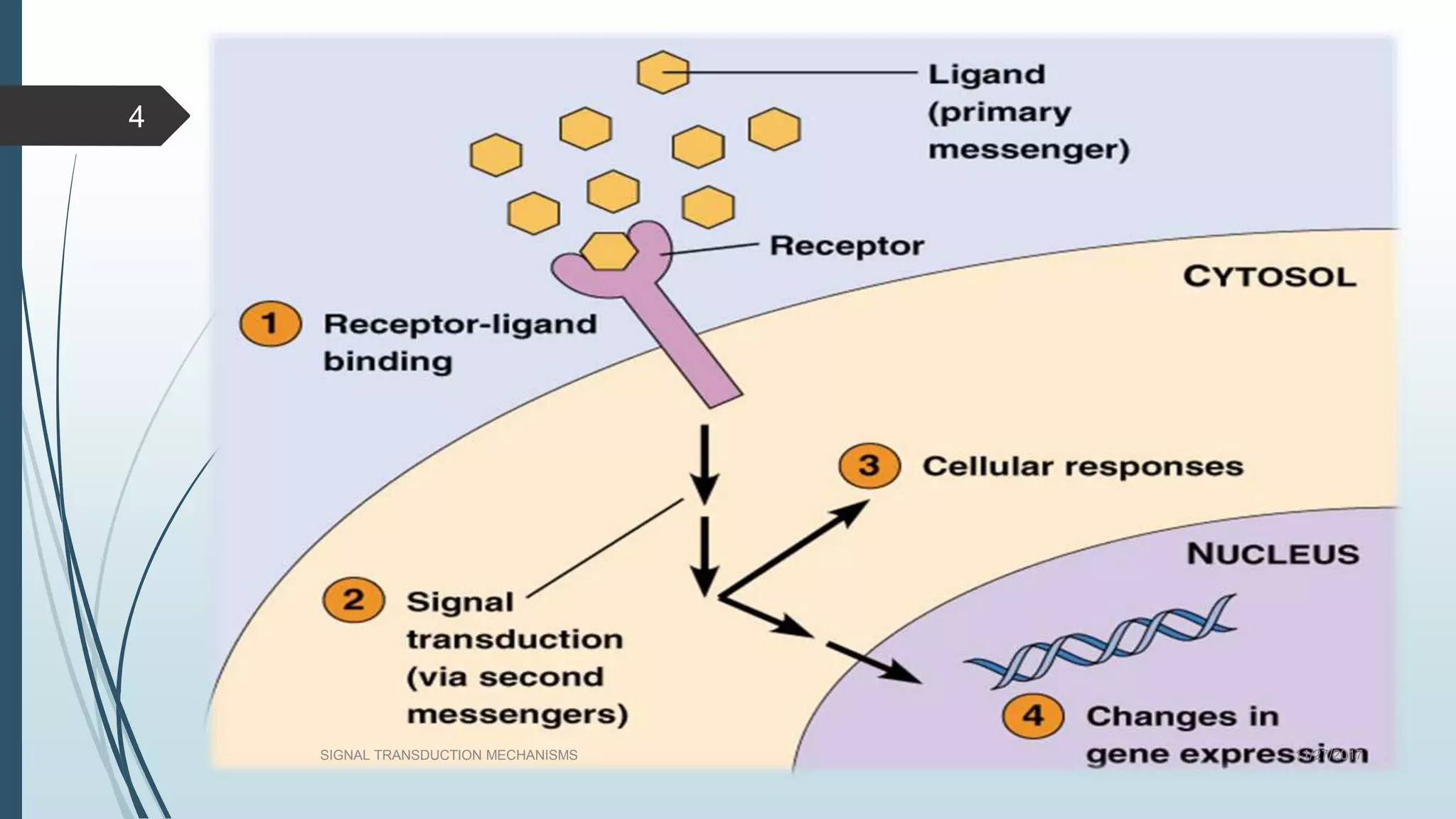
