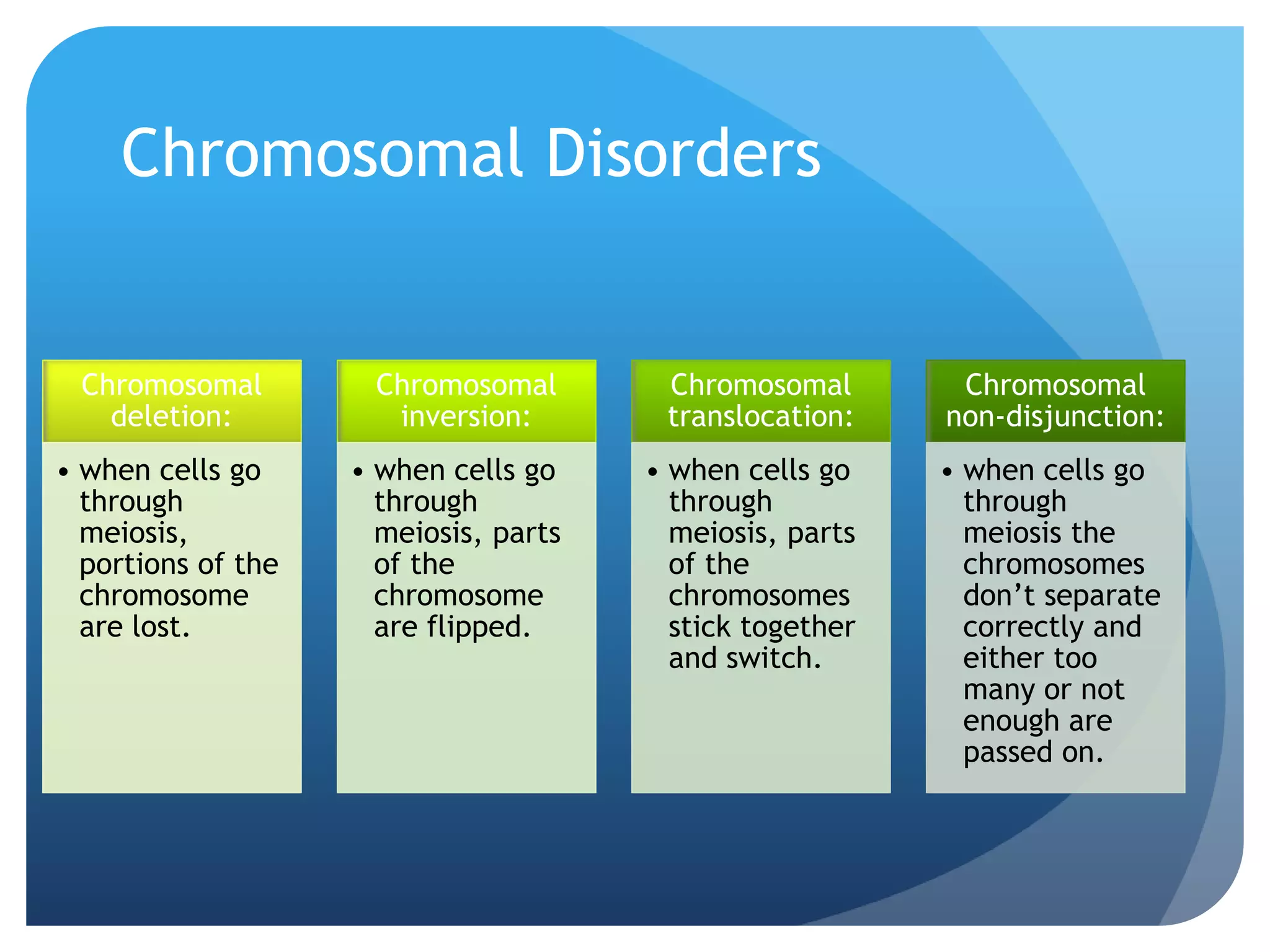
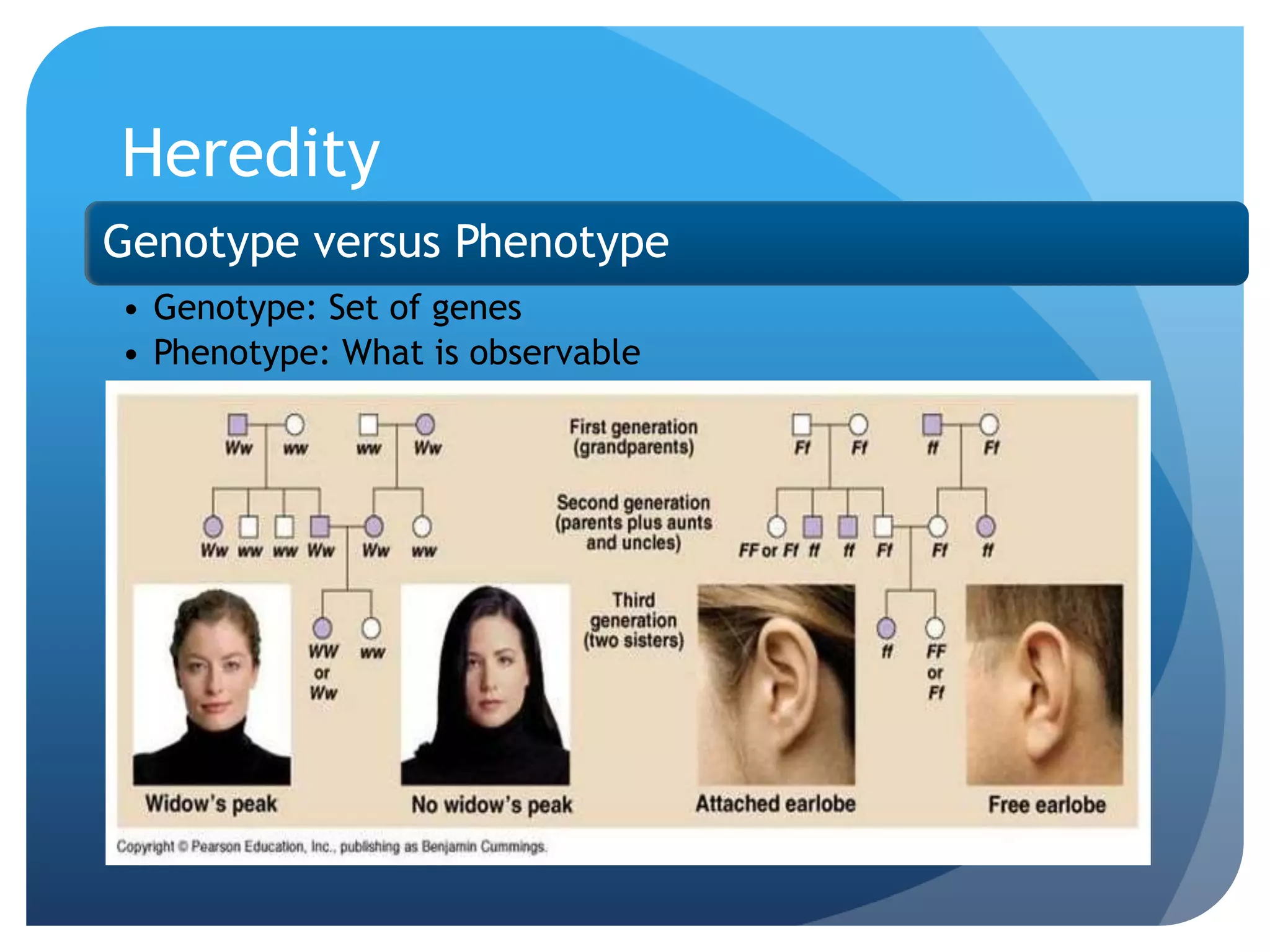
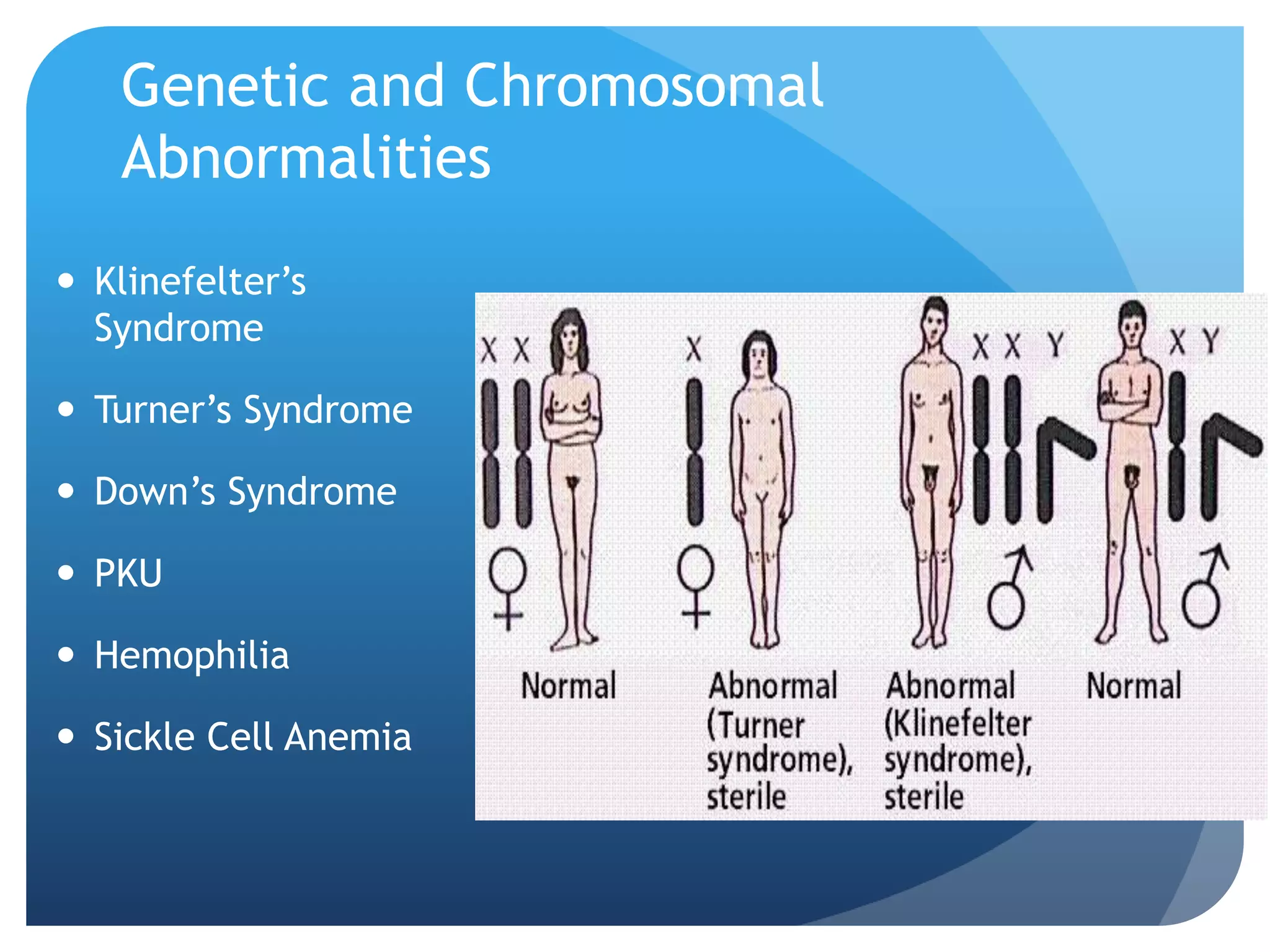
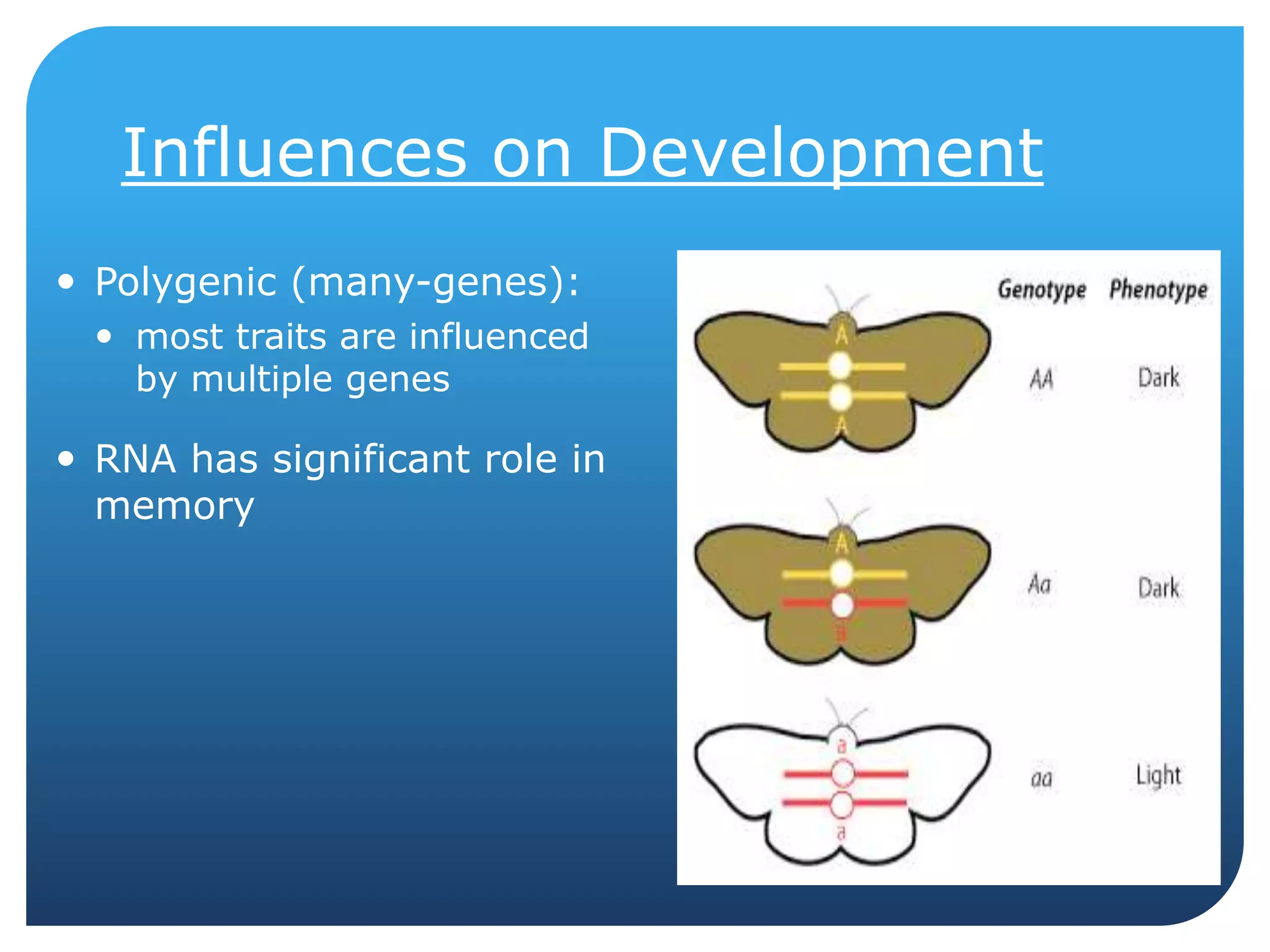
