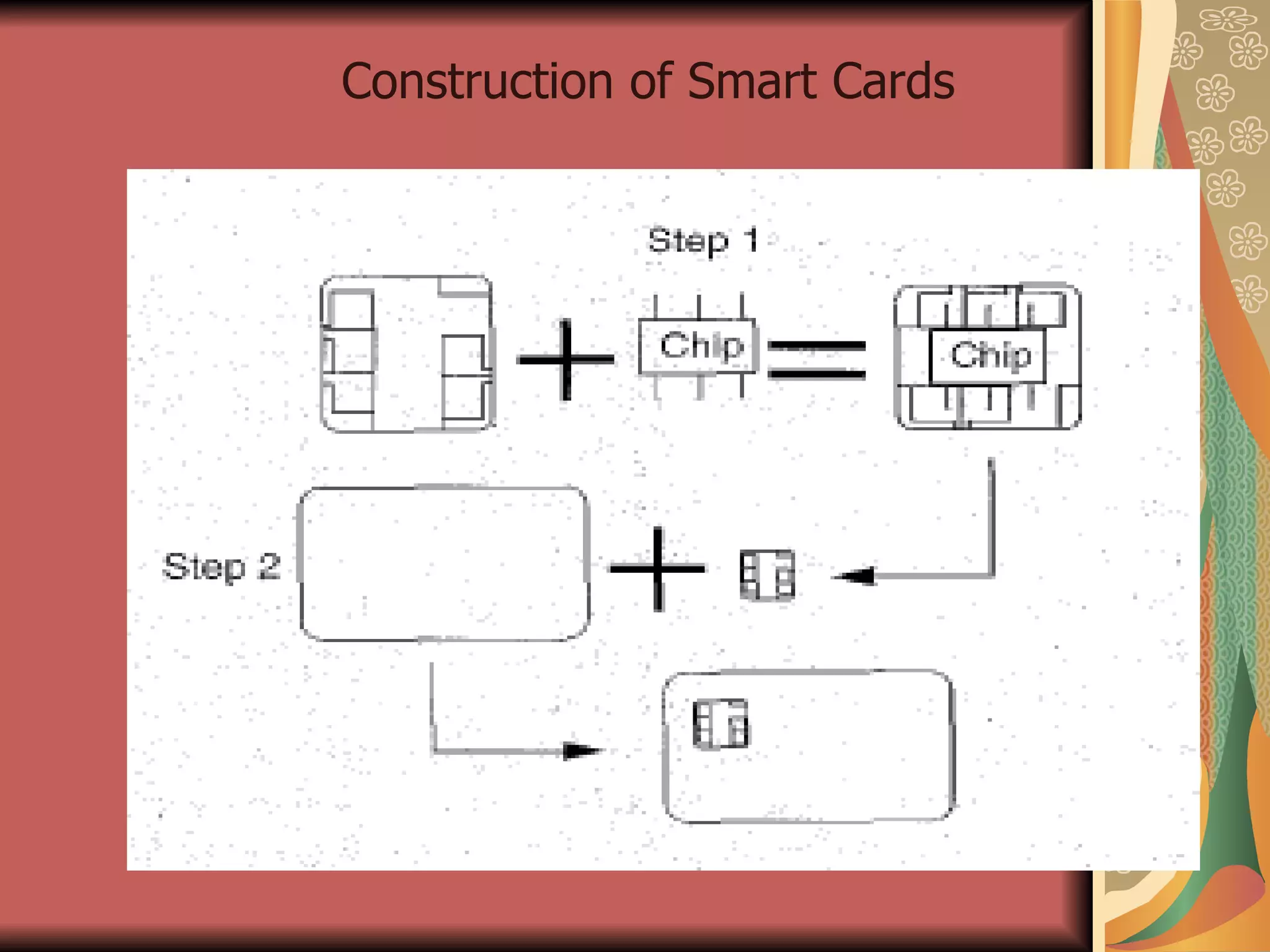
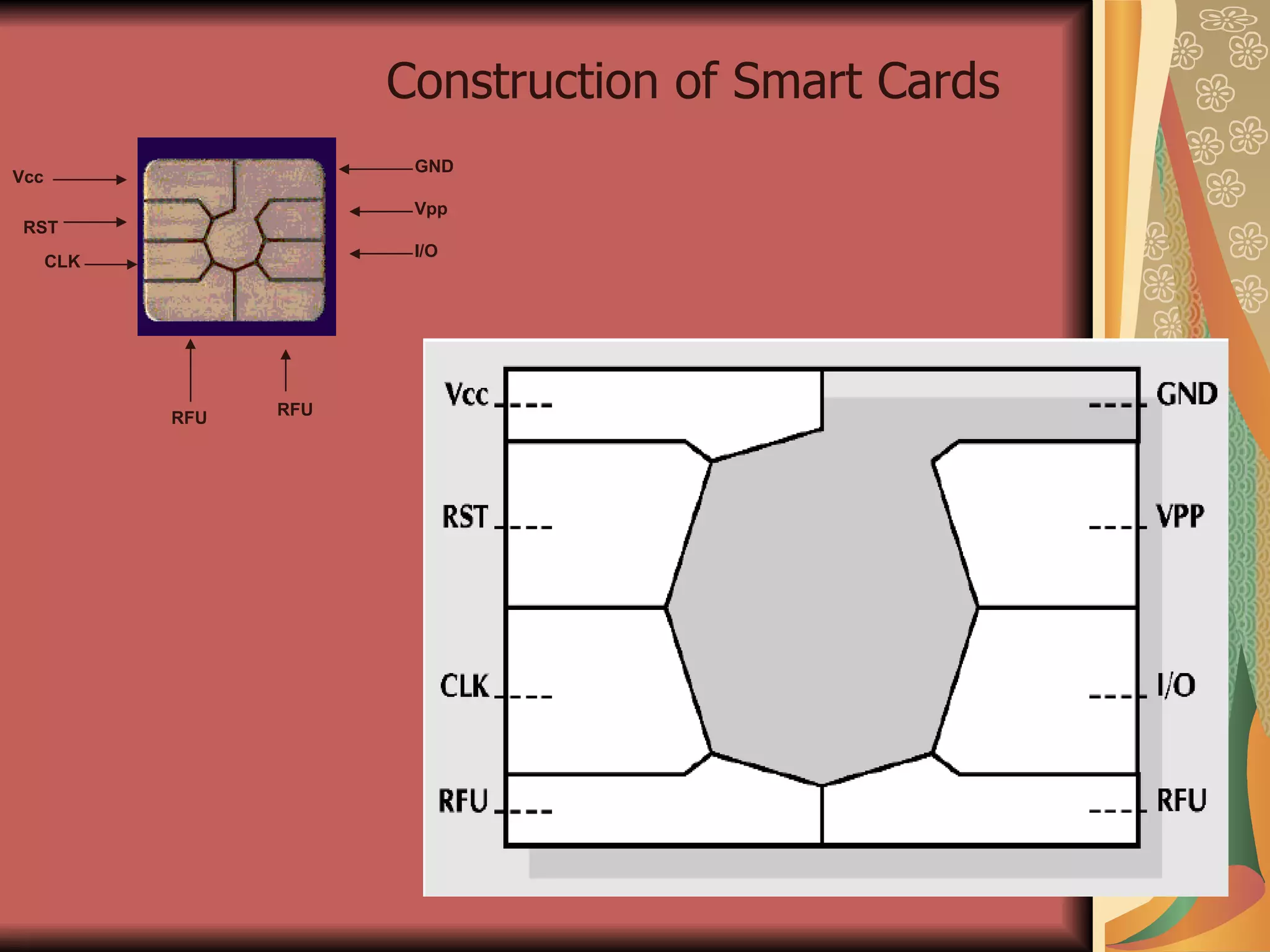
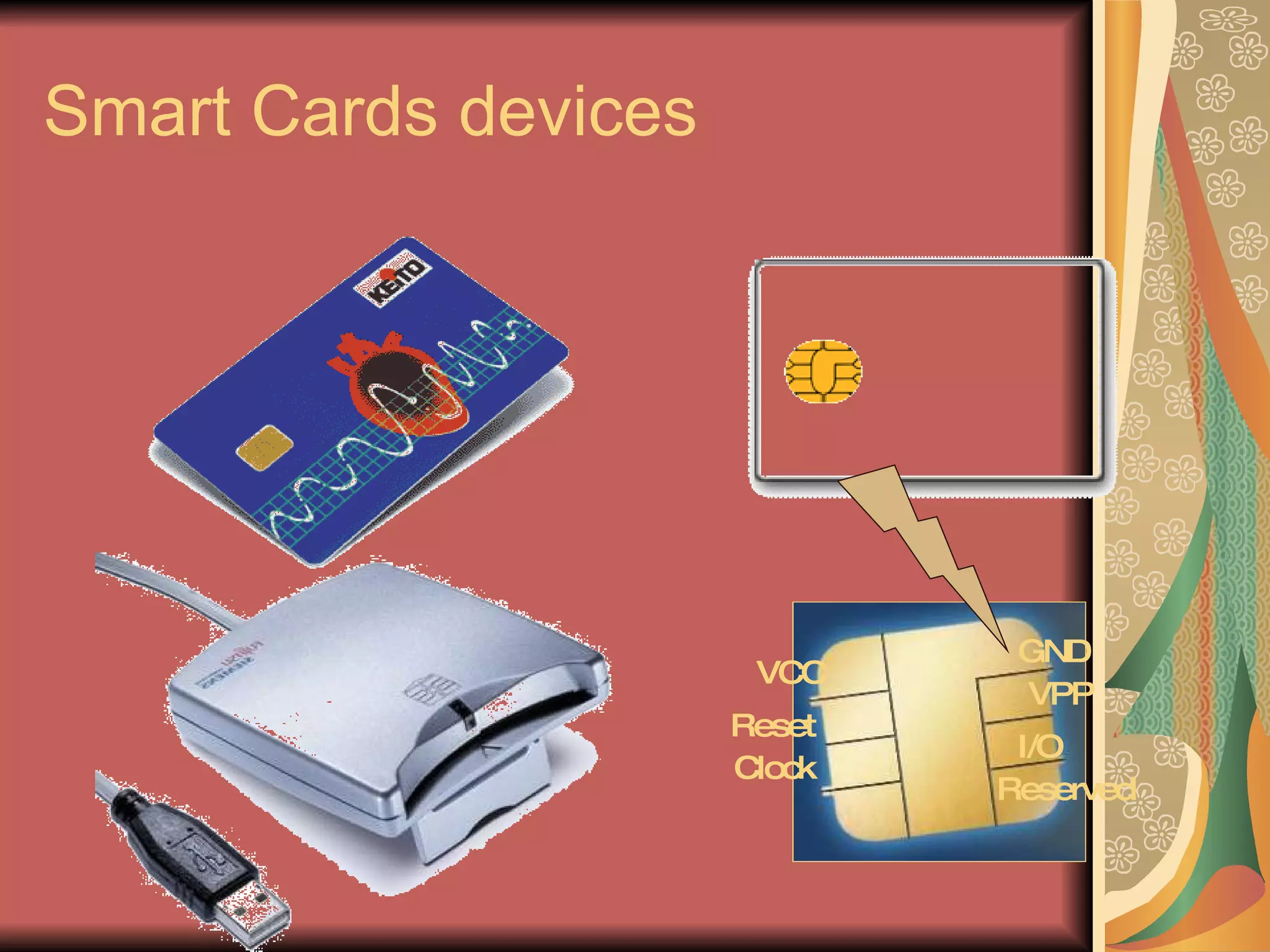
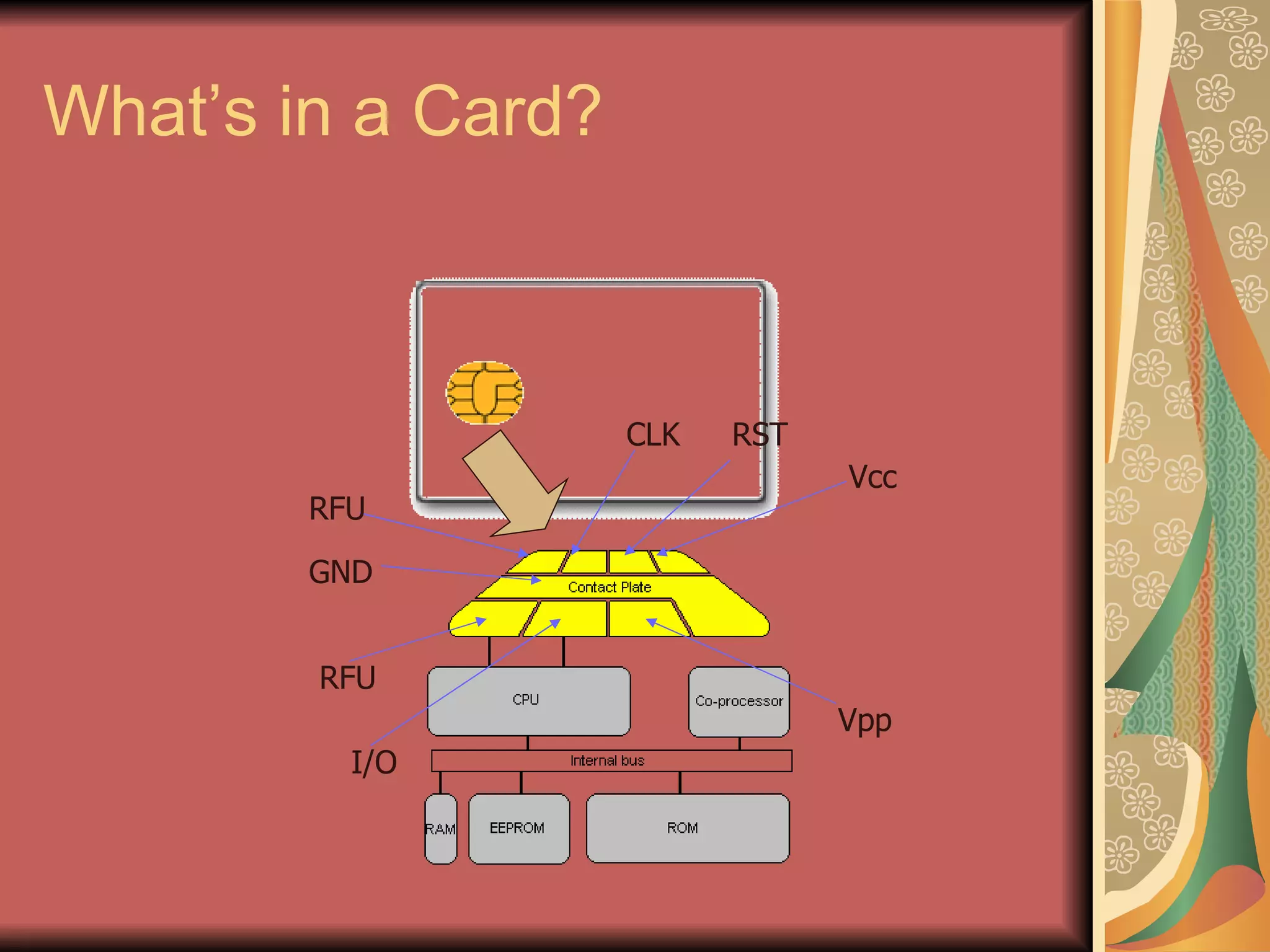
The document discusses smart cards, which are portable devices containing non-volatile memory and a microprocessor that provide improved security for transactions. Smart cards come in two types - memory-only chips and microprocessor chips. They allow for tamper-proof storage of user identity and provide security mechanisms like passwords, cryptographic challenges, and biometric authentication. Communication between smart cards and readers is standardized using the ISO 7816 protocol. Current applications of smart cards include payments, mobile communications, banking, electronic purses, healthcare, and ID verification.