1. Language is a system of symbols used to communicate ideas between individuals that must be learnable by children and understandable by adults.
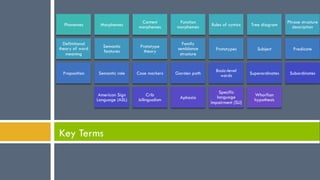
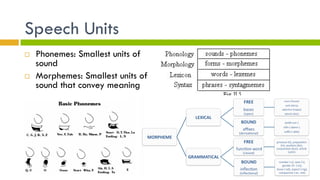
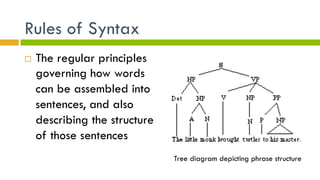
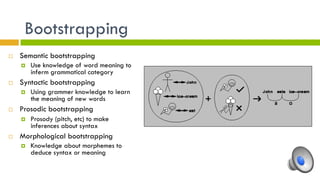
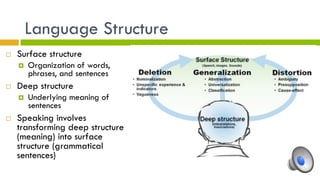
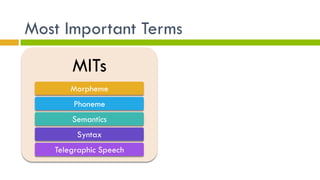
2. Language has building blocks including phonemes, morphemes, phrases, sentences, and rules of syntax. It conveys meaning through semantic features, prototypes, and semantic roles.
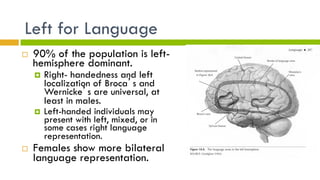
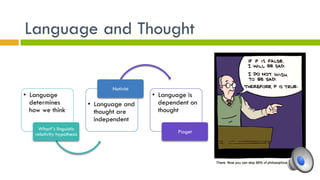
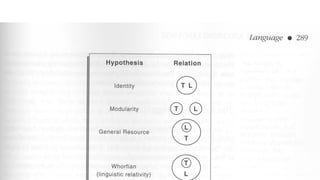
3. Theories of language development include nativist, nurturist, and interactionist views. Children progress from babbling to first words to telegraphic speech to grammatically correct sentences according to developmental stages.