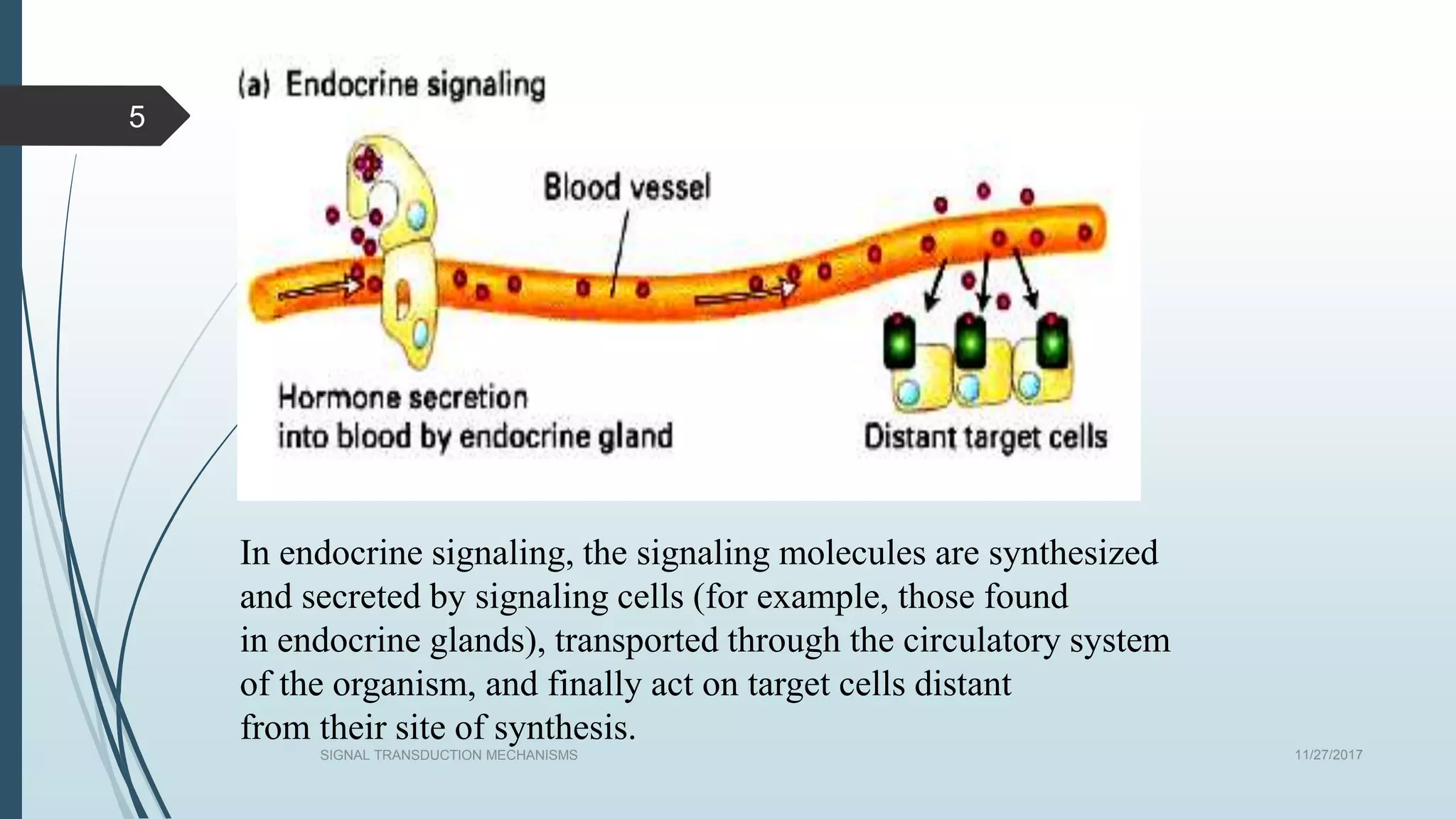
