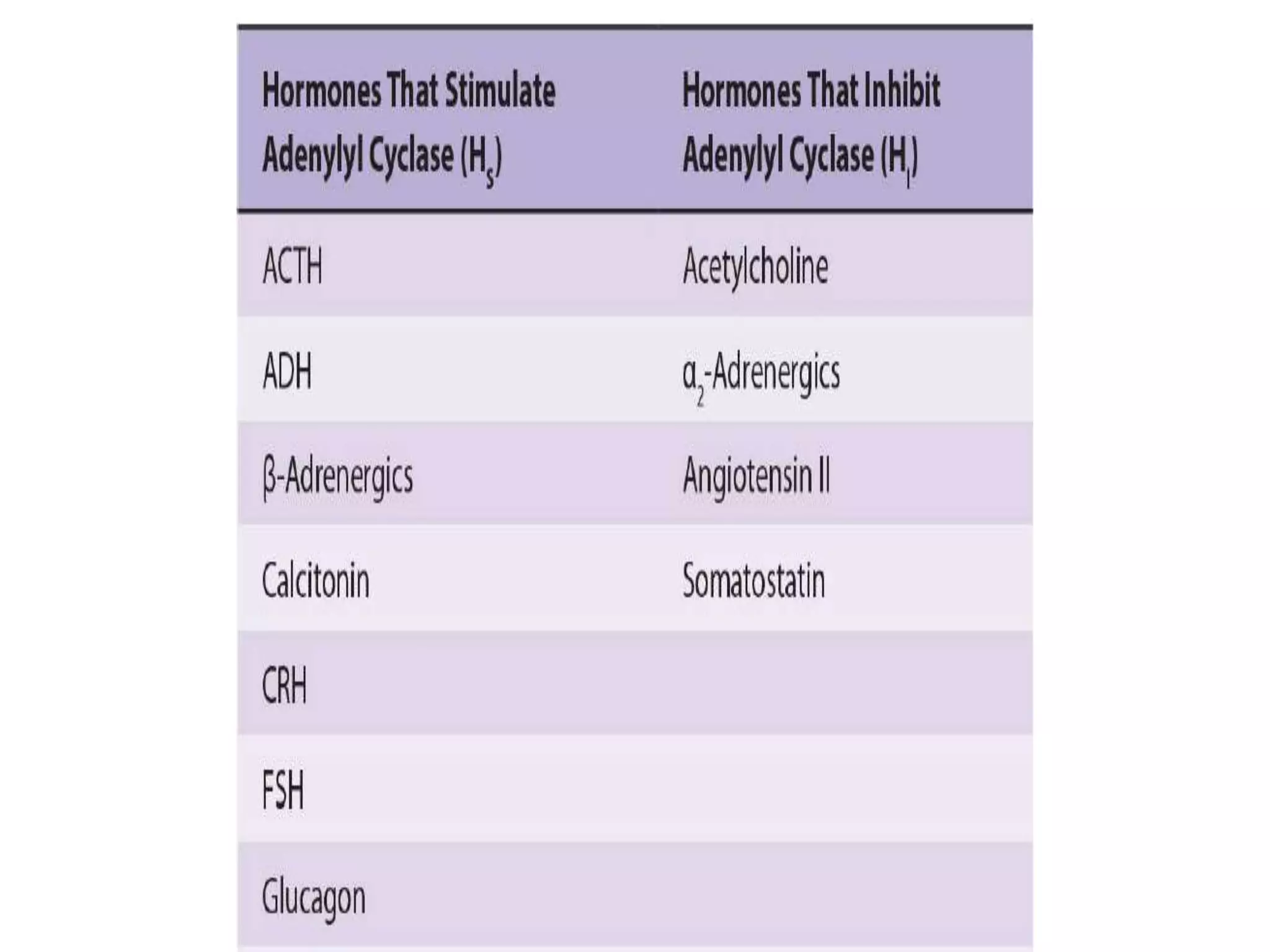
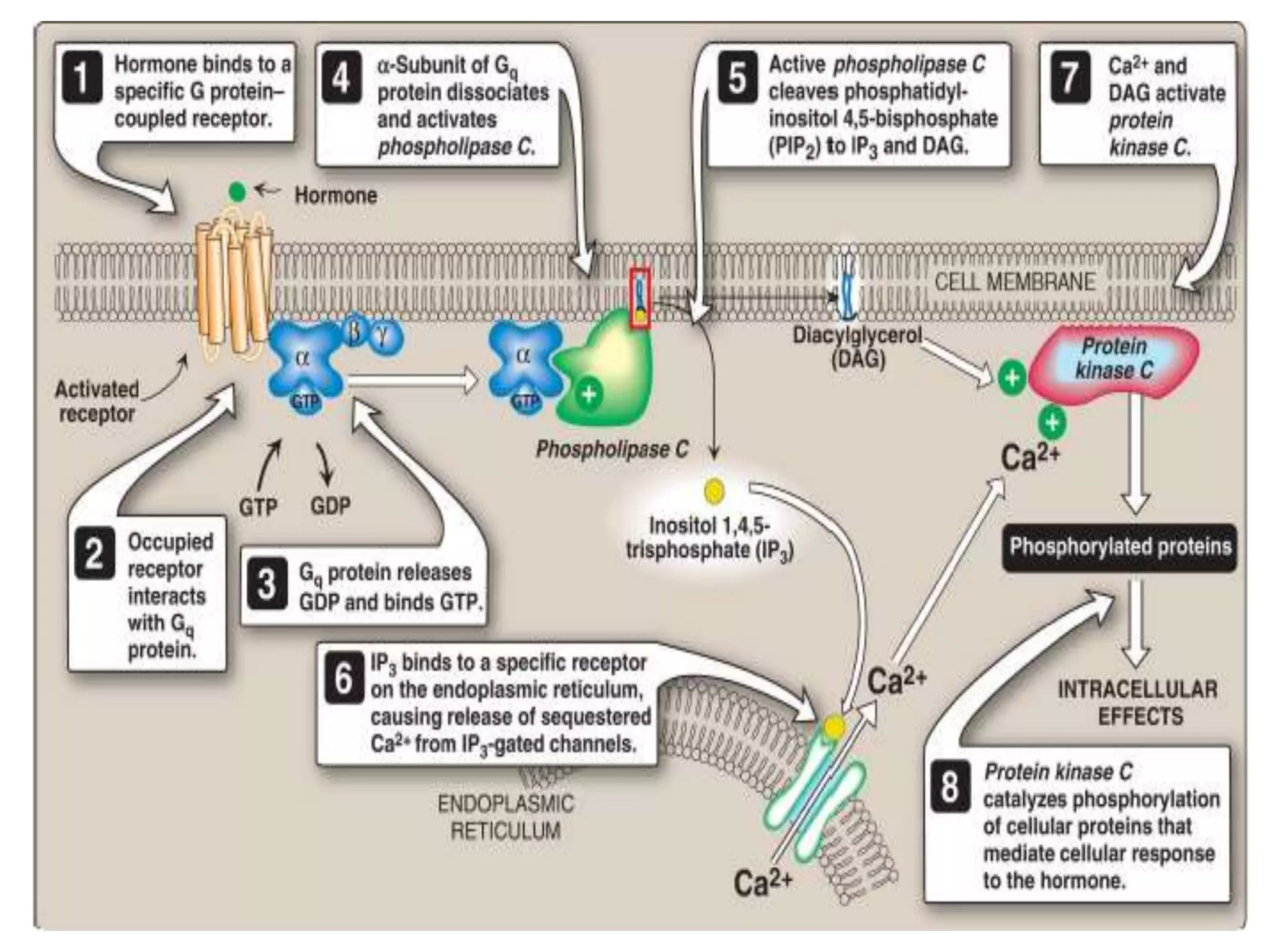
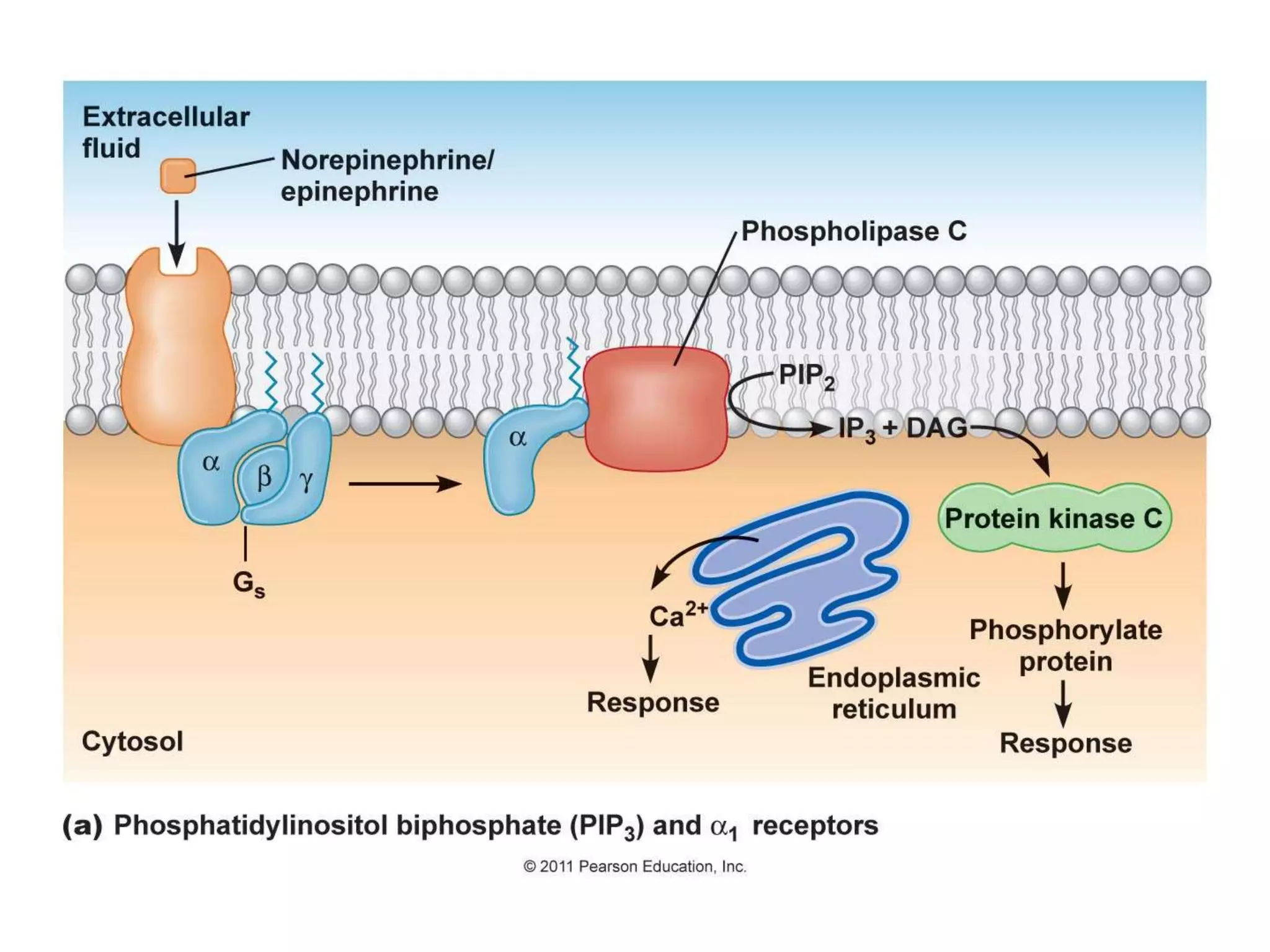
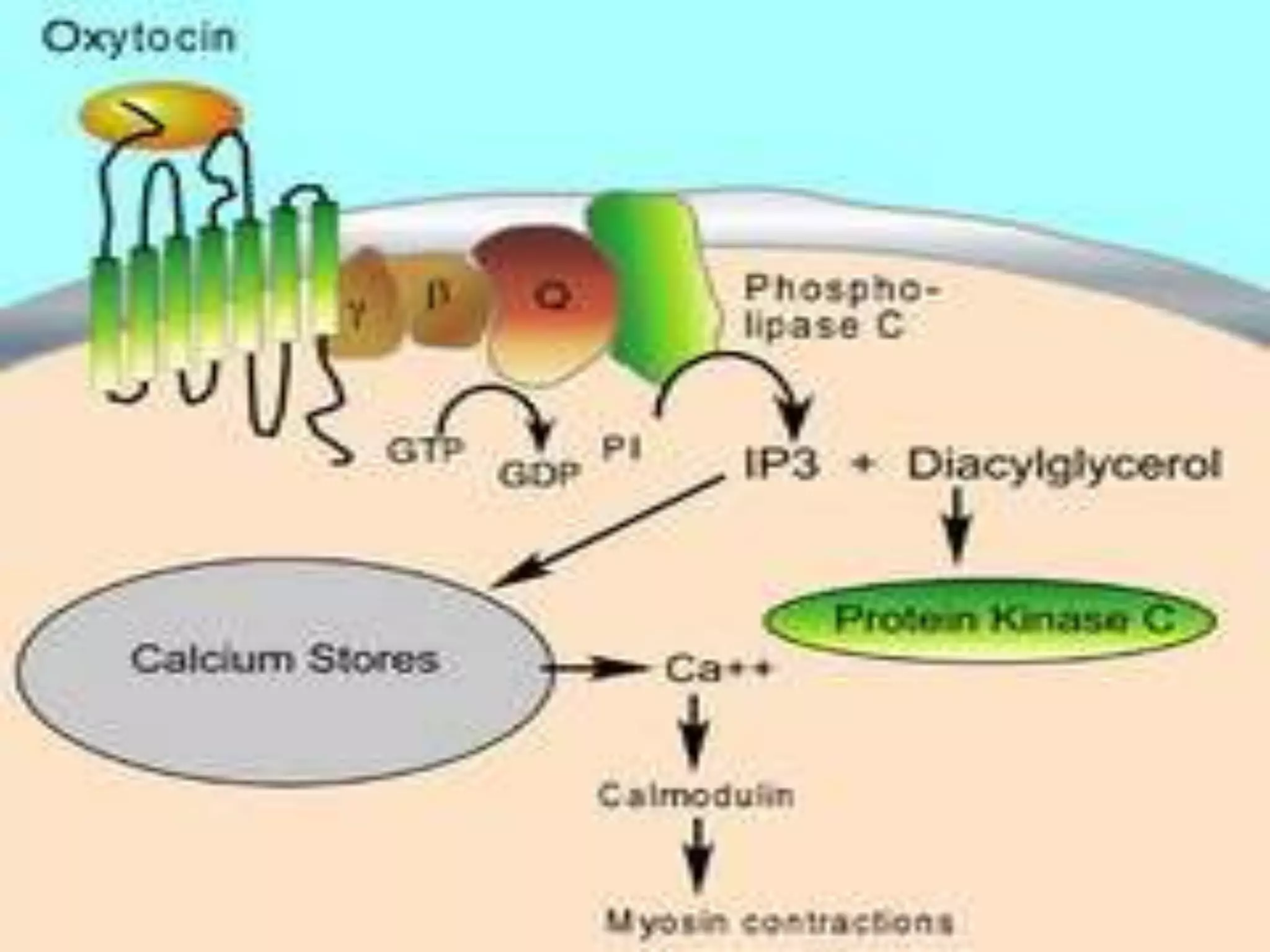
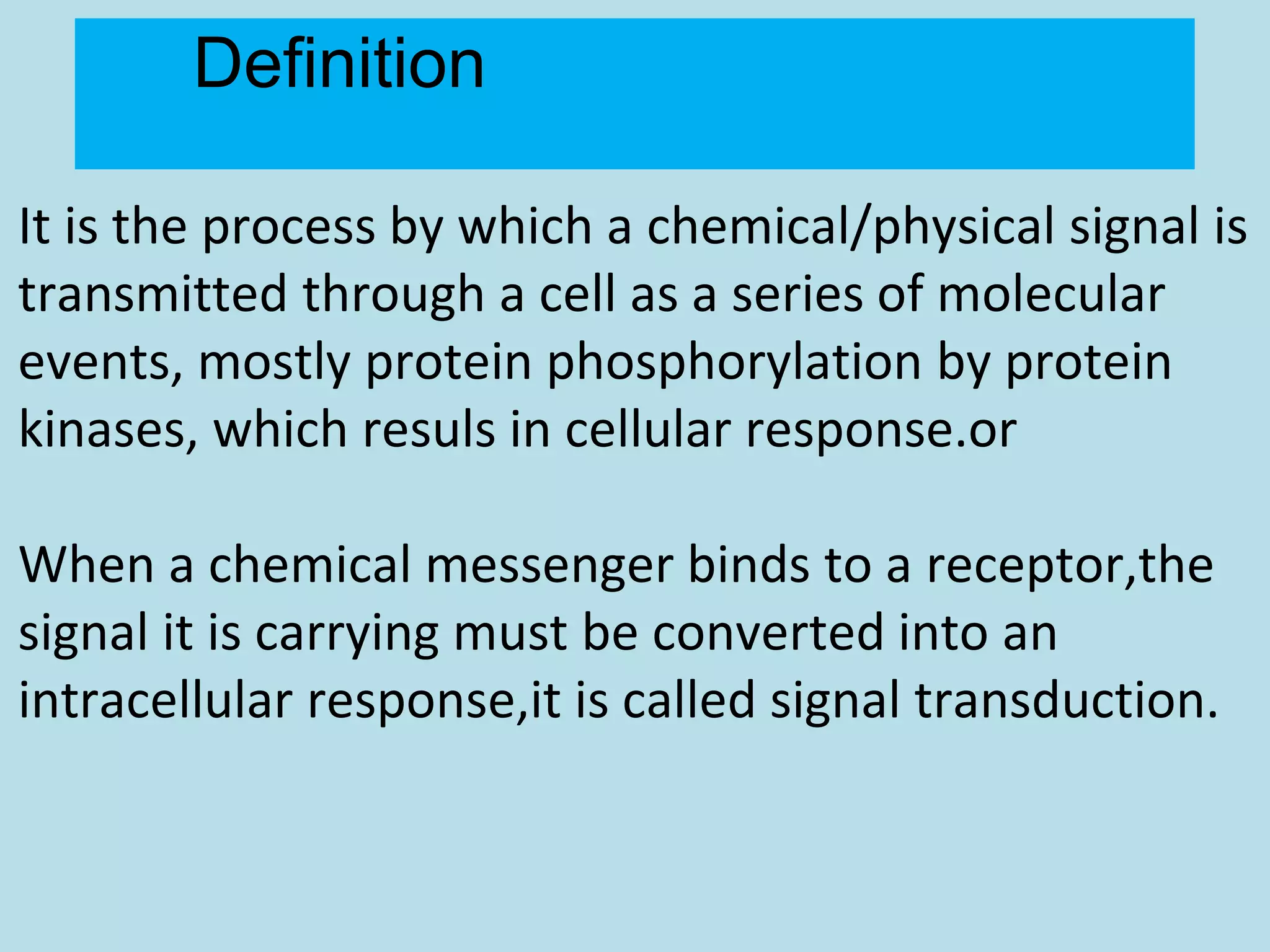
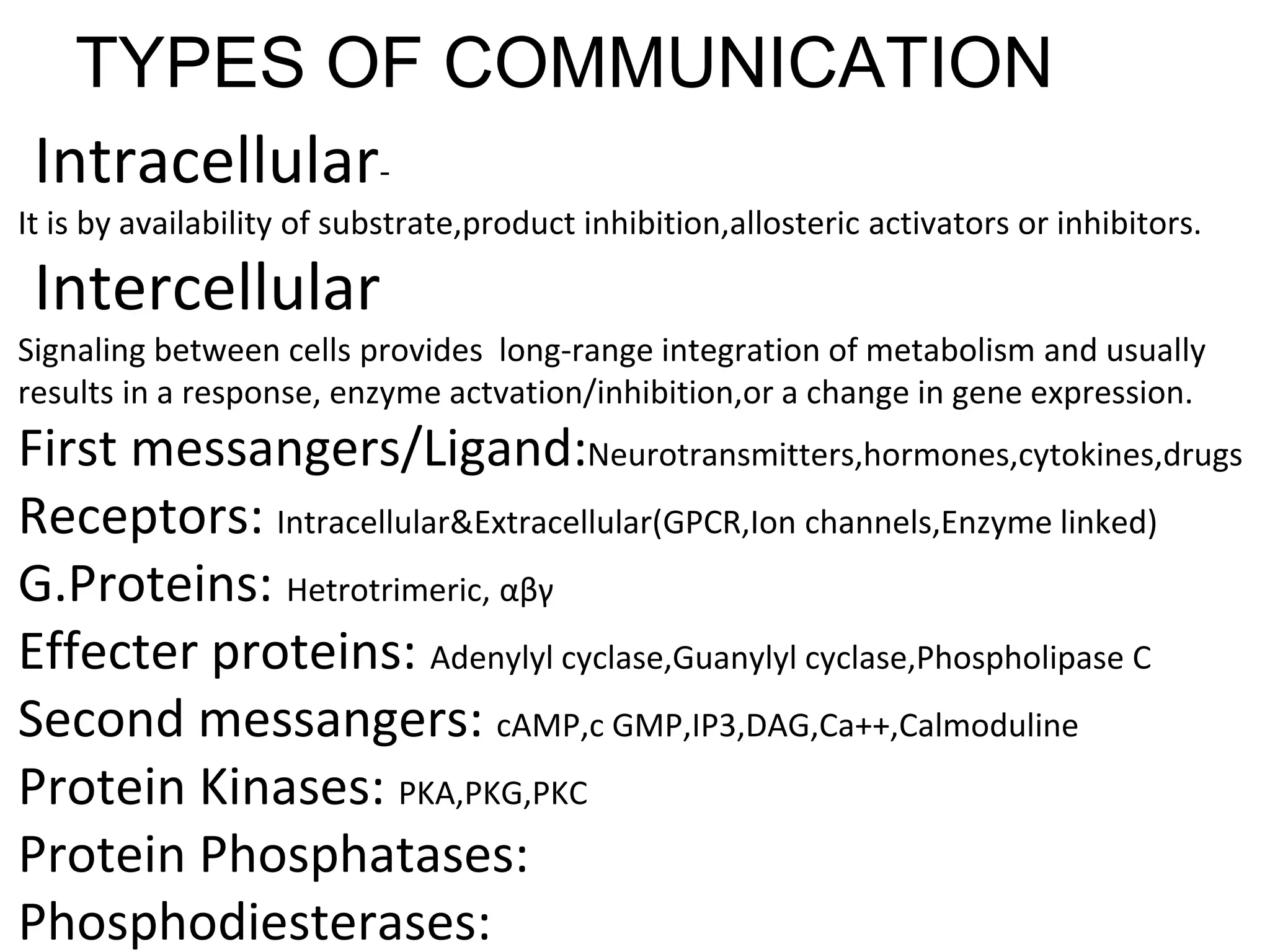
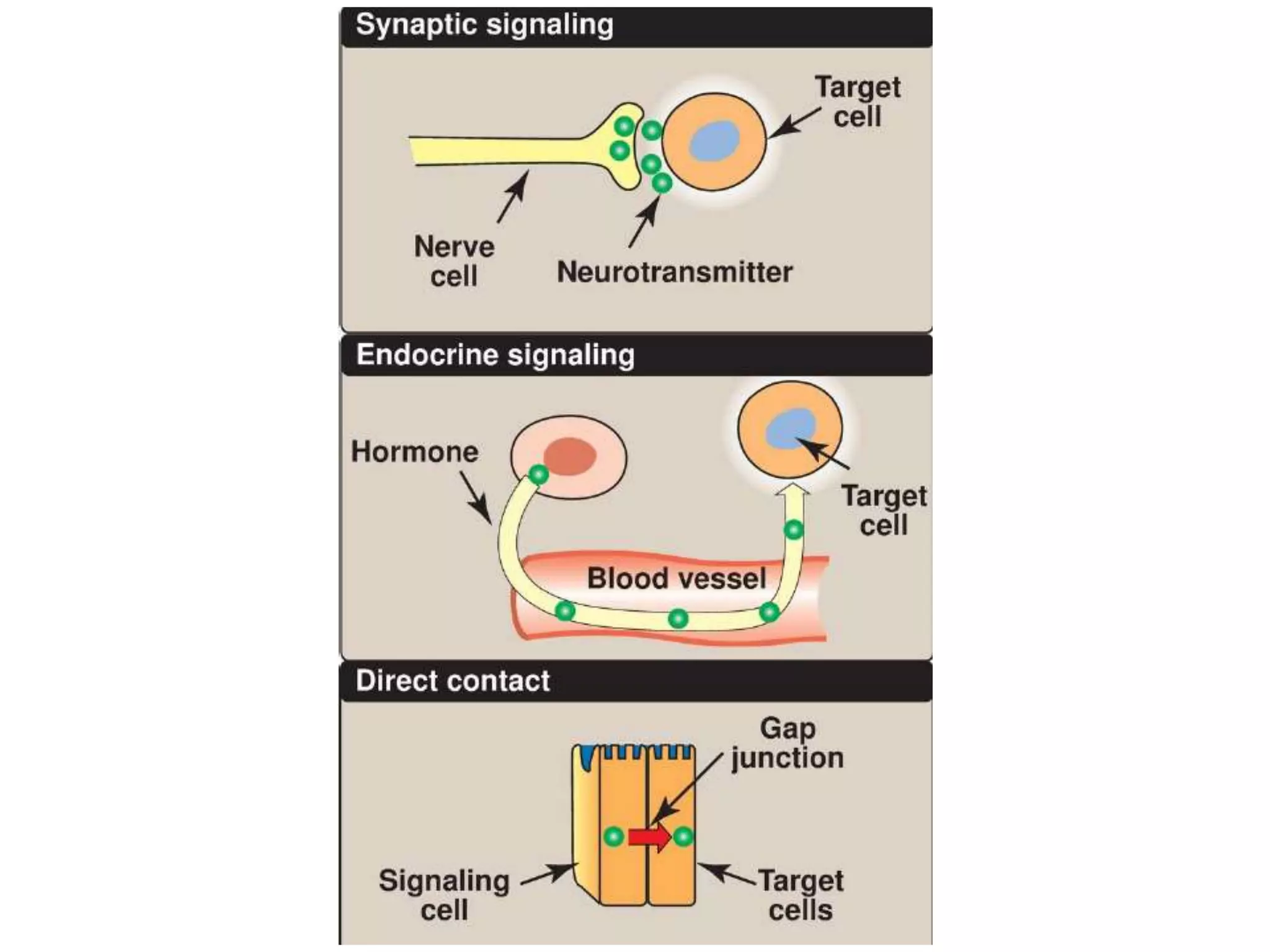