This document provides an overview of a course on the genetic and evolutionary roots of behavior. It covers several key topics:
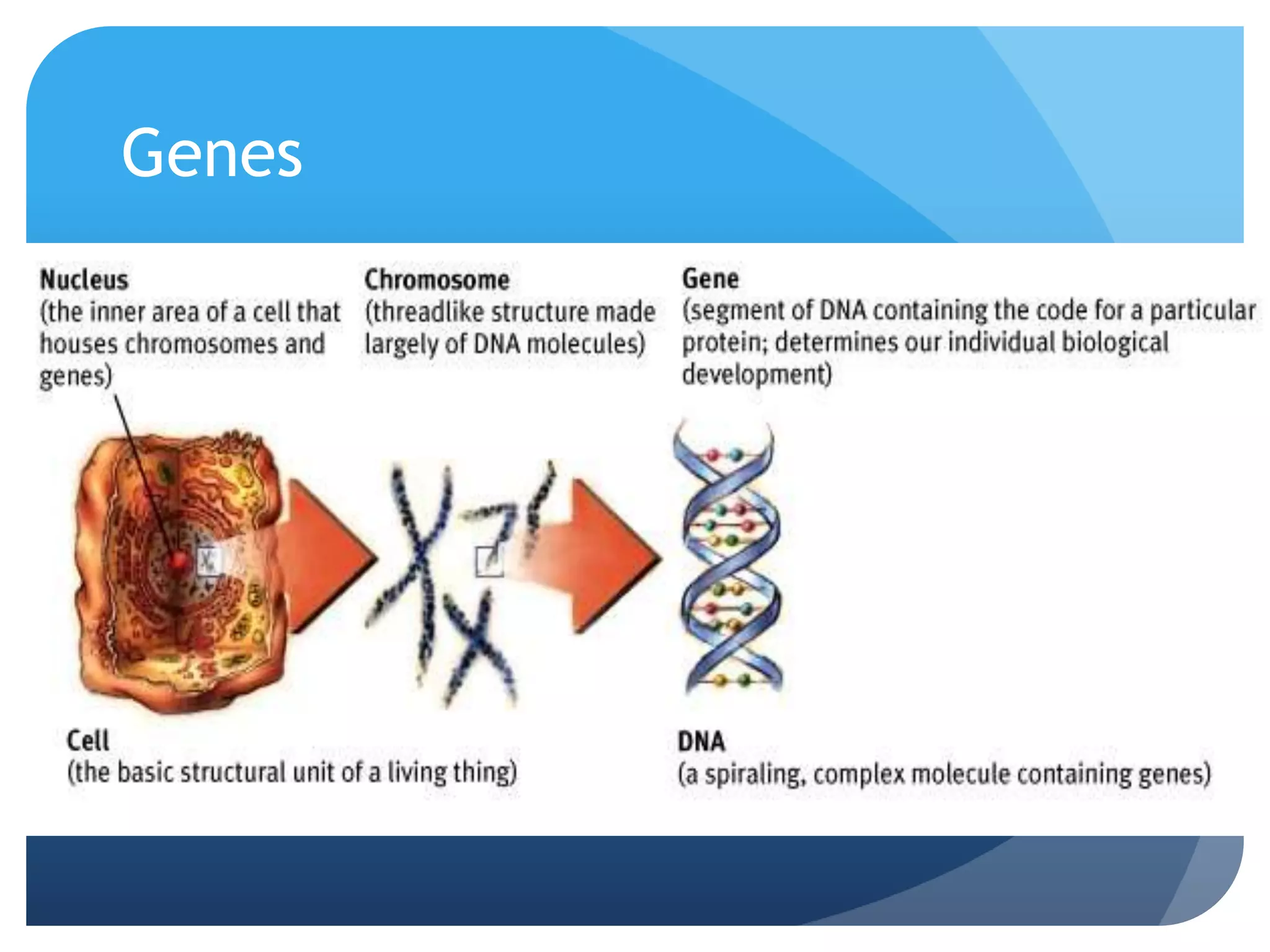
