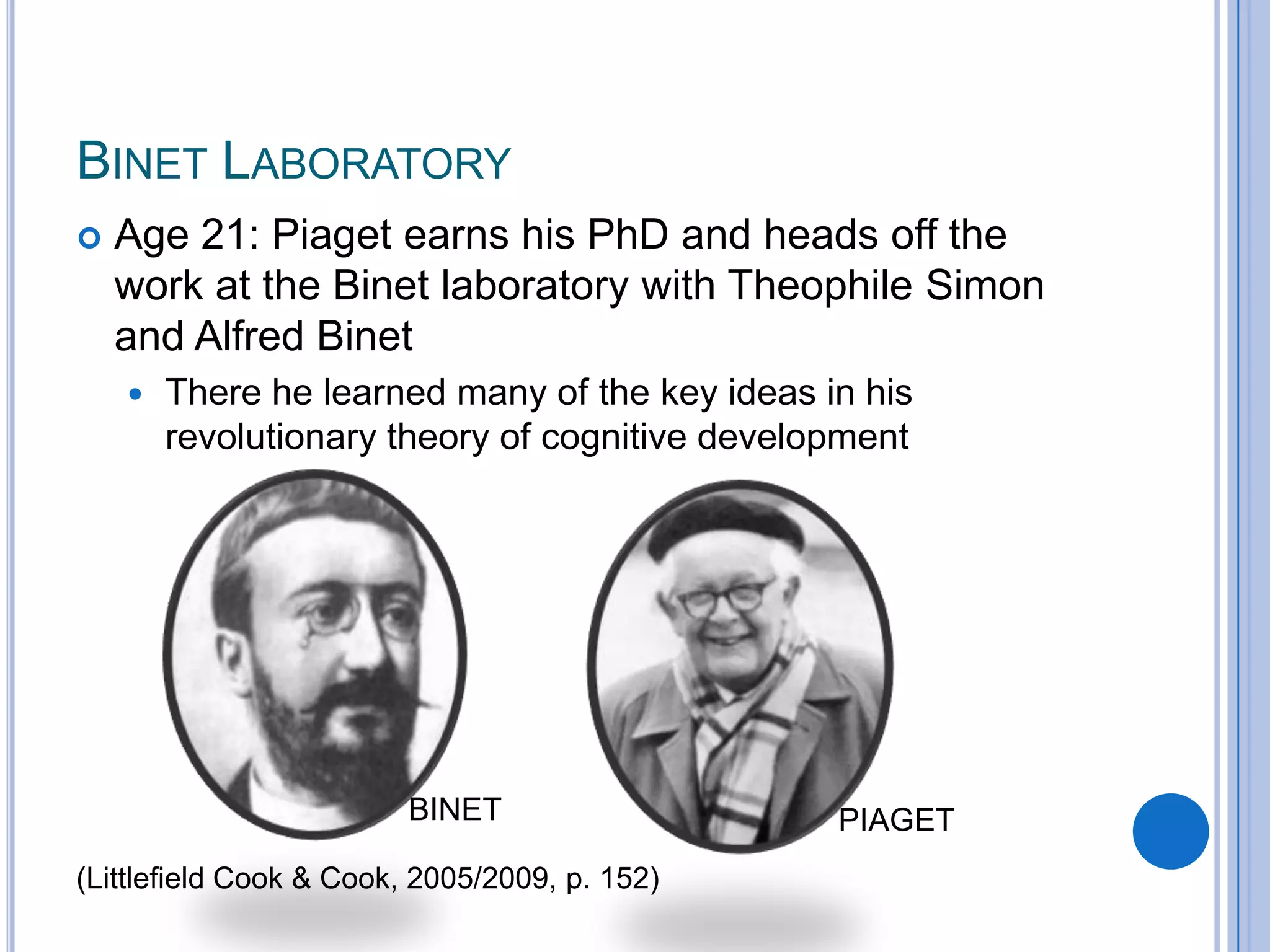
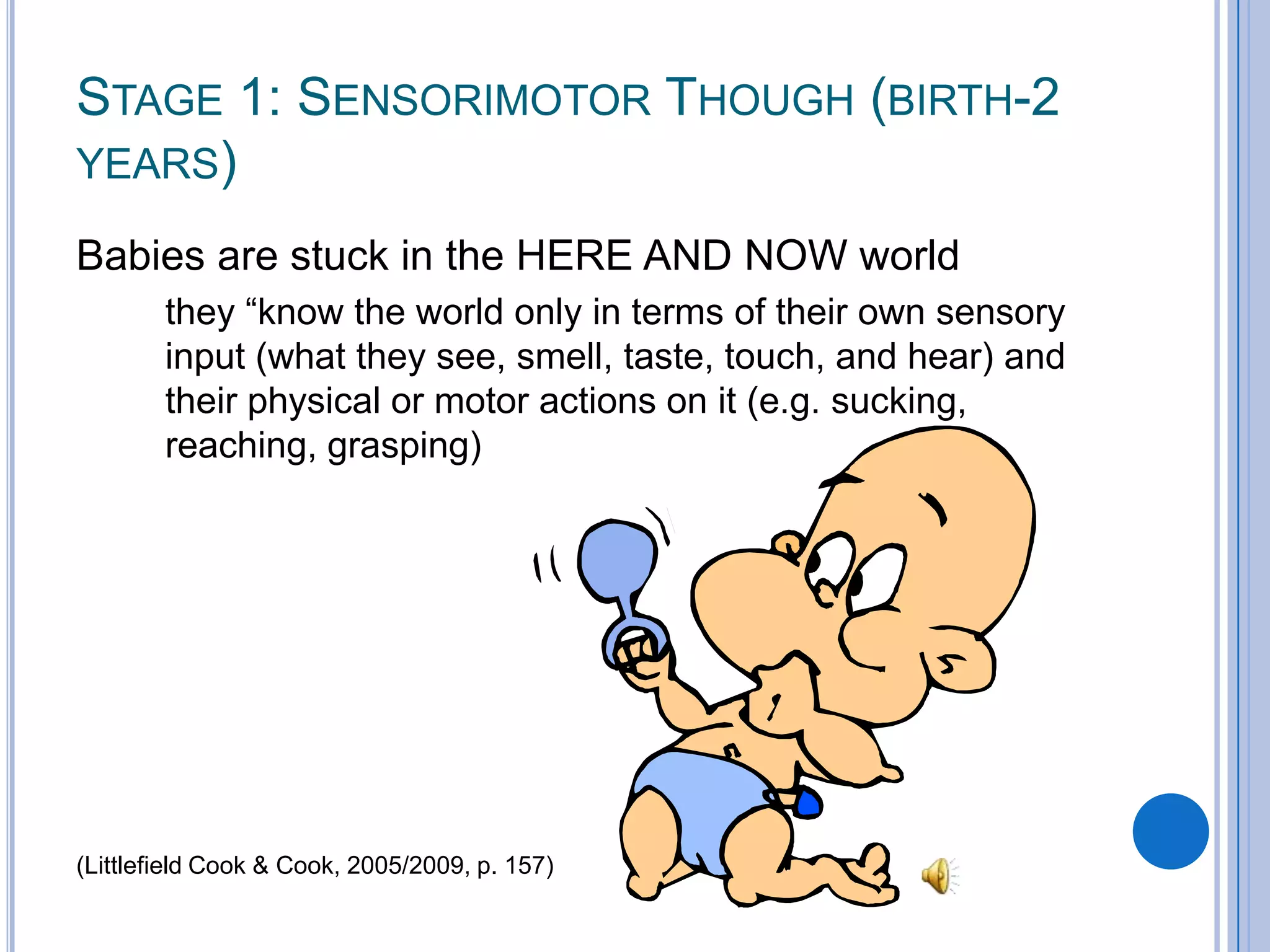
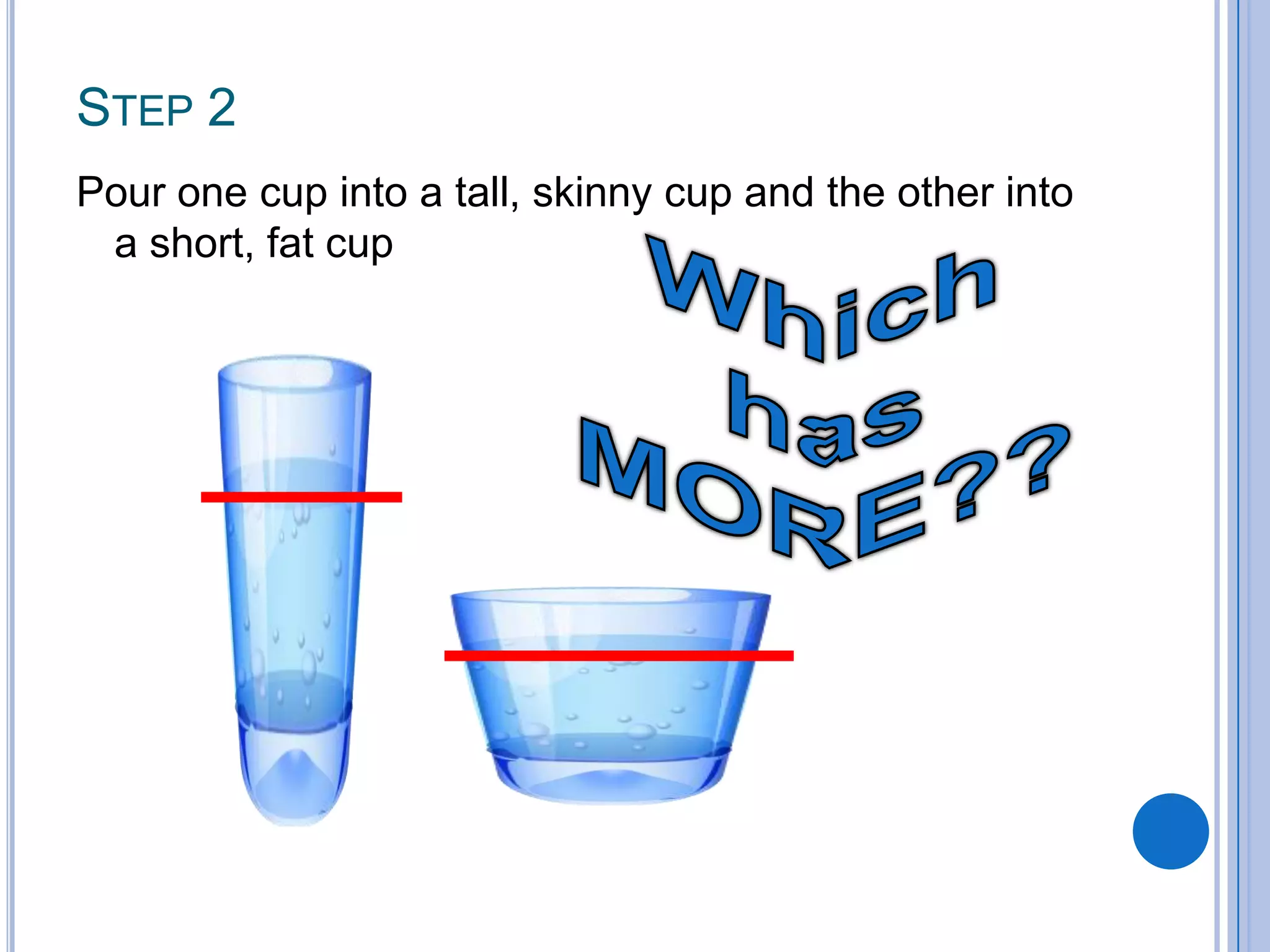
Piaget's theory of cognitive development outlines 4 stages of development: sensorimotor (birth-2 years), preoperational (2-7 years), concrete operational (7-11 years), and formal operational (12 years and up). The stages are characterized by the development of object permanence, representational thought, logical reasoning, and abstract thought. Children with cognitive disabilities may not progress through all the stages. Down syndrome is provided as an example of a cognitive disability where individuals often do not complete all stages of Piaget's theory.