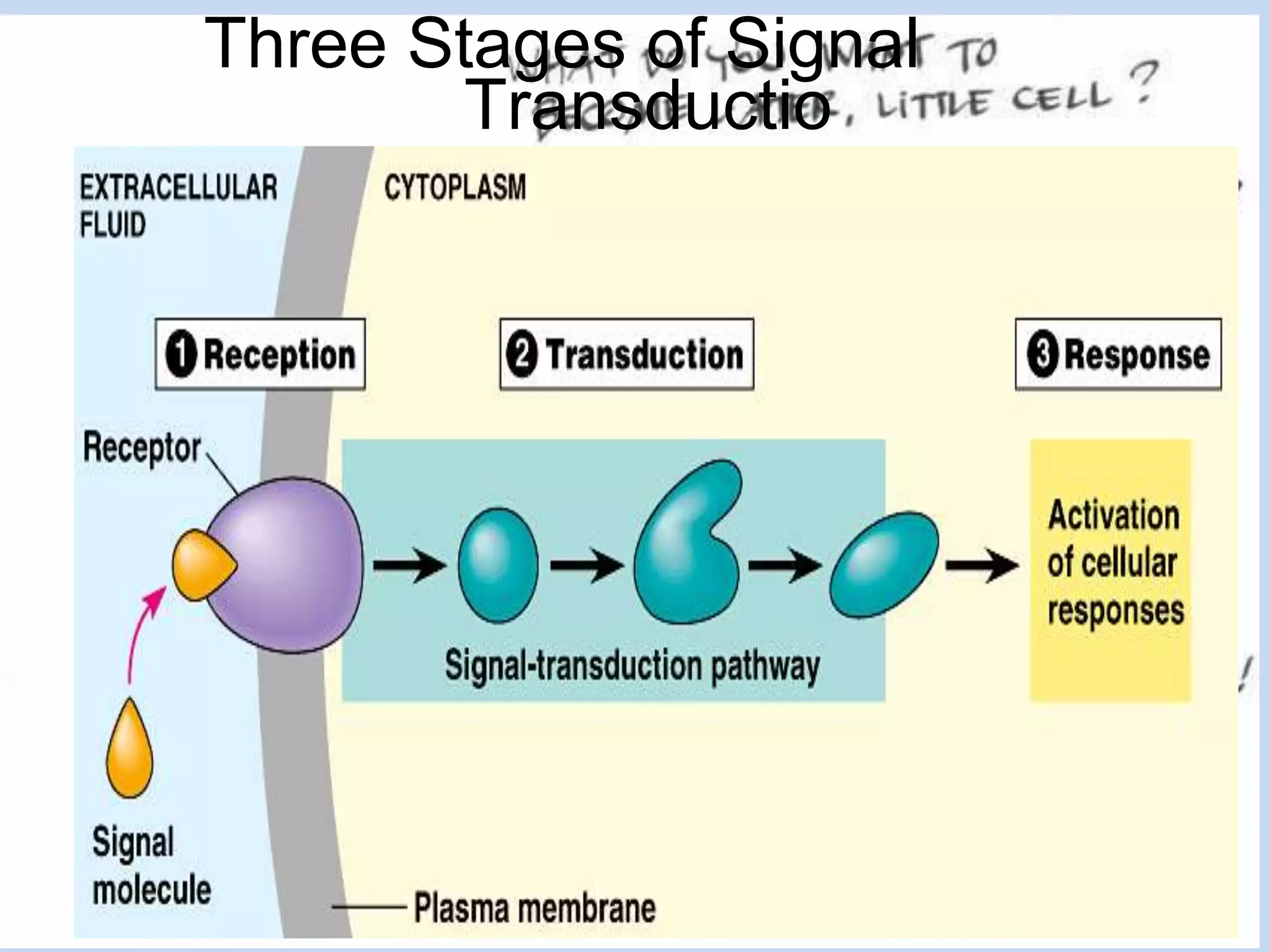
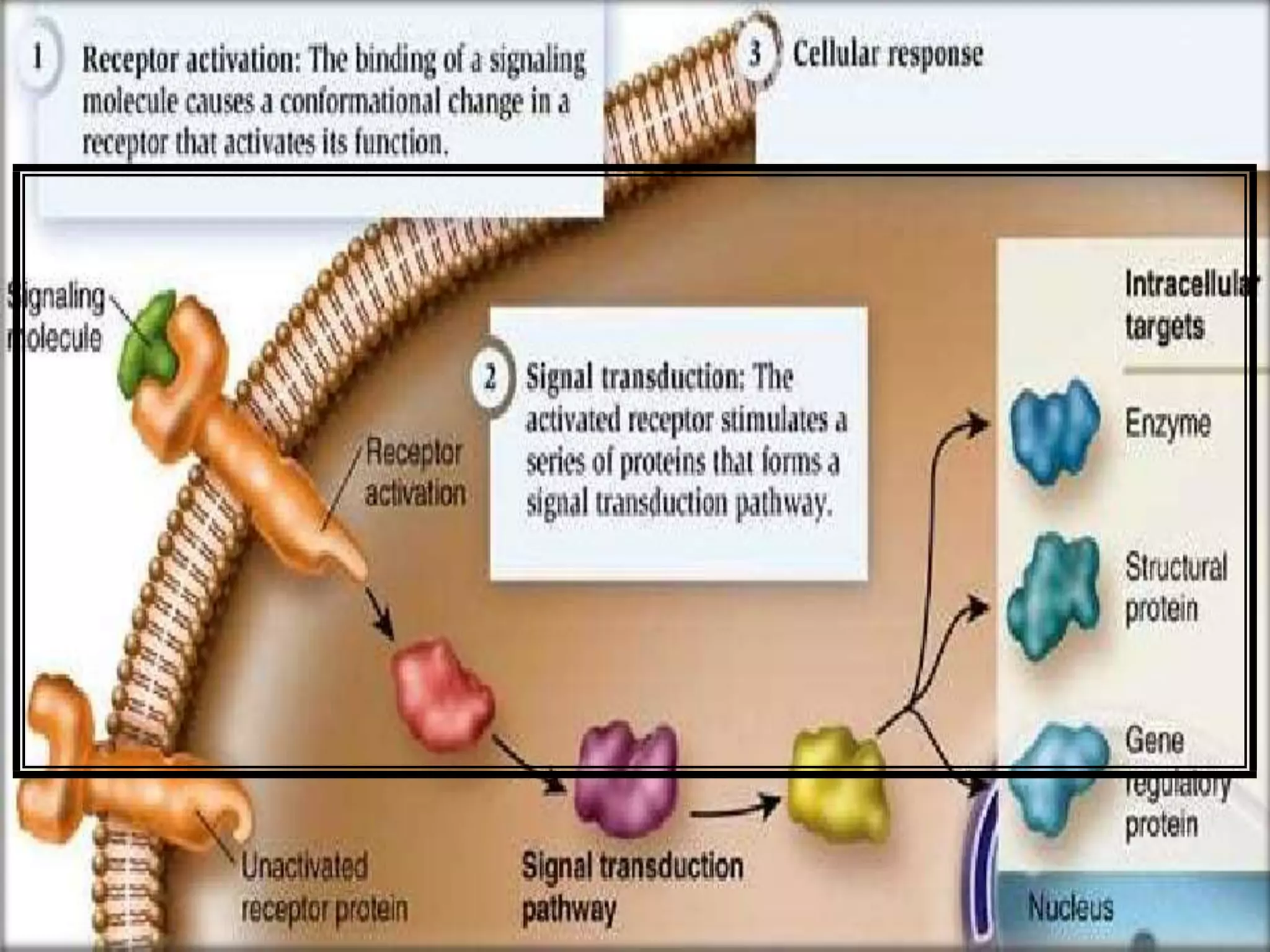
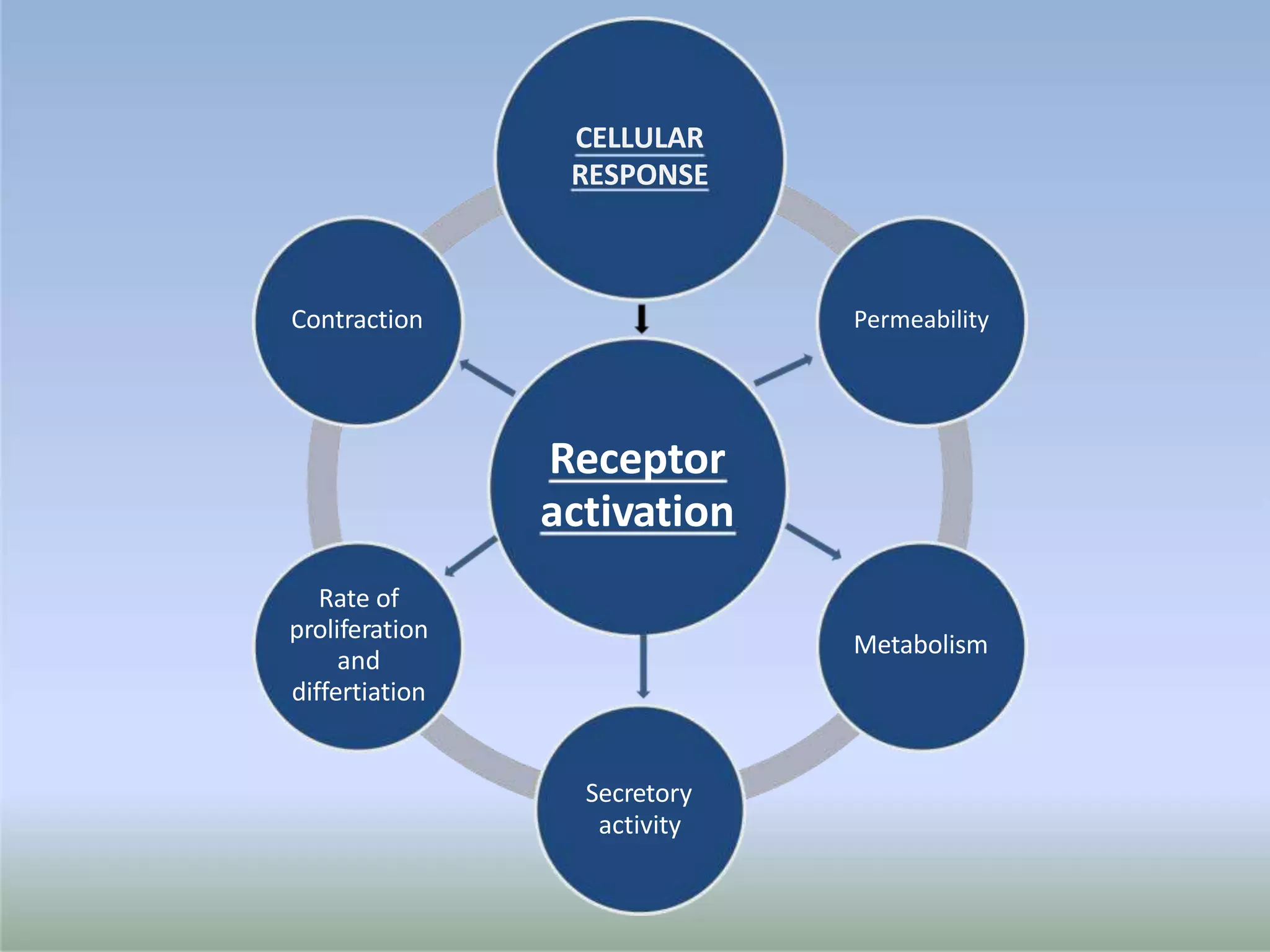
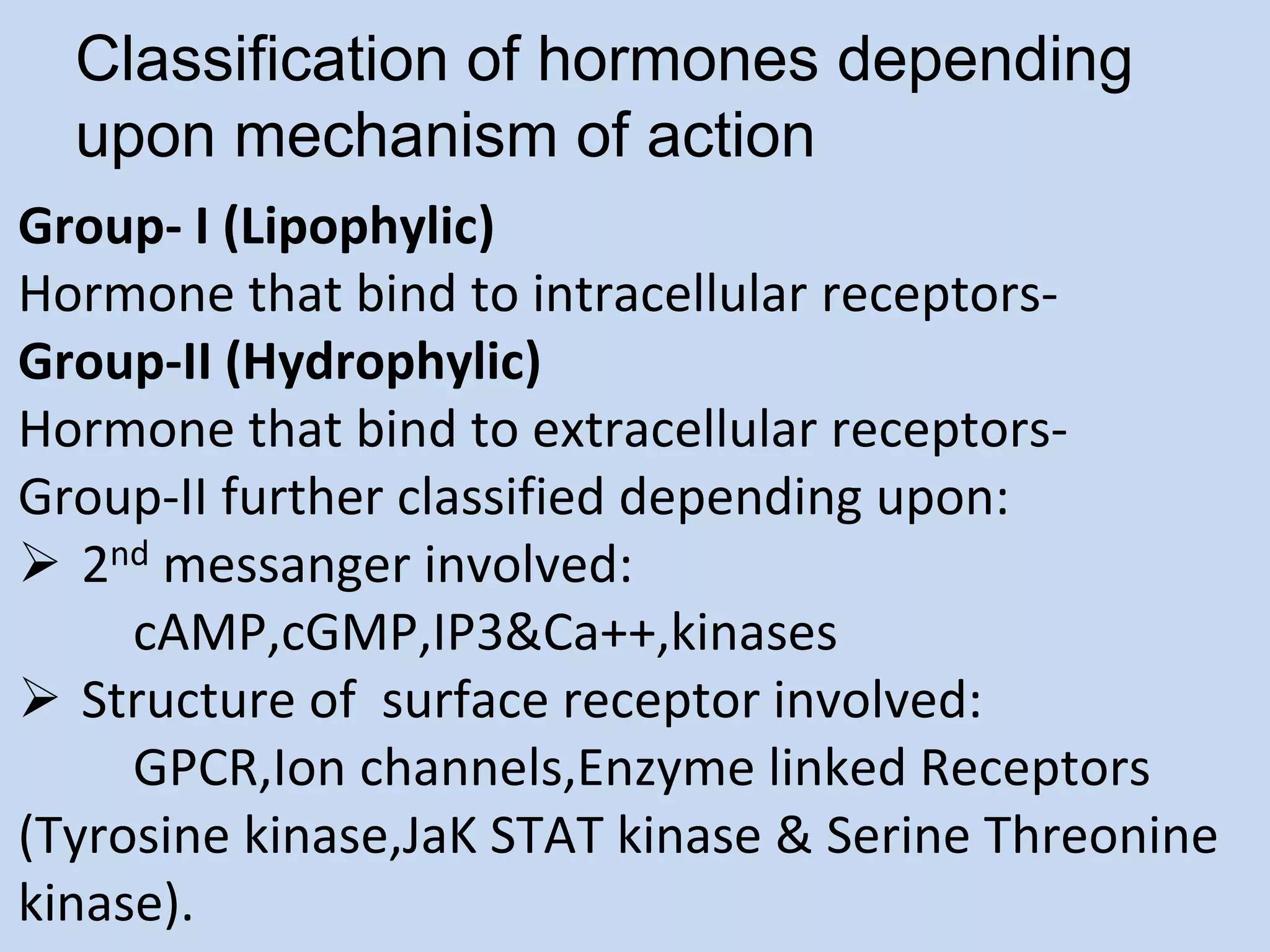
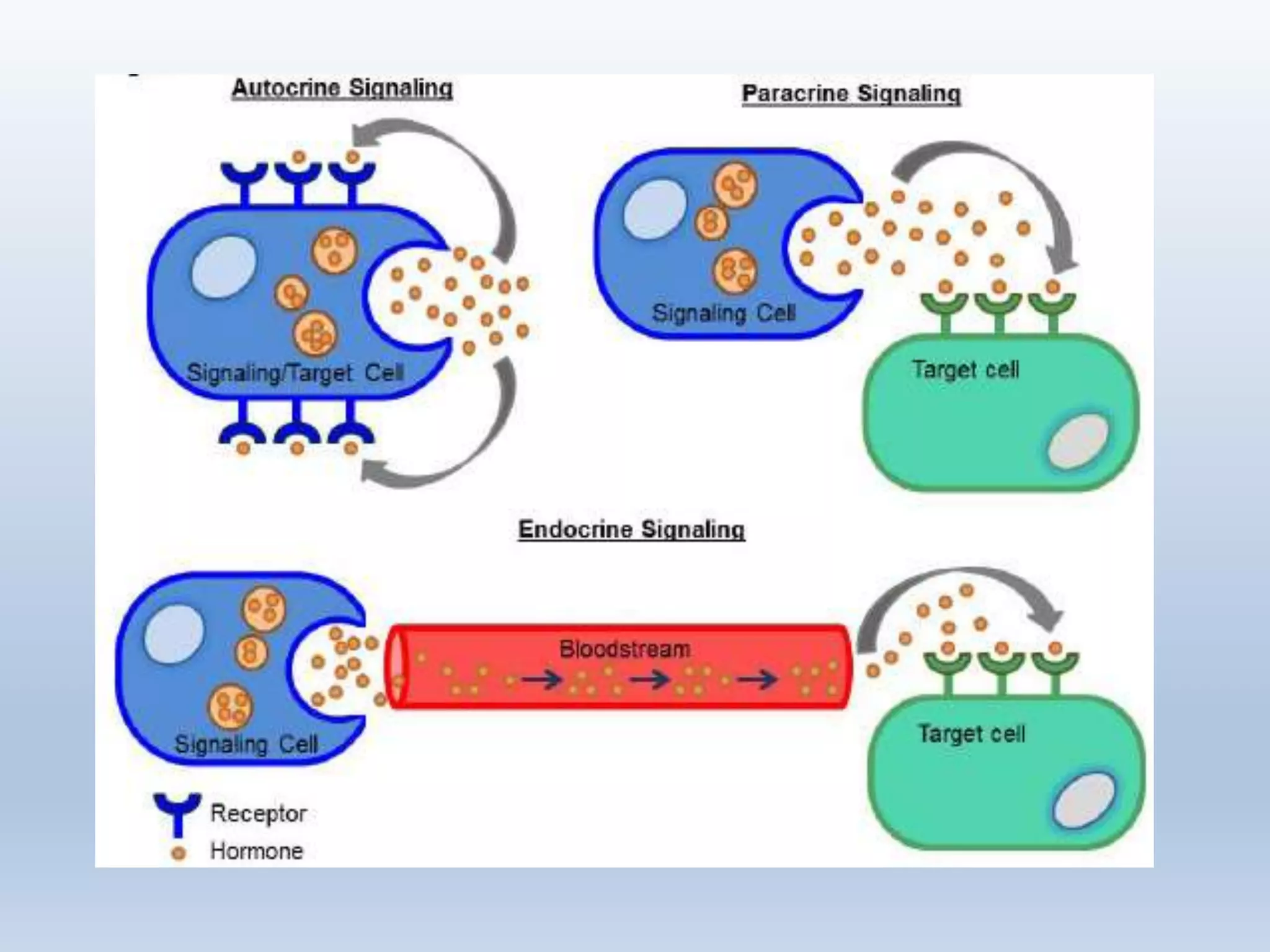
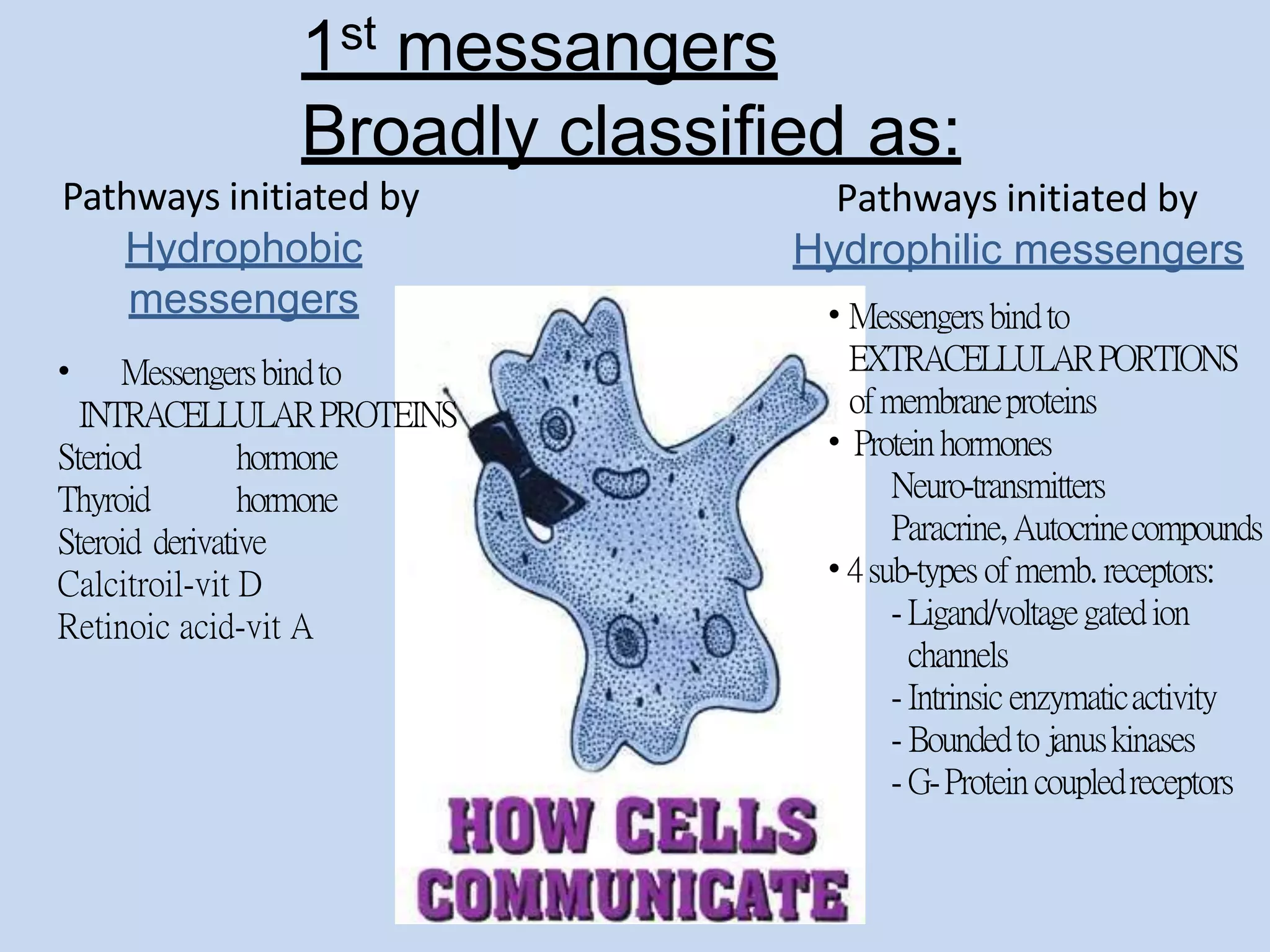