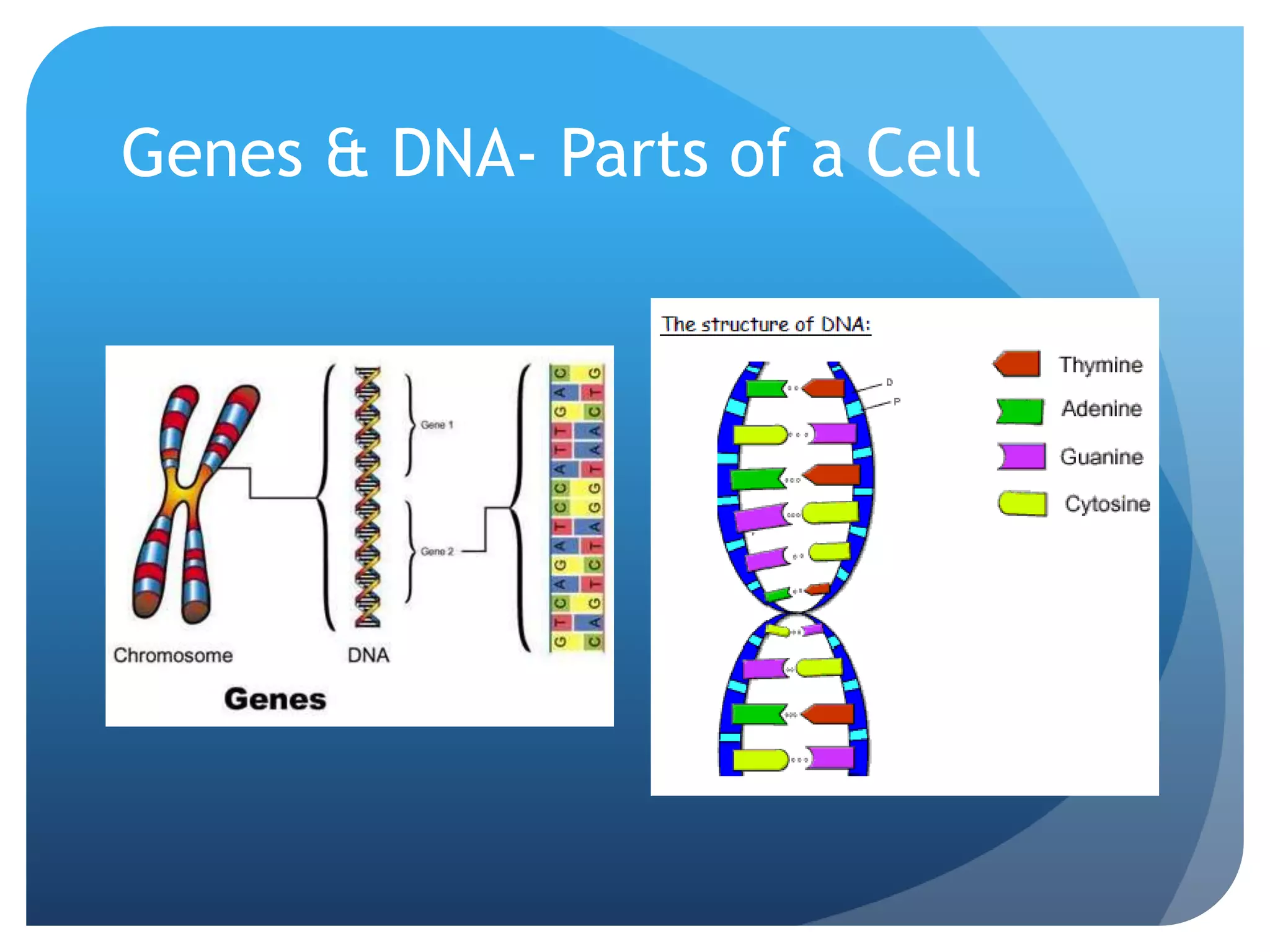
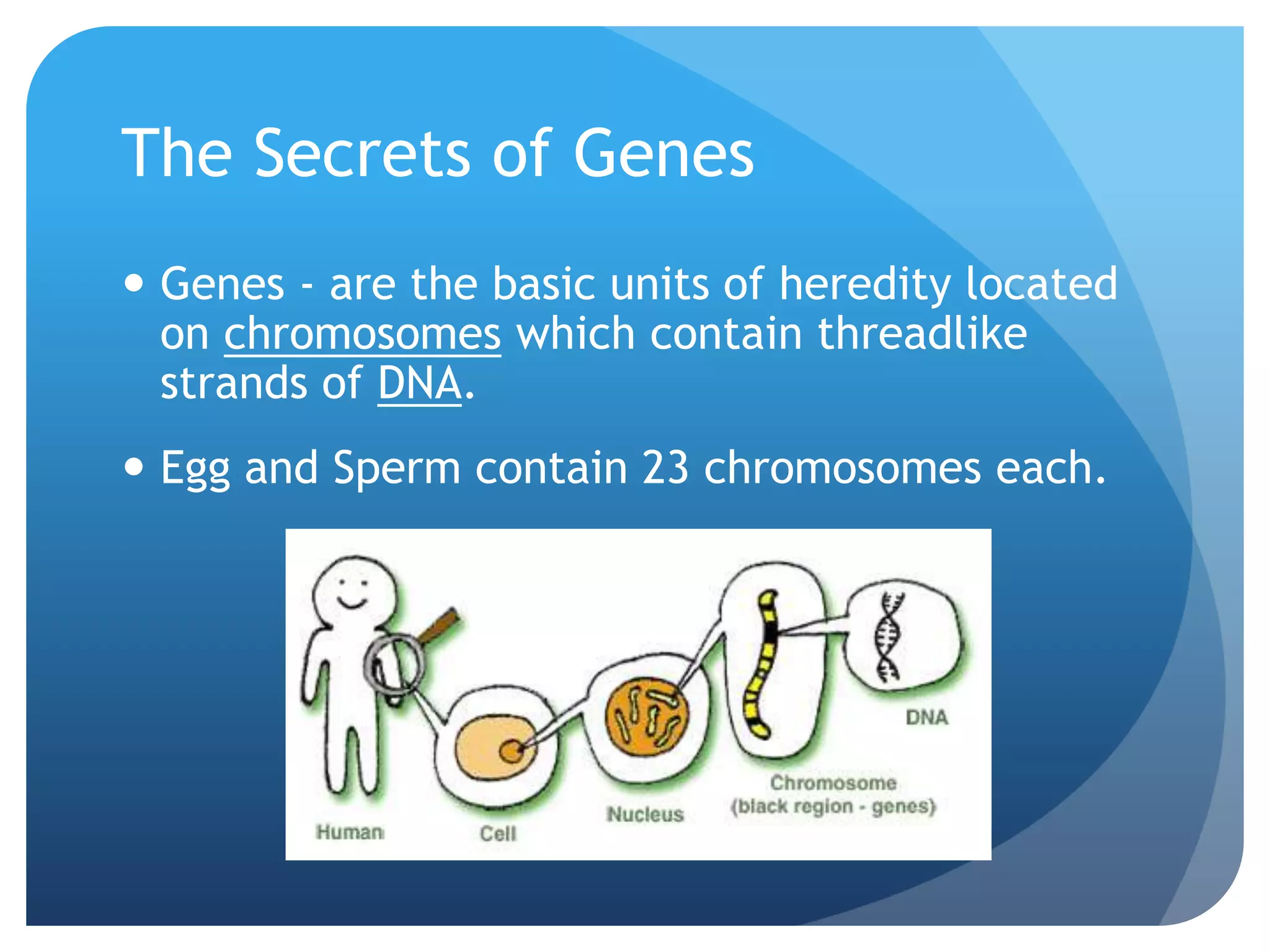
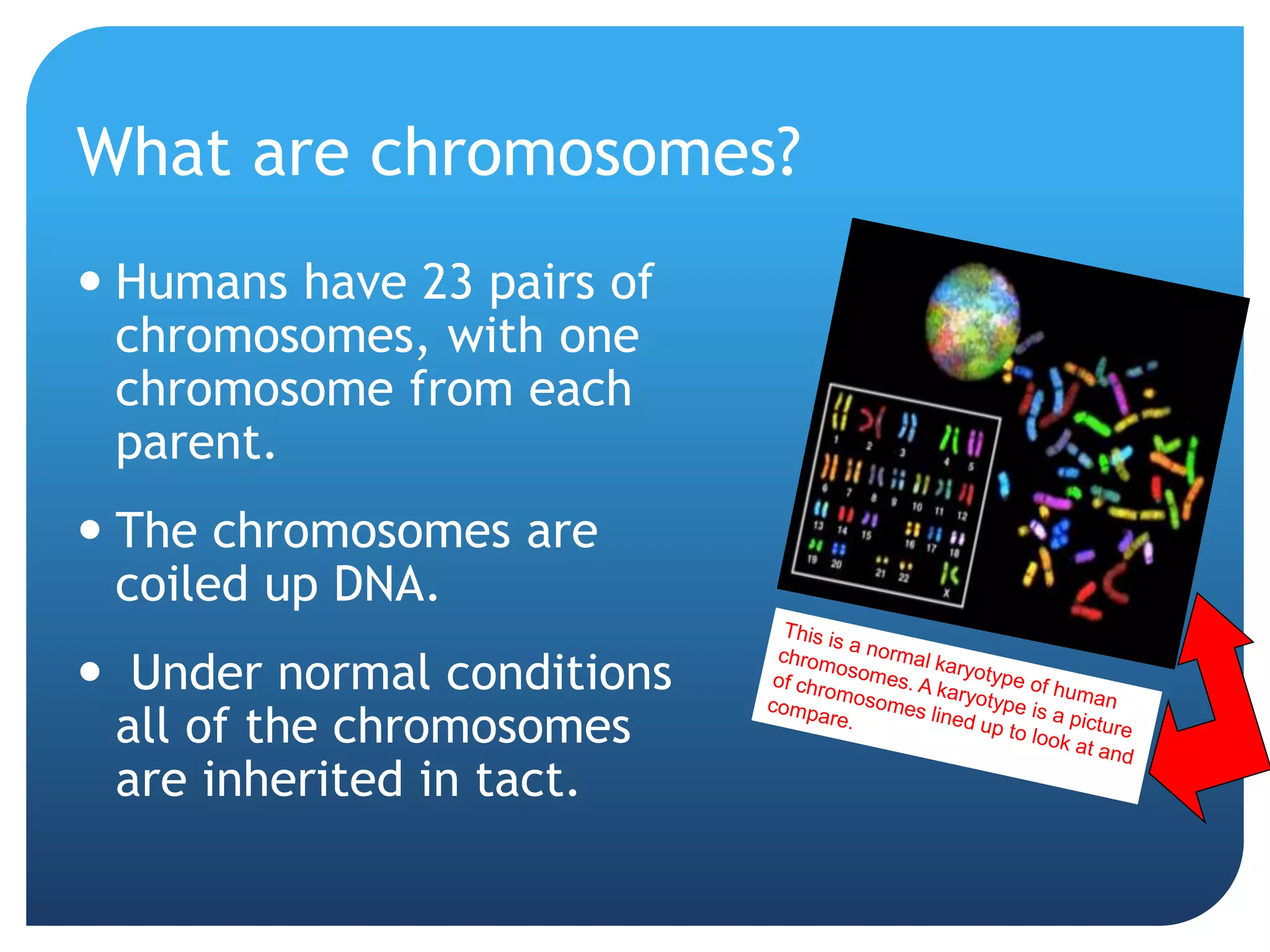
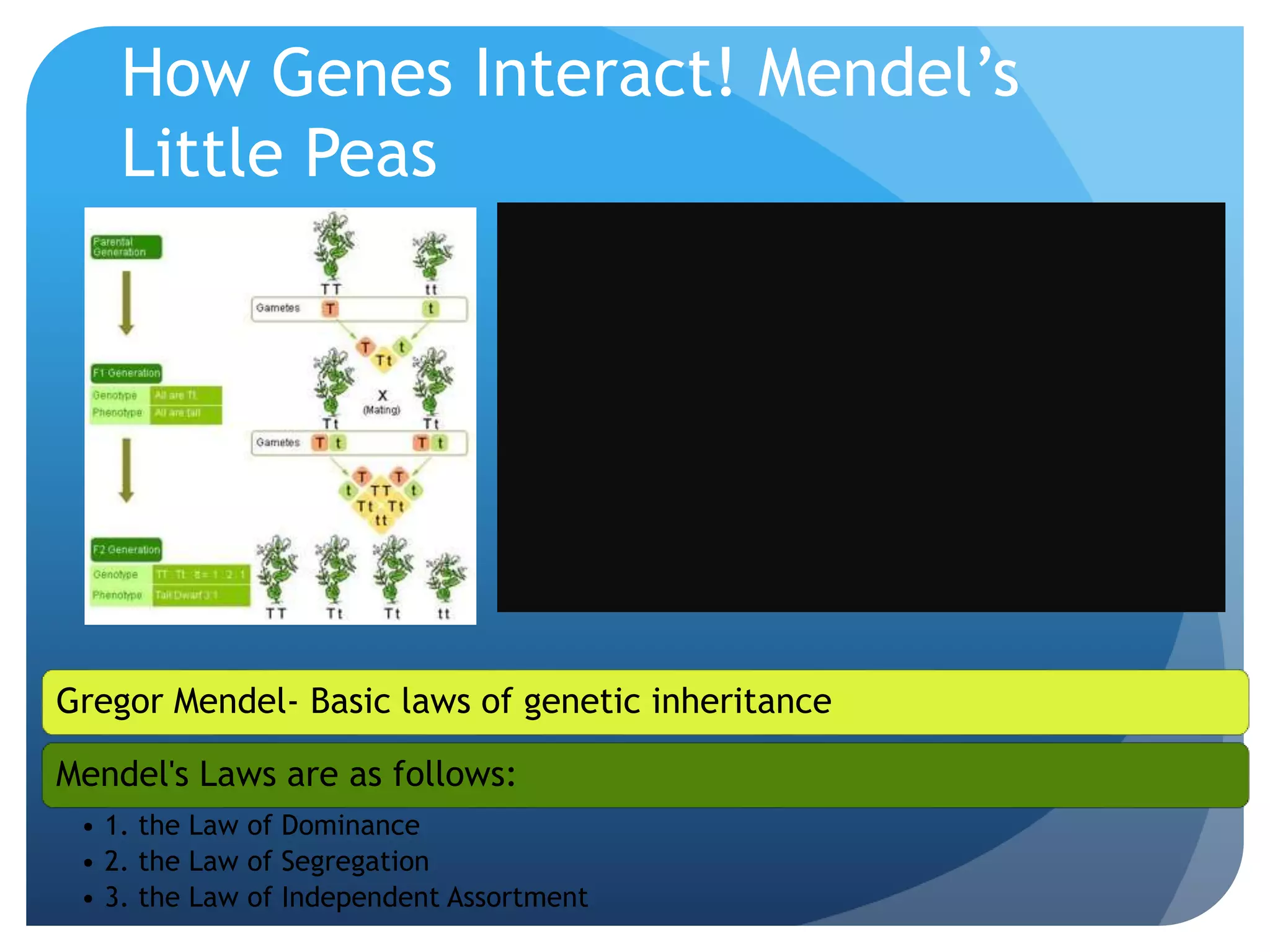