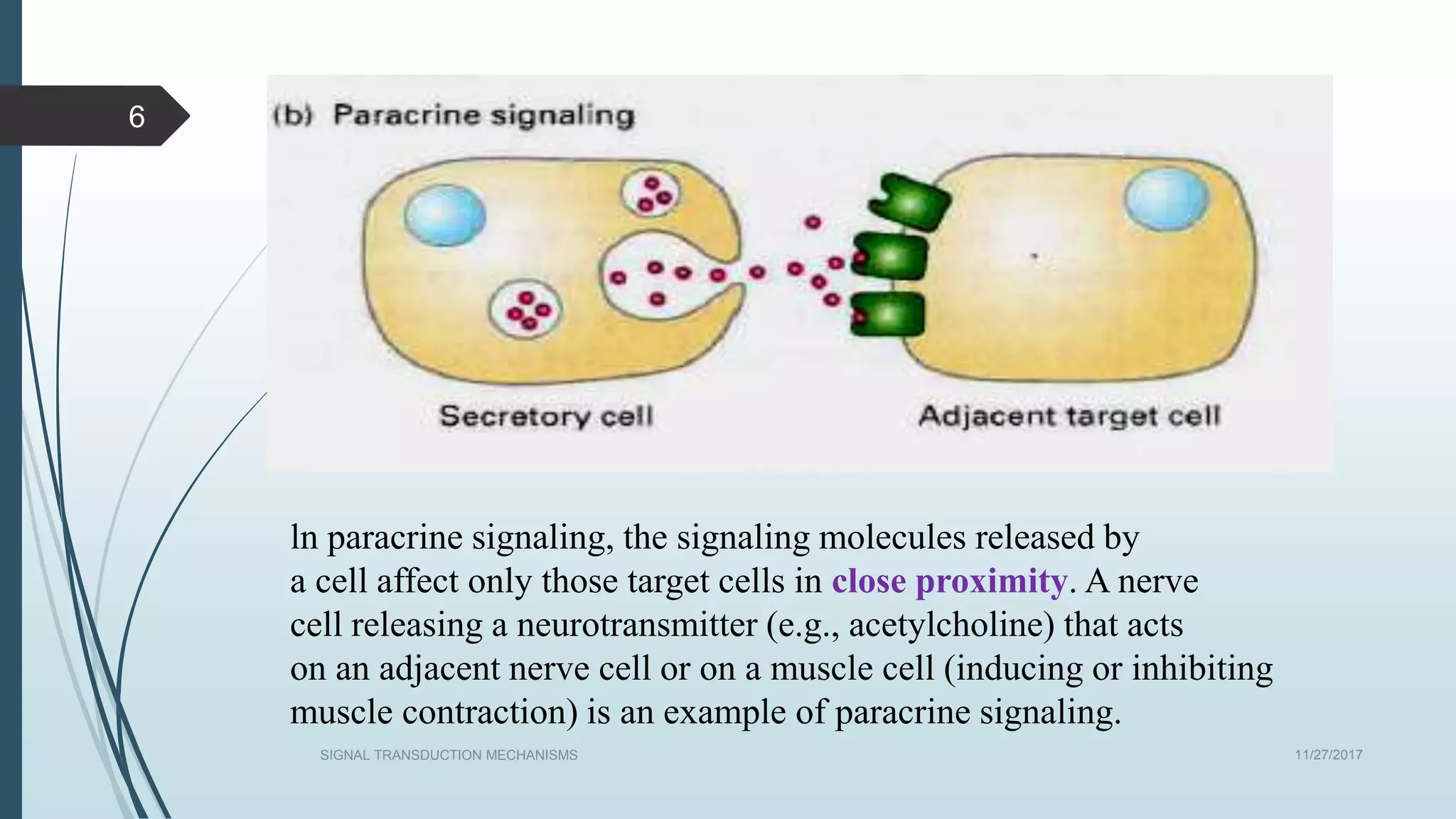
