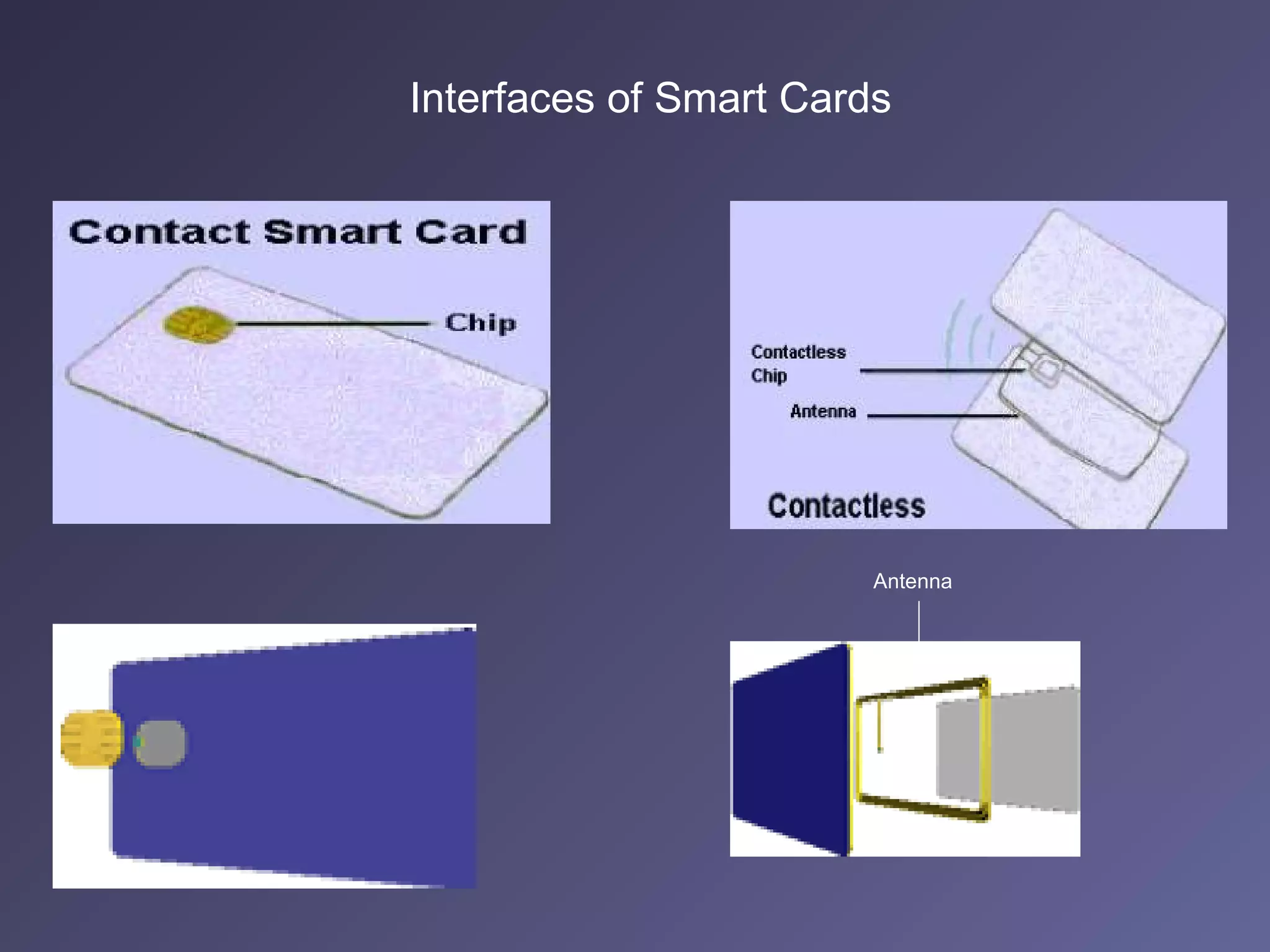
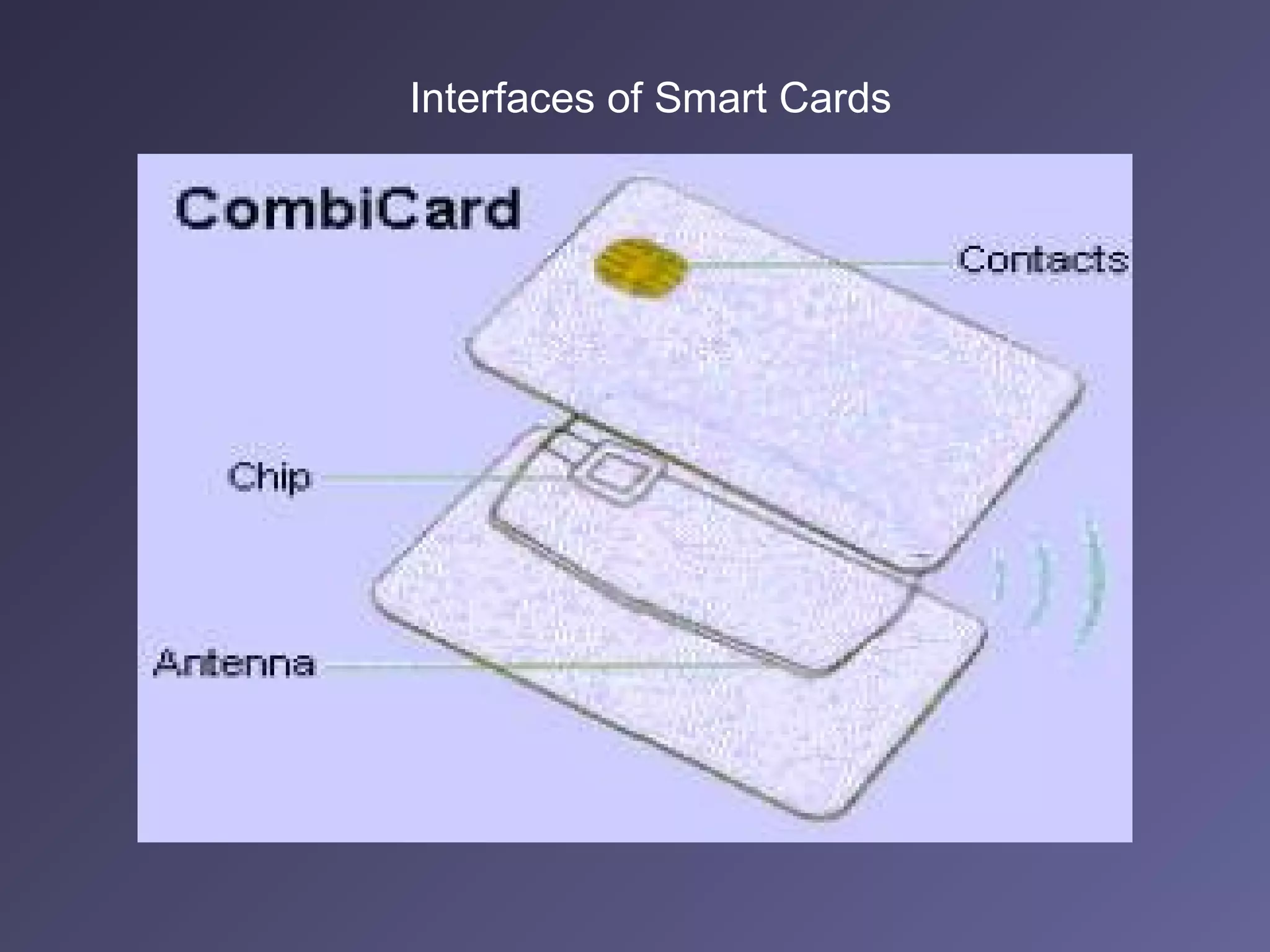
Standard credit card-sized plastic cards contain an embedded silicon microchip, known as a smart card. There are two main types: memory-only chips and microprocessor chips. Smart cards can receive, process, and make decisions based on information. They can hold up to 32,000 bytes of data and include math co-processors to perform encryption routines quickly. Smart cards provide flexibility, security, portability and increasing data storage capacity for applications like banking, retail, mobile communications, electronic purses, ID verification, and access control. While advantageous, security remains a disadvantage that developers continue working to address for the future of uses in health, education, transportation, and telecommunications.