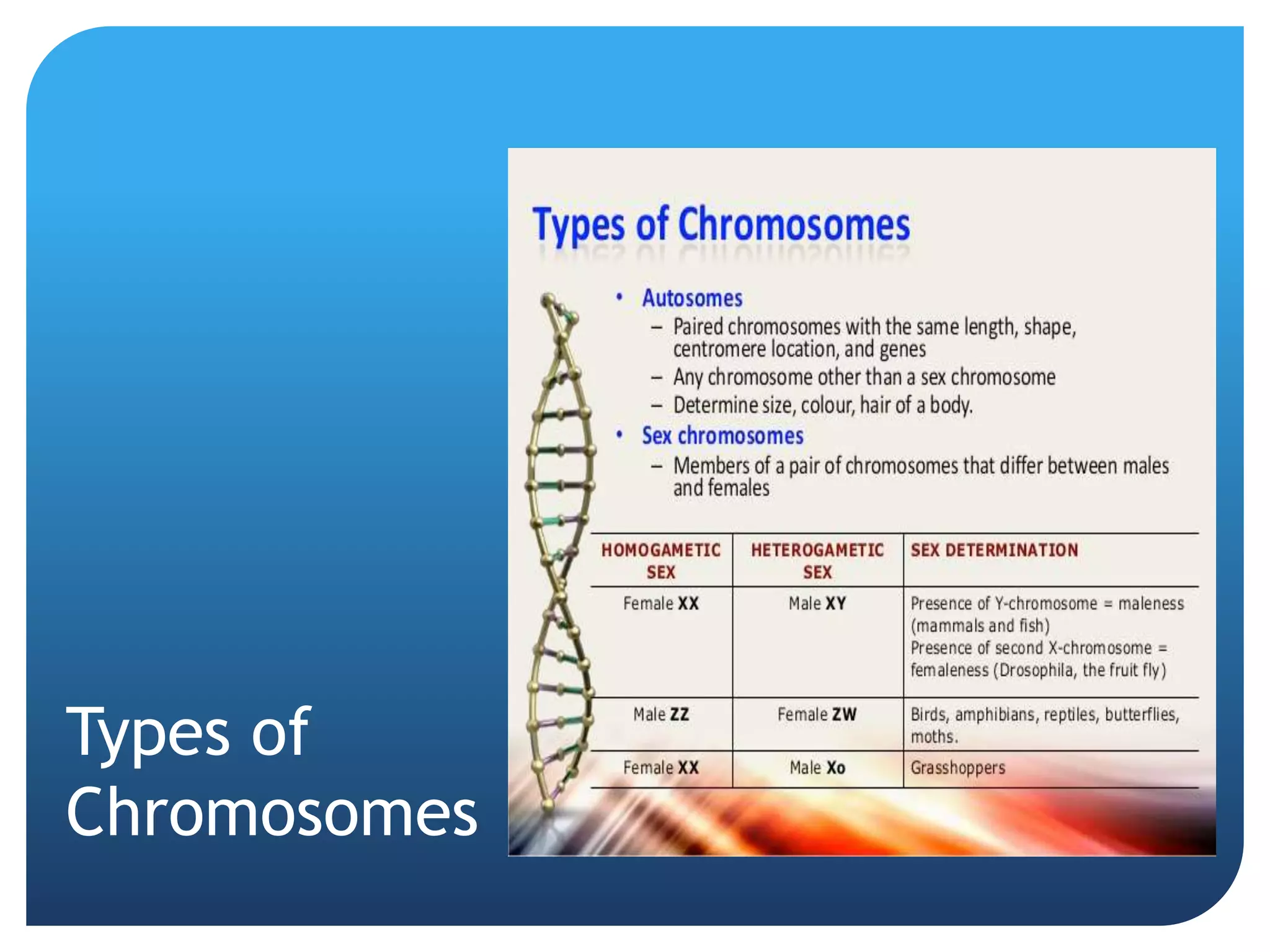
1. Genetics including DNA, genes, chromosomes, genetic transmission, and genetic influences on traits.
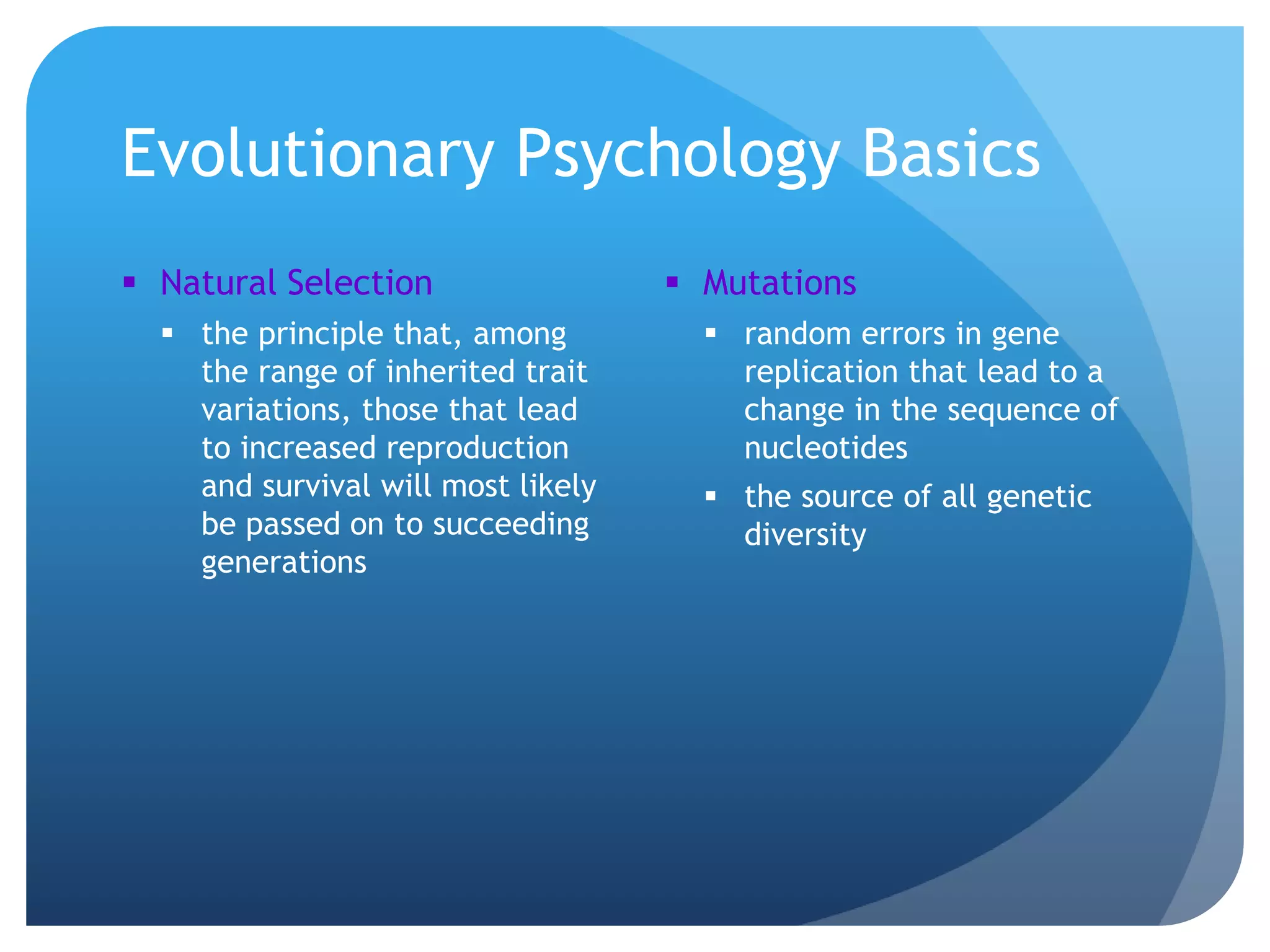
2. Evolution by natural selection, including concepts like adaptation, mutations, and the focus on proximate and ultimate causes in evolutionary psychology.