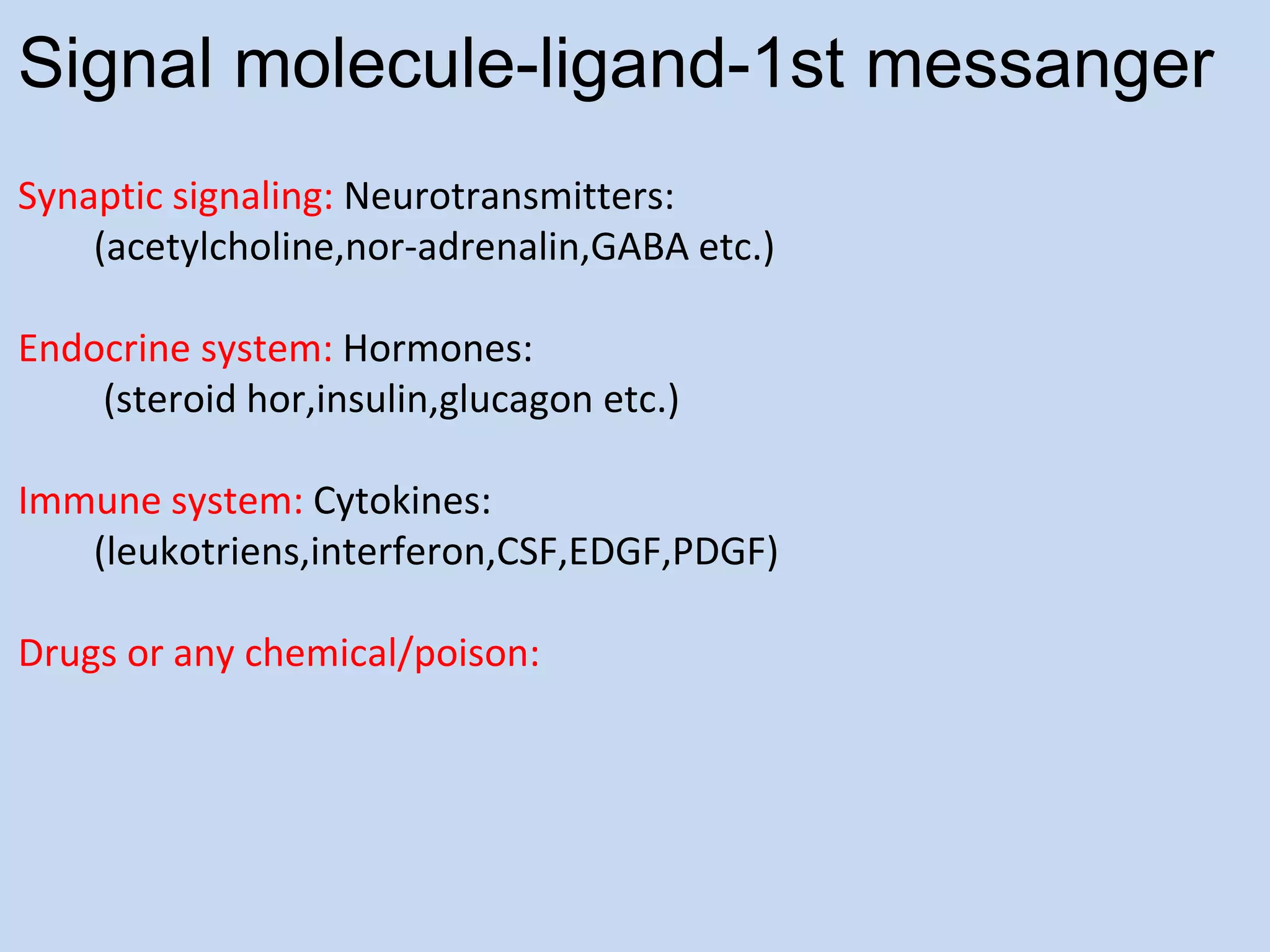
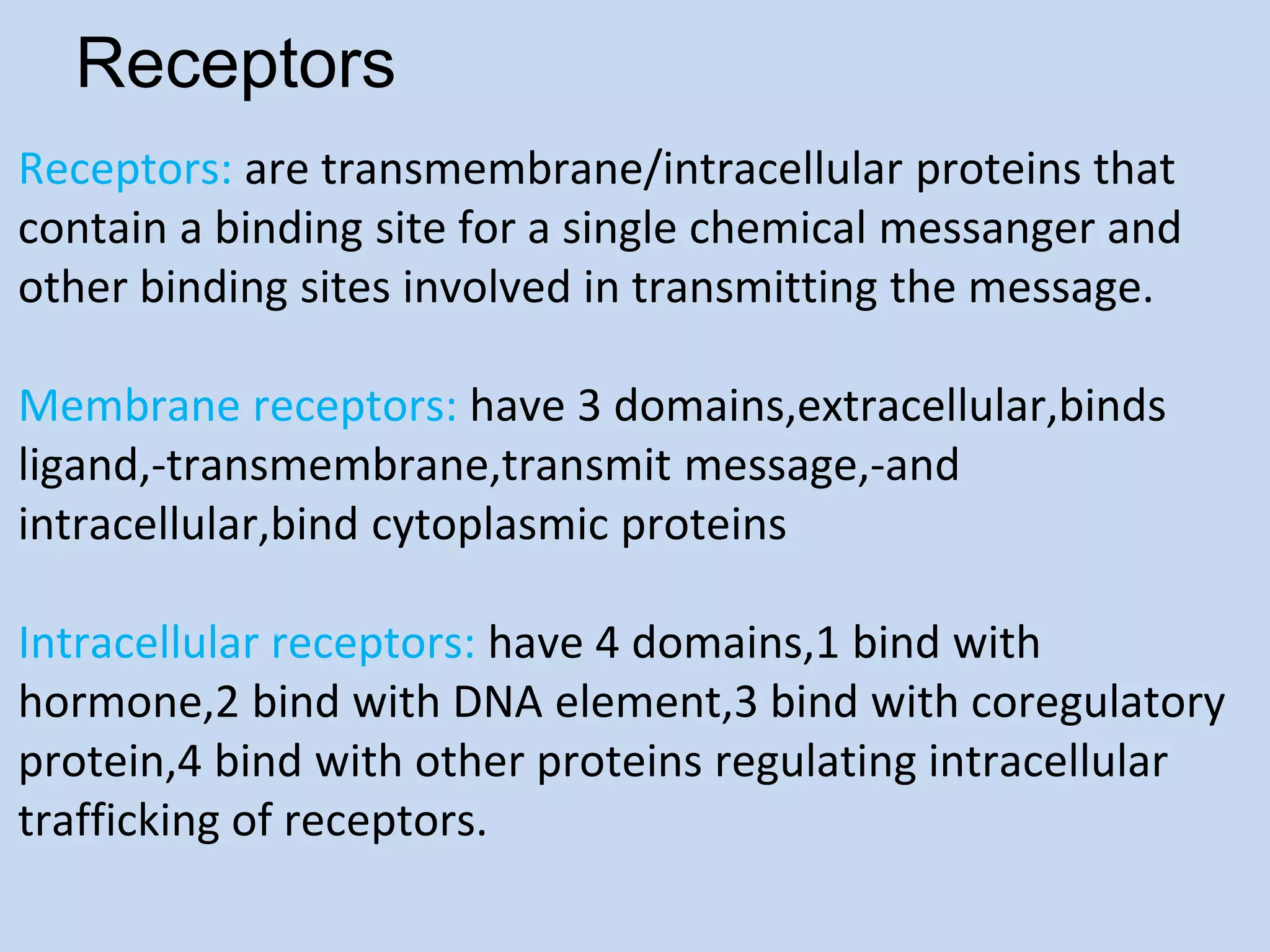
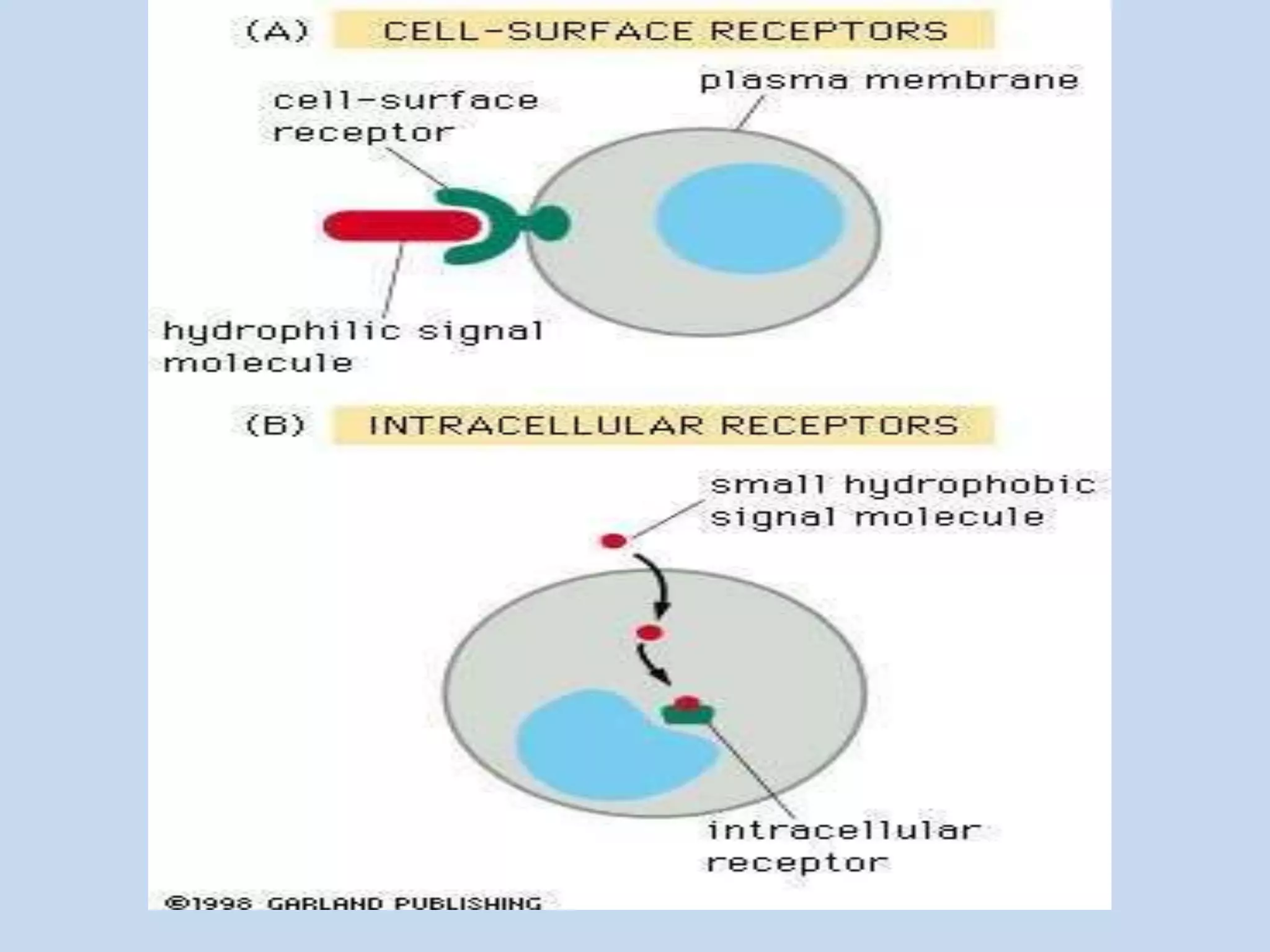
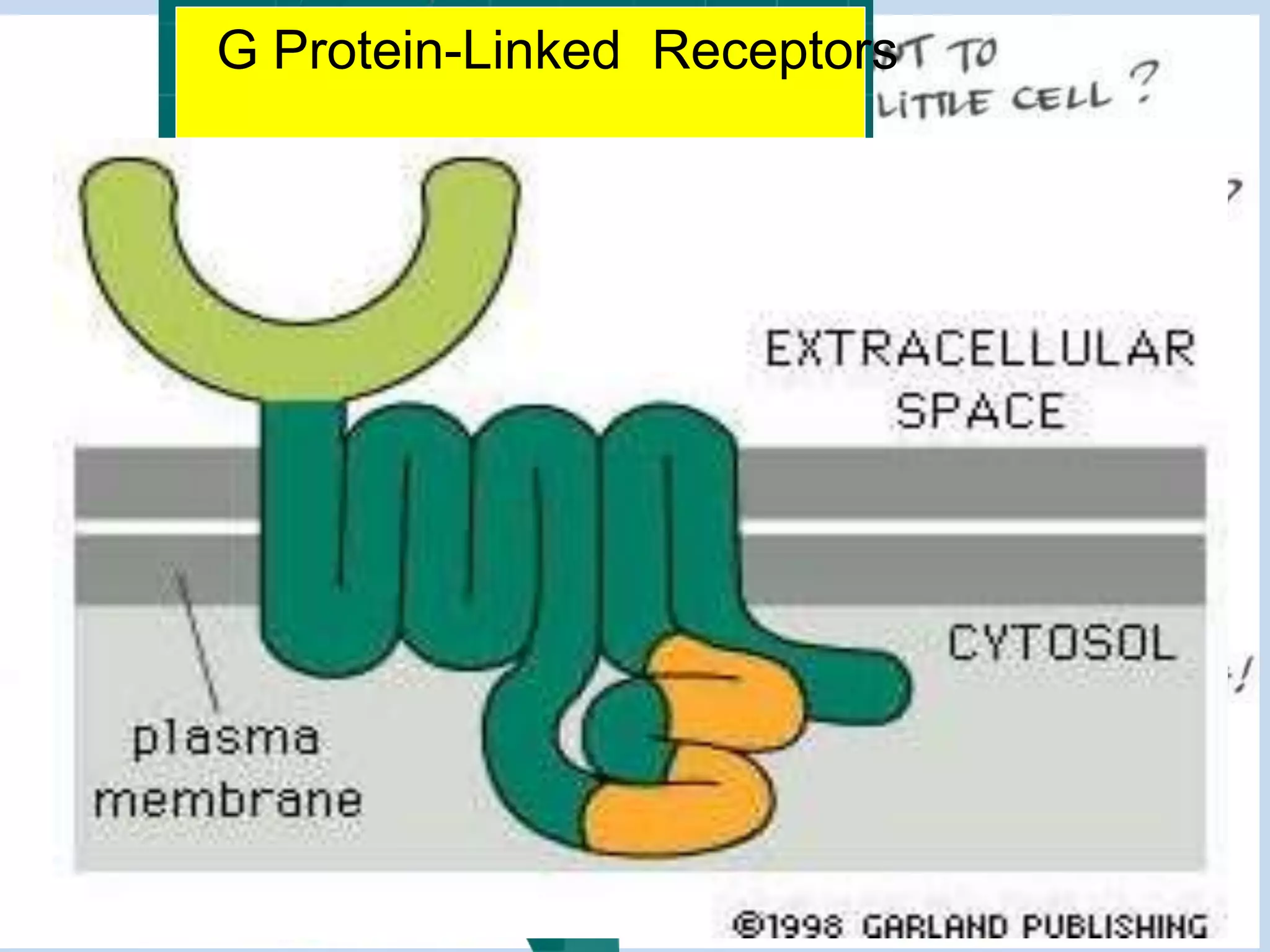
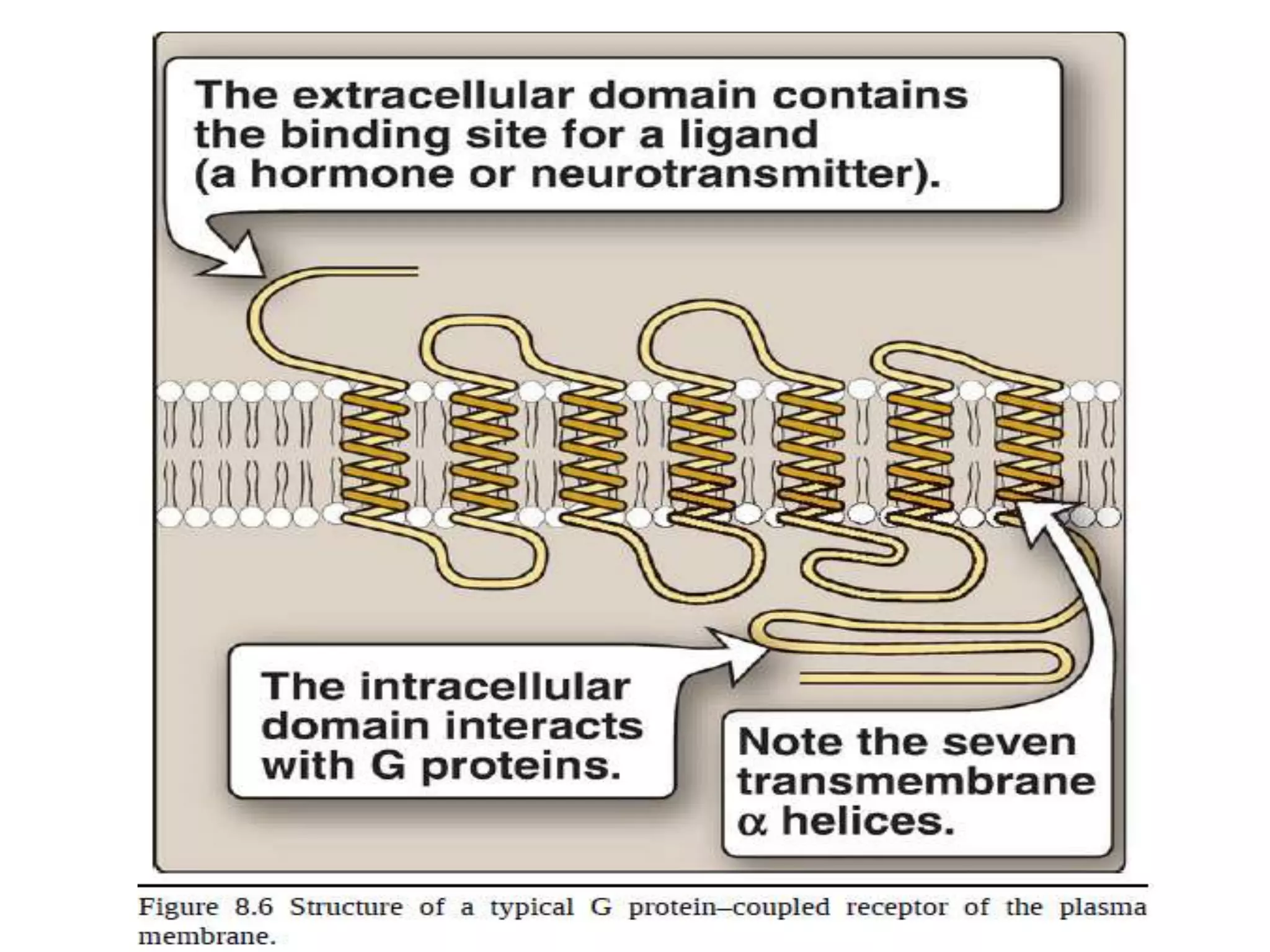
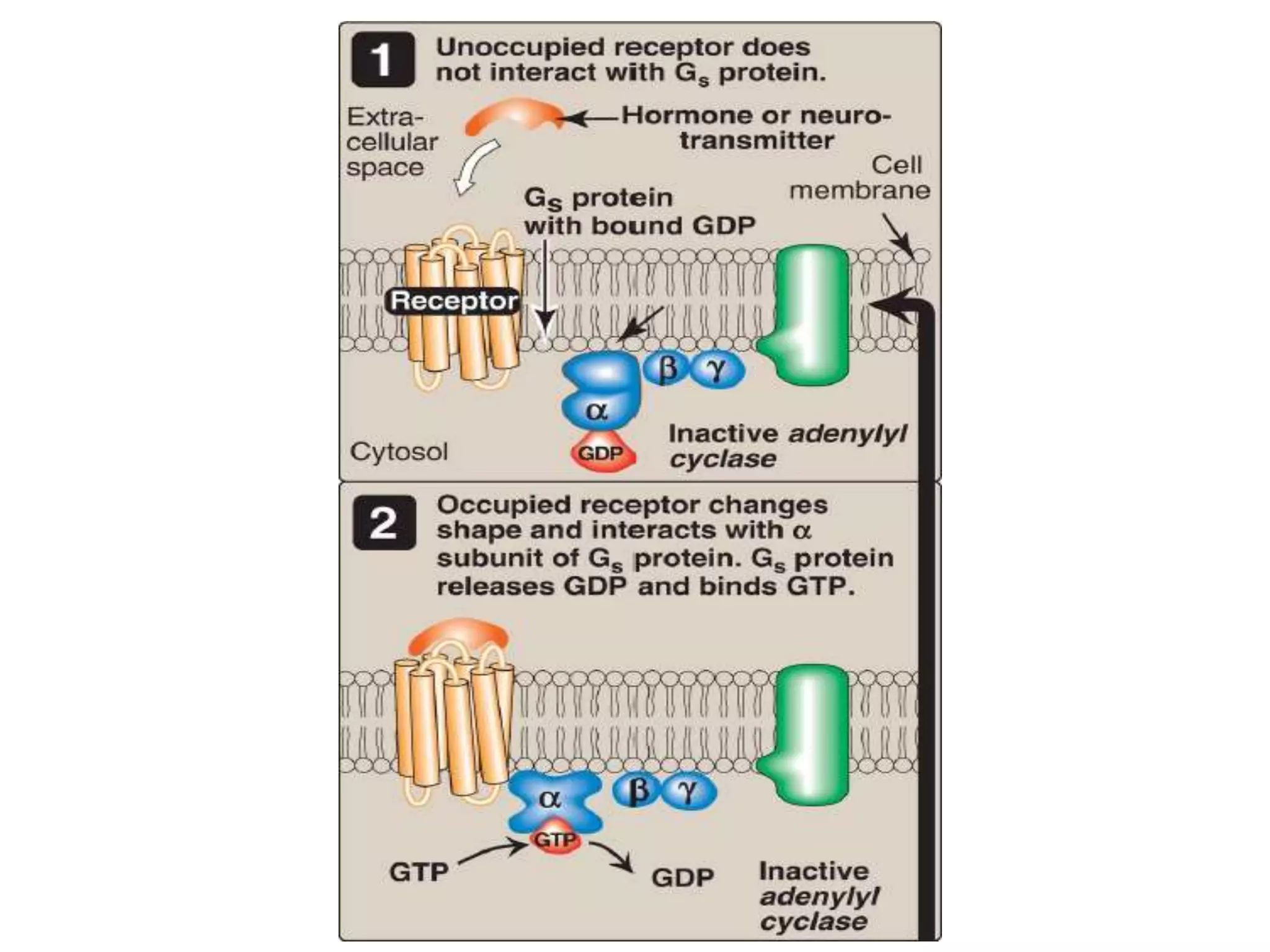
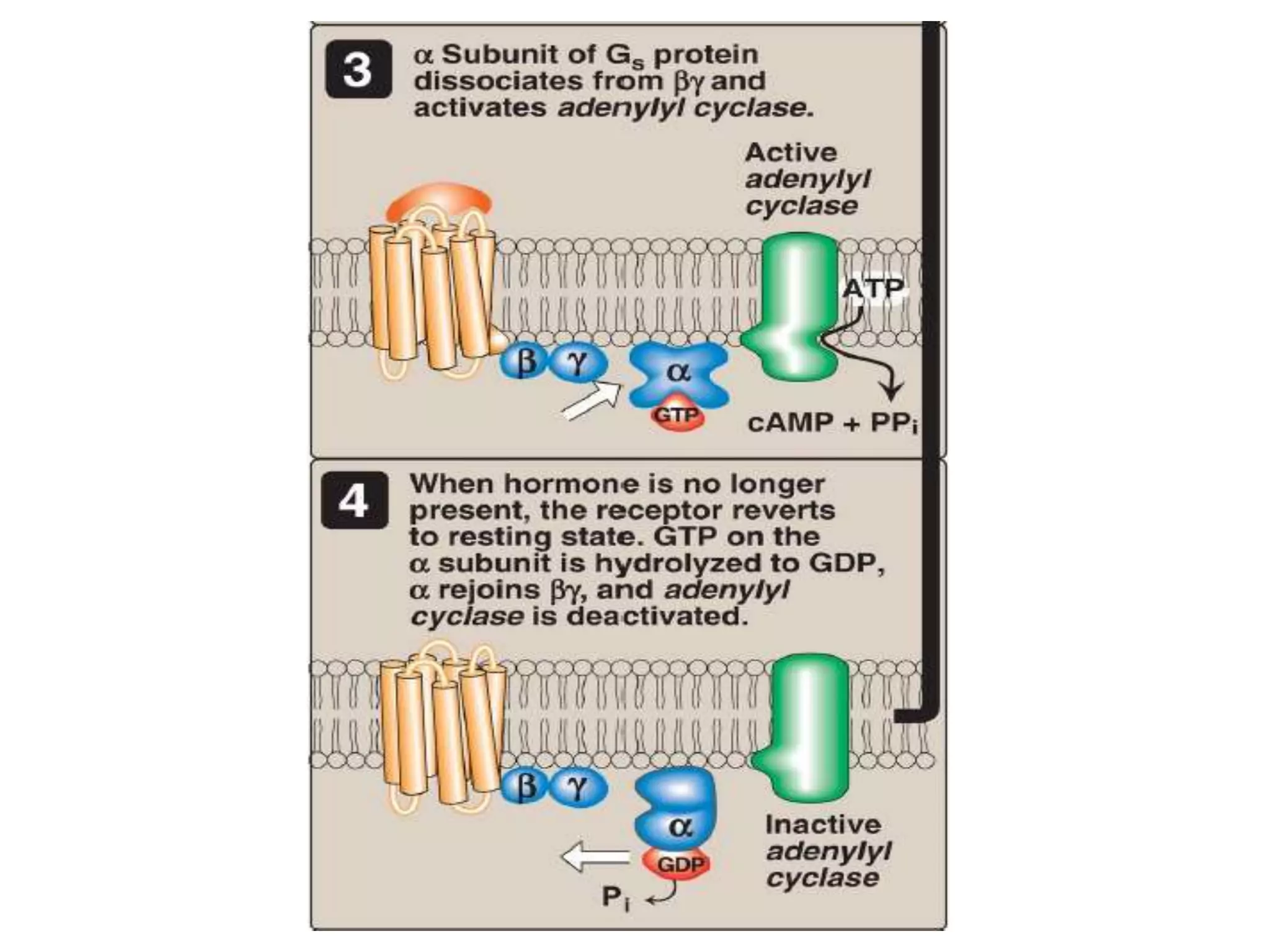