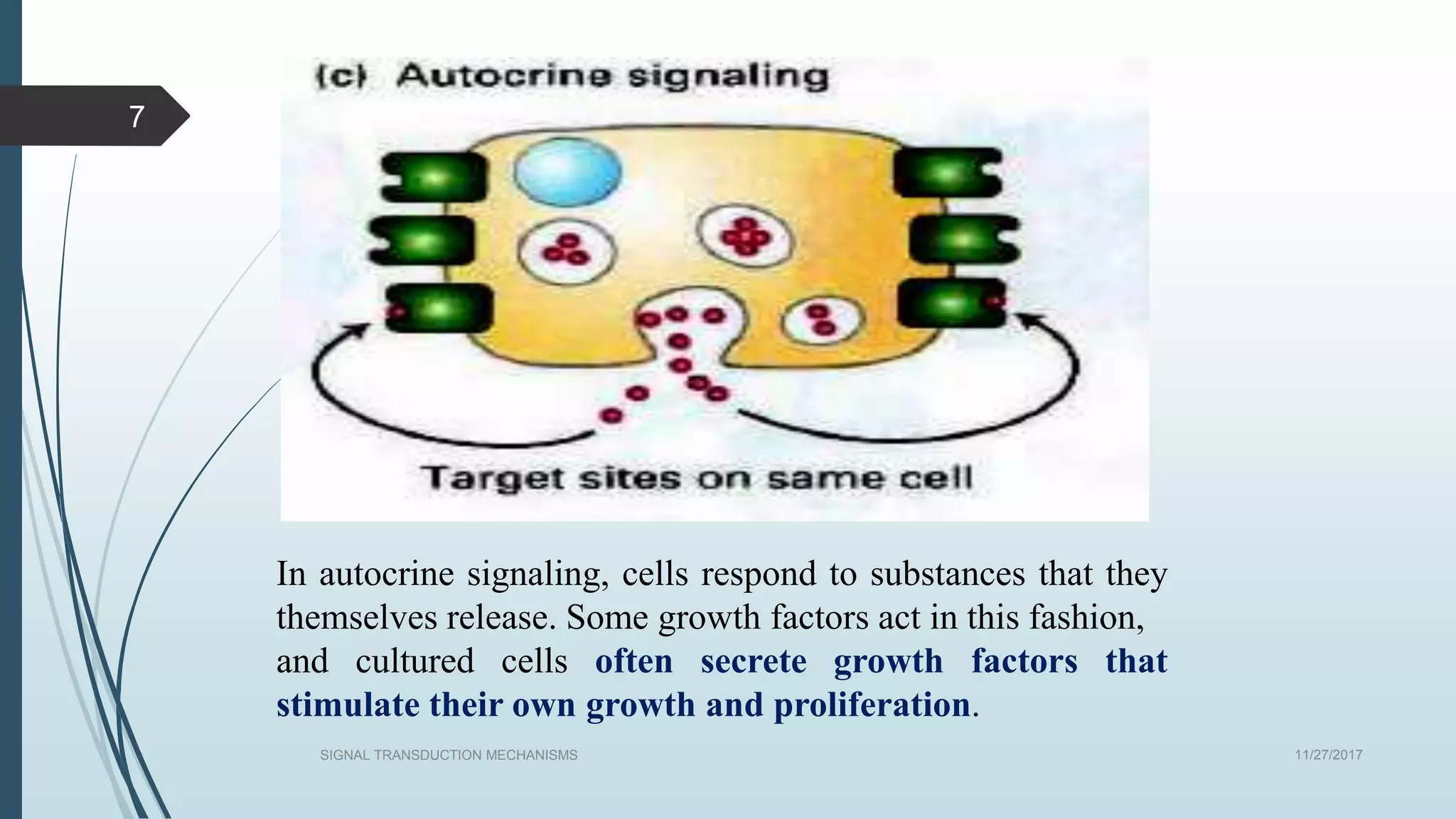