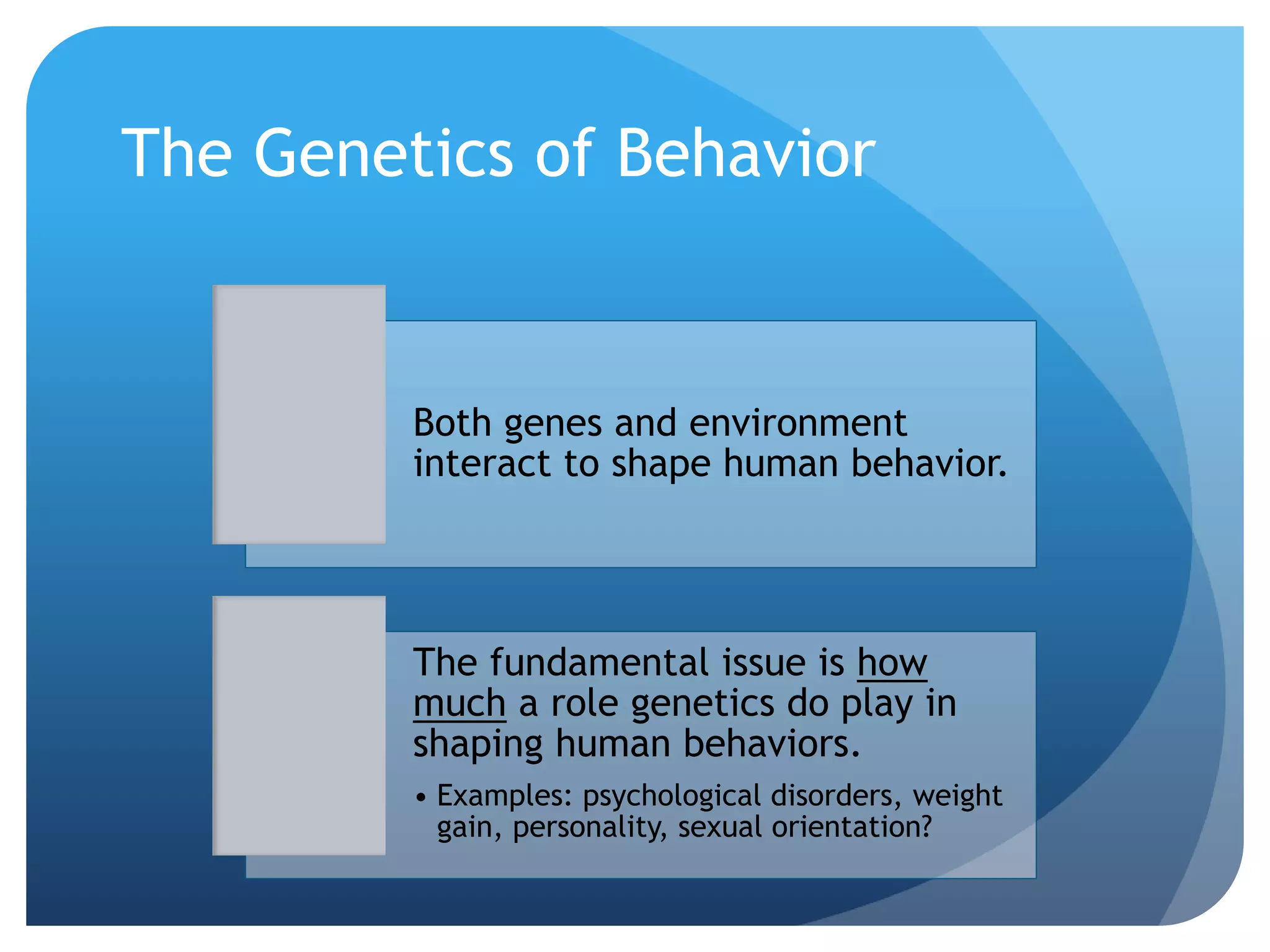
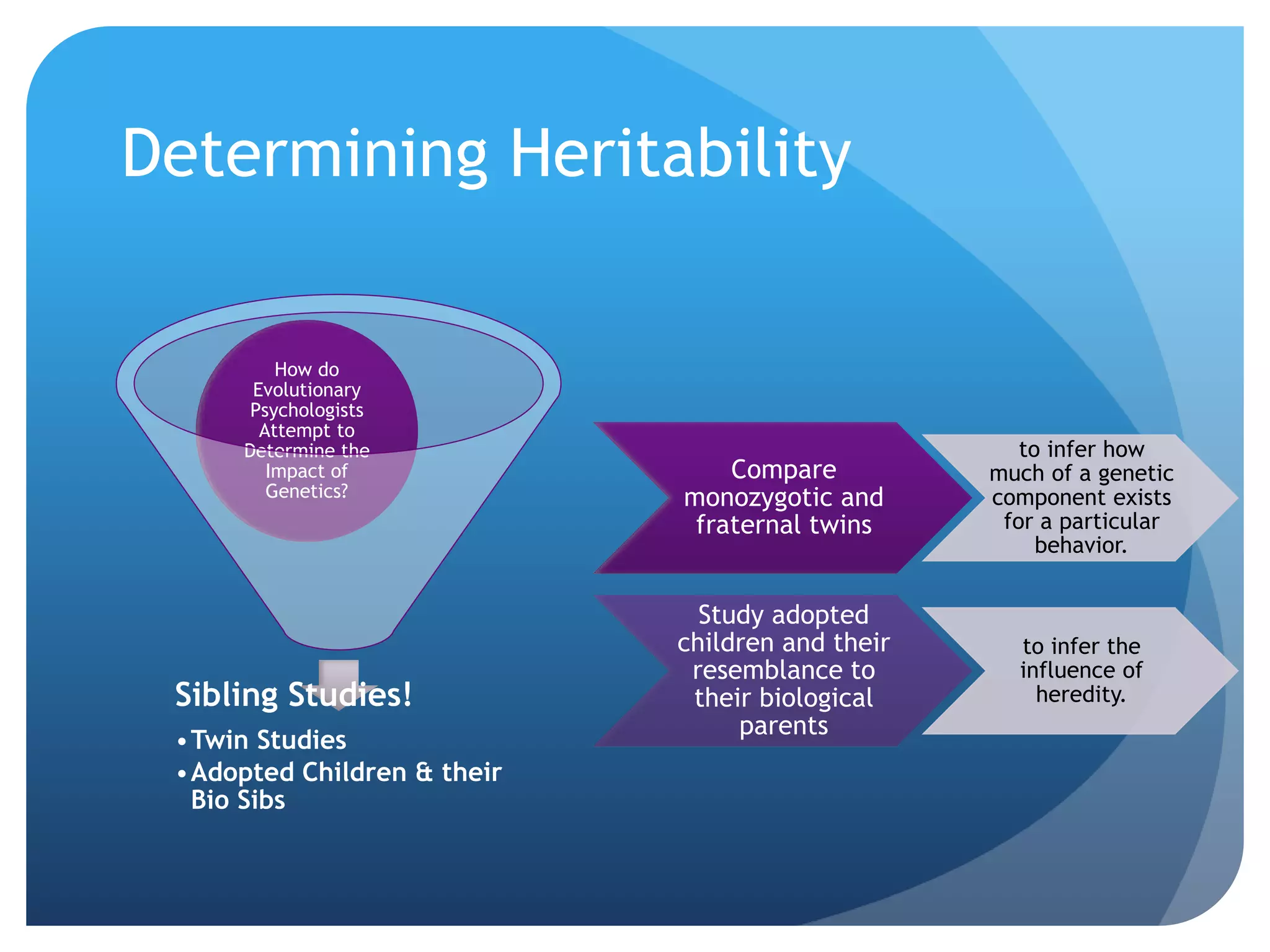
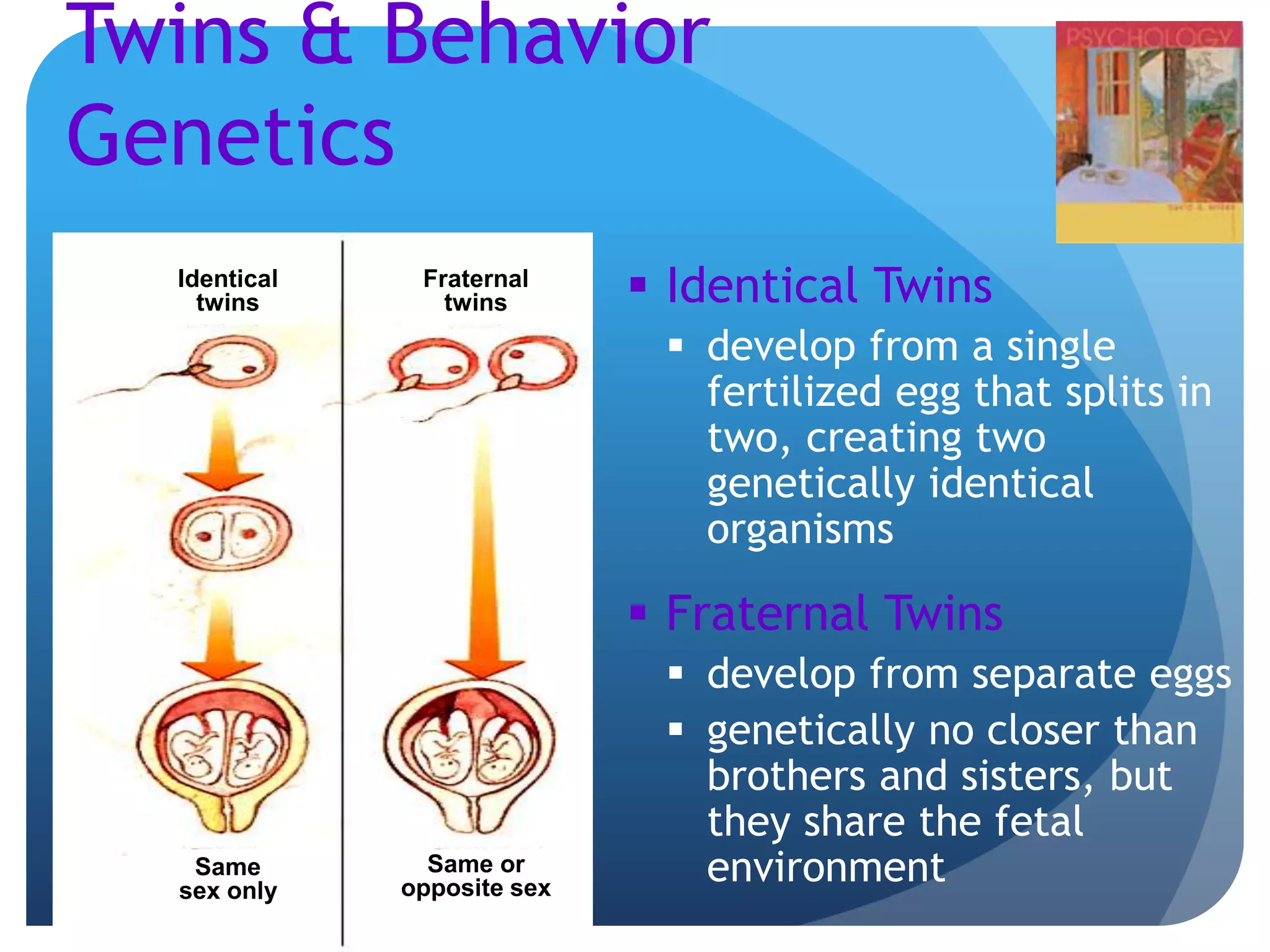
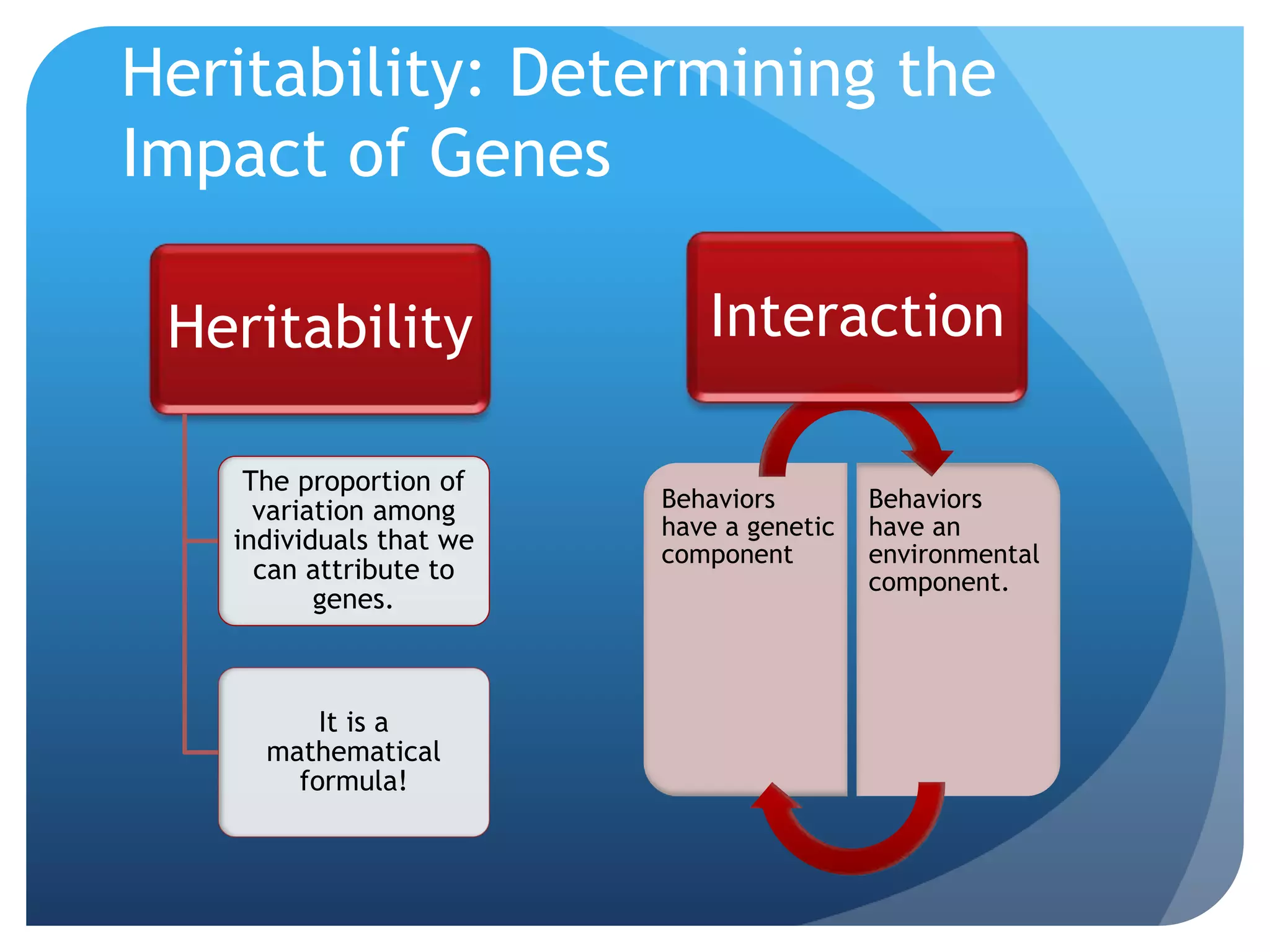