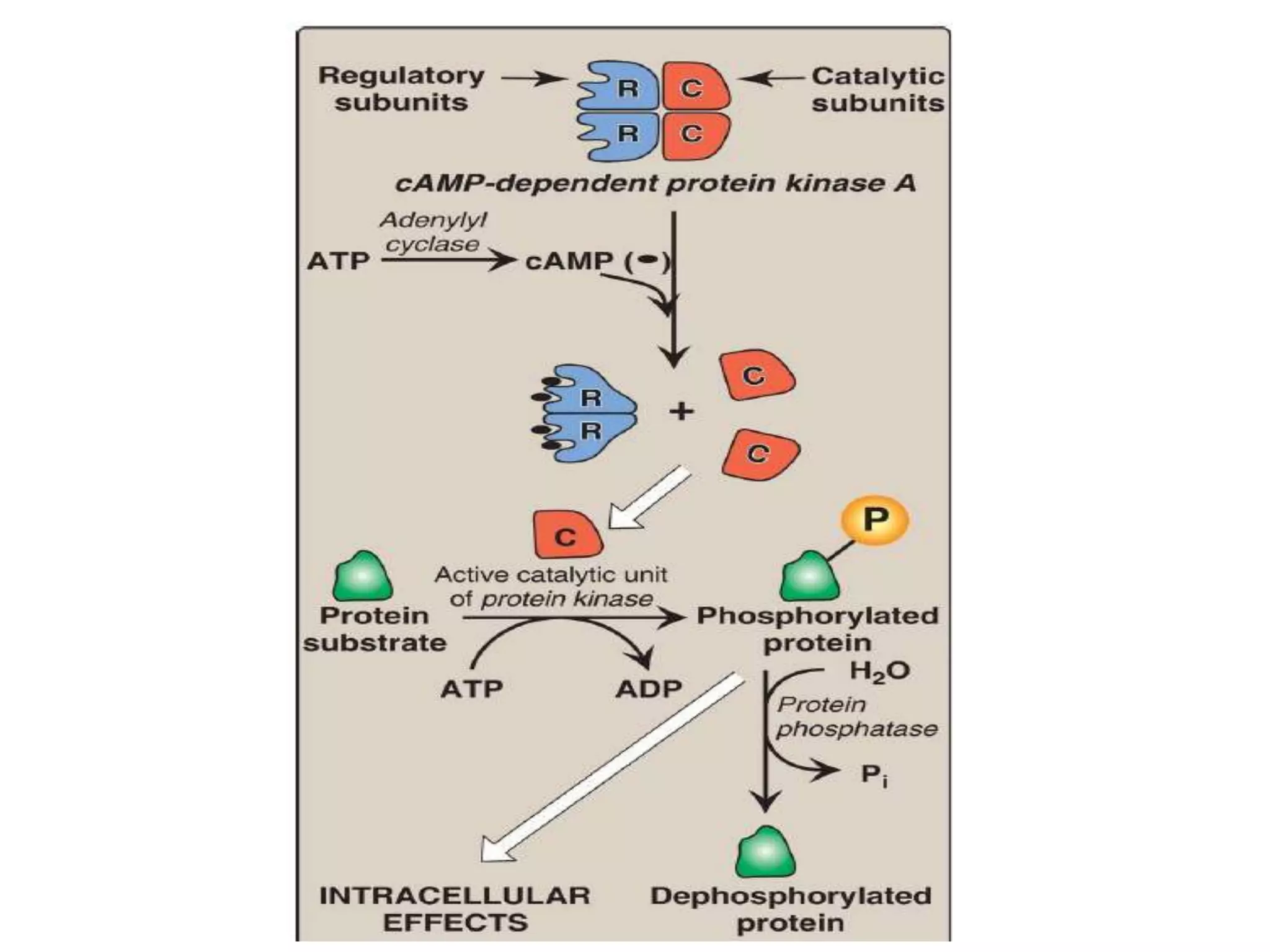
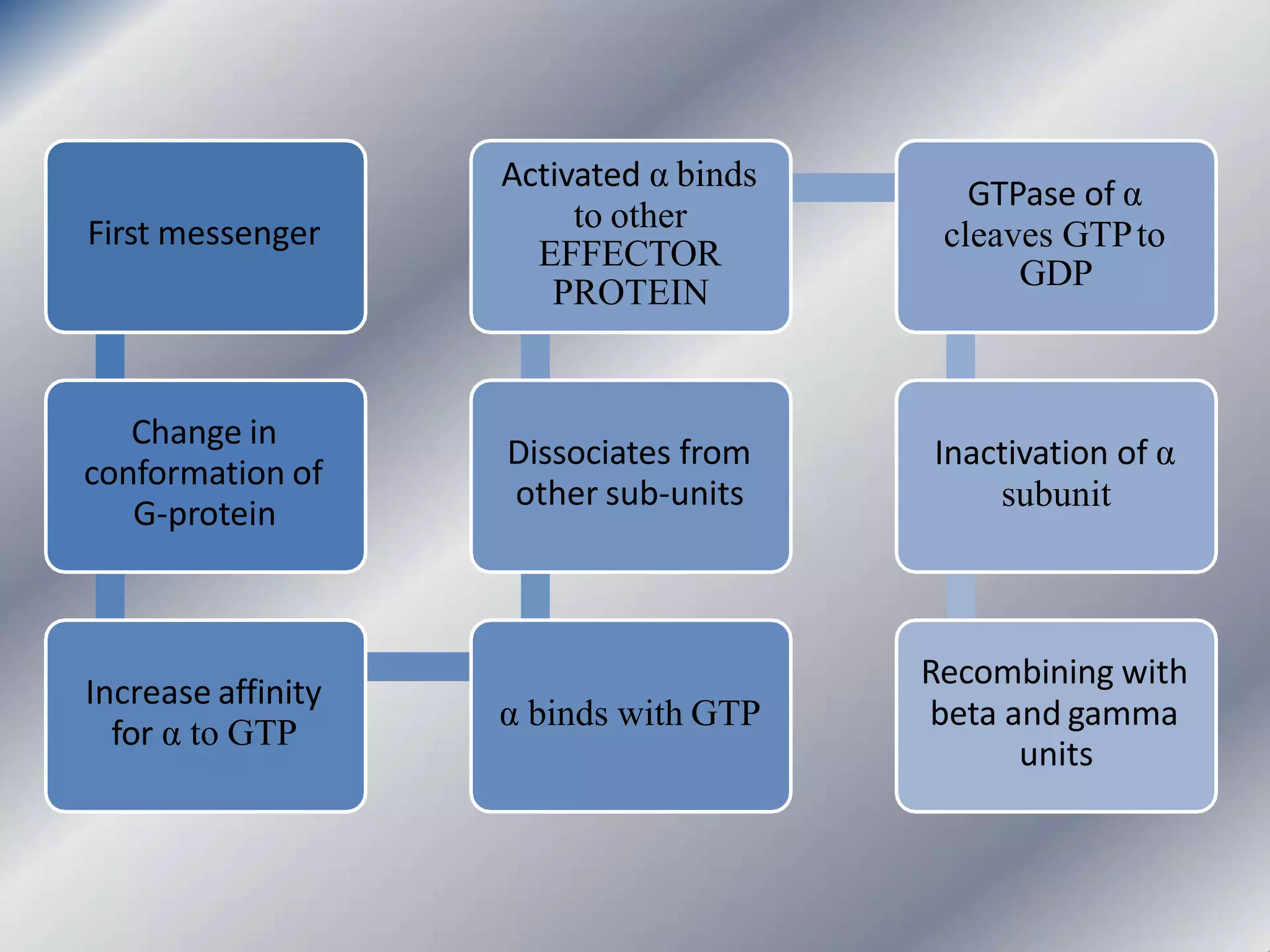
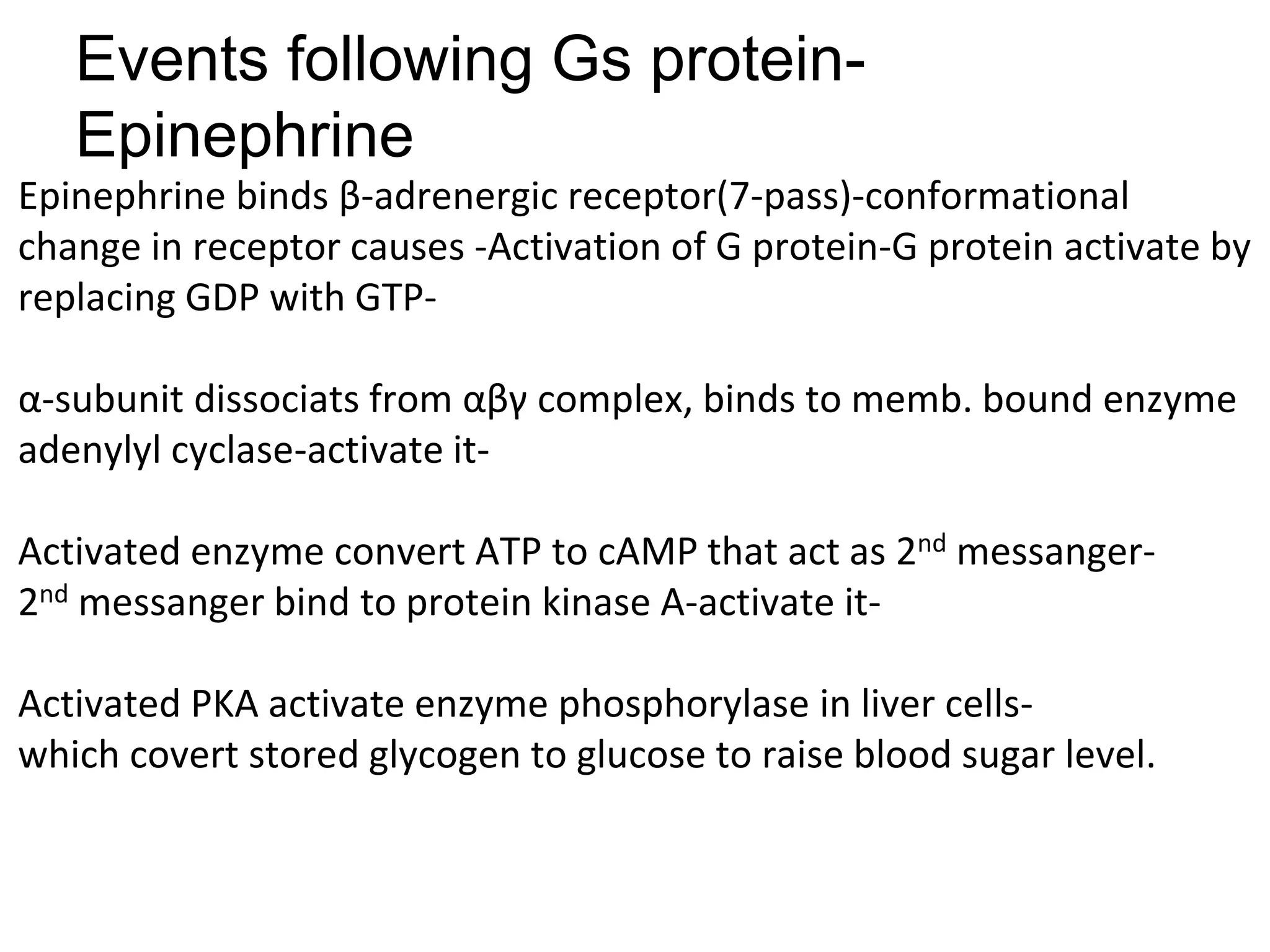
This document provides an overview of cellular signal transduction. It defines signal transduction as the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell via a series of molecular events, mostly protein phosphorylation by protein kinases, resulting in a cellular response. It classifies signal transduction pathways based on their initiation by lipid-soluble or water-soluble messengers and describes the major components involved, including receptors, G proteins, second messengers, and protein kinases. Specific examples of signal transduction pathways mediated by G protein-coupled receptors, receptor tyrosine kinases, and ligand-gated ion channels are discussed.










![Induction of enzyme synthesis
Glucagon increases transcription of thegene for PEPCK and G6P for
gluconeogenesis.
It is via the transcription factor cAMP response element–binding (CREB)
protein, thereby increasing the availability of this enzyme as levels of
its substrate rise during fasting.
[Note: Cortisol (a glucocorticoid) also increases expression of the gene,
whereas insulin decreases expression.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecsignaltransduction-140413033710-phpapp01-200207142349/75/signal-transduction-AIMC-44-2048.jpg)