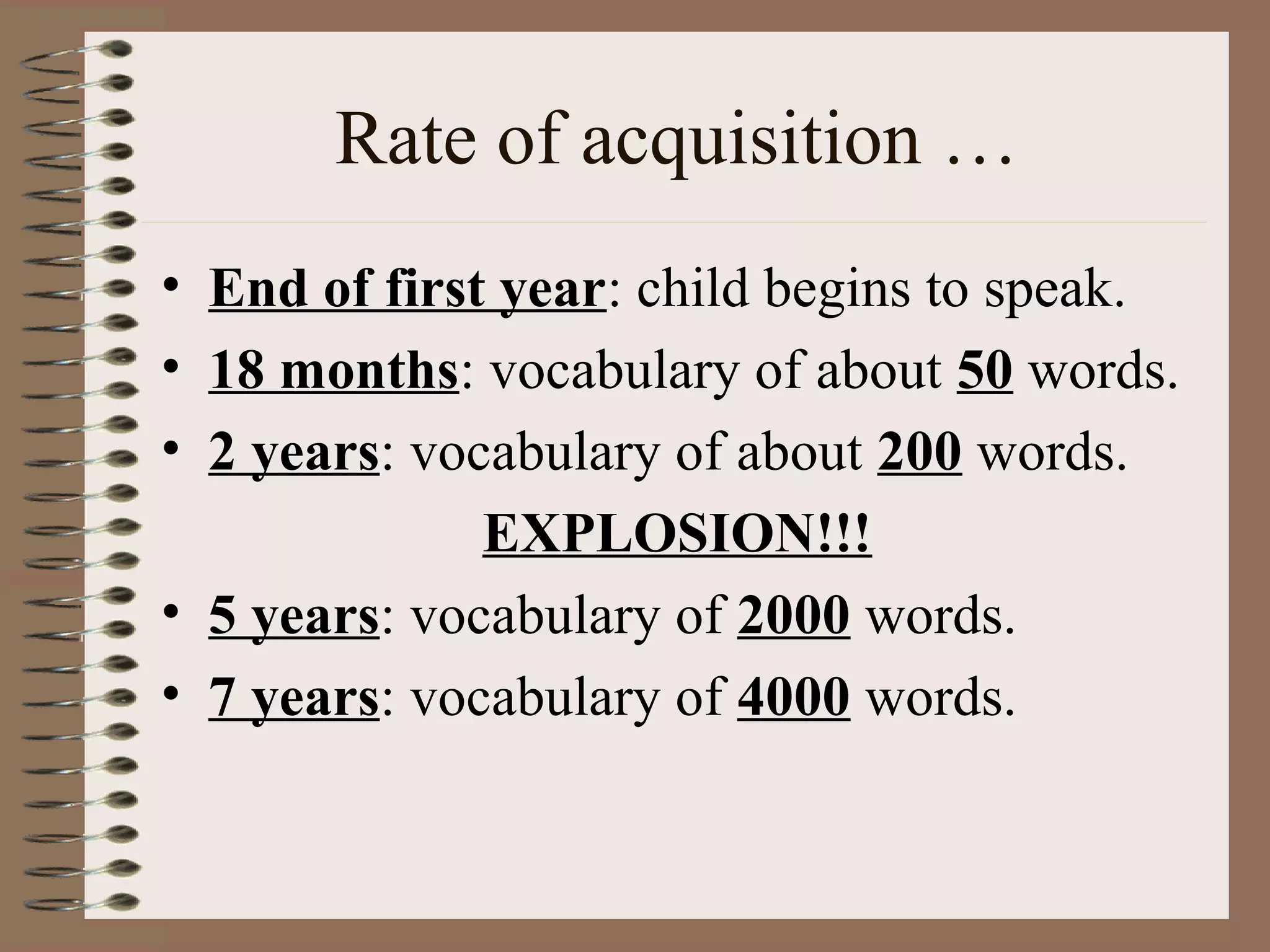
This document discusses lexical and semantic development in children. It outlines that lexical development refers to a child's acquisition of words, while semantic development is a child's understanding of word meanings. It provides details on the typical growth of a child's vocabulary from 50 words at 18 months to 2000 words by age 5. It also notes that children understand more words than they can produce at each stage of development. The document examines common errors like overextension and underextension of word meanings as children learn. It outlines three stages of vocabulary acquisition: labelling, packaging, and network building to fully understand word meanings.