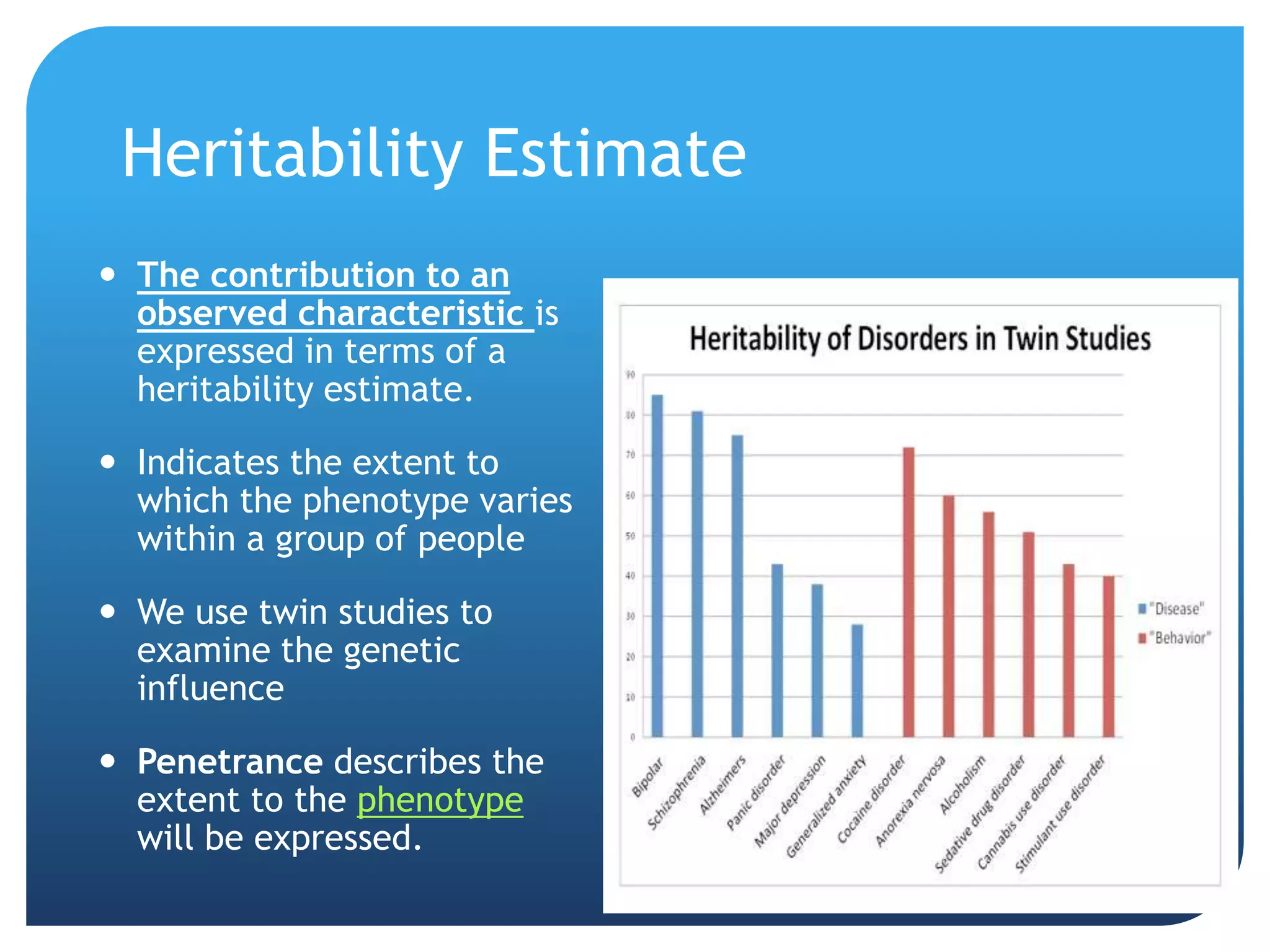
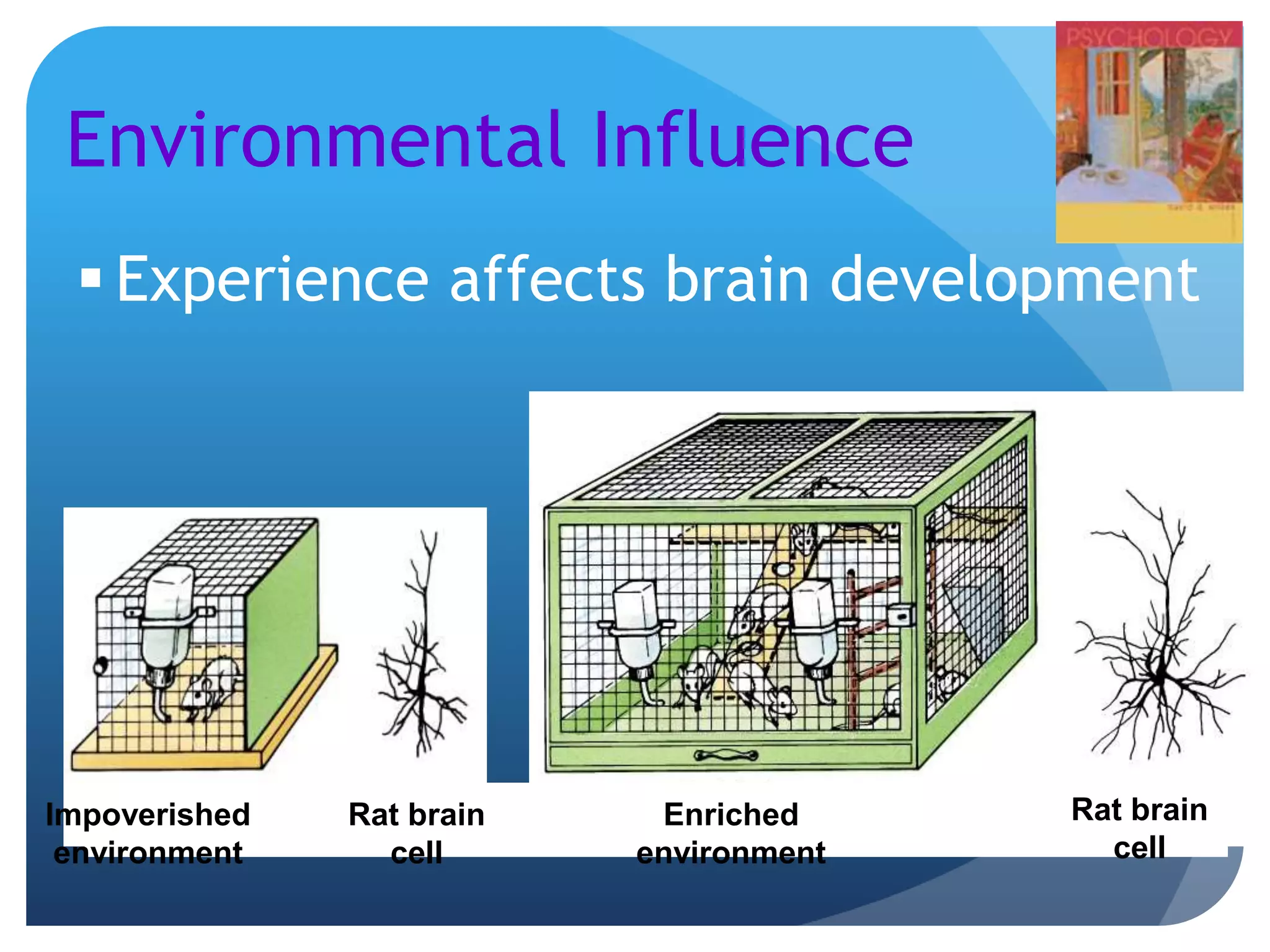
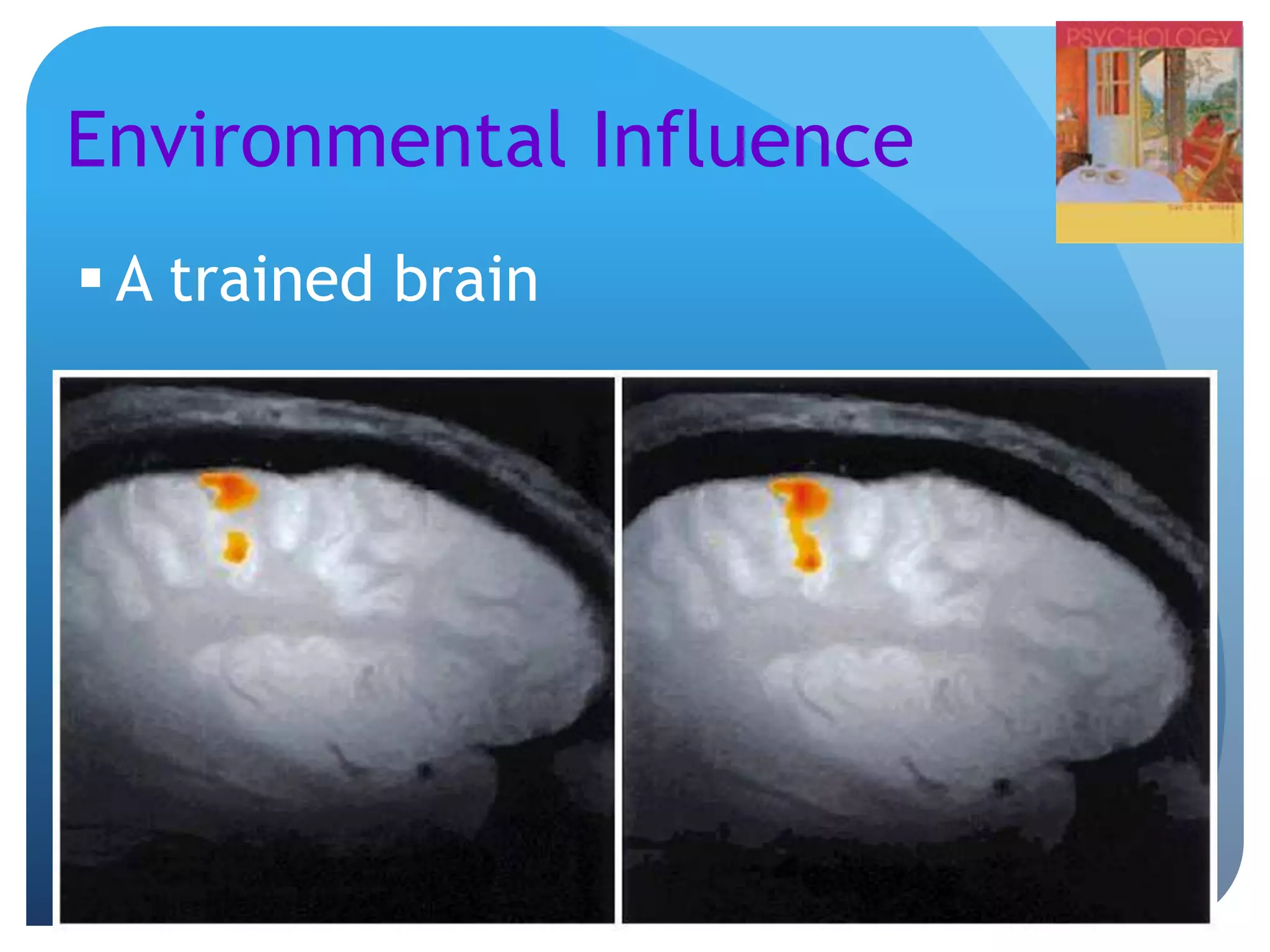
3. The genetics and evolution of behavior, exploring topics like behavior genetics, heritability estimates from twin studies, and how both genes and environment influence traits. Specific examples like intelligence and sexuality are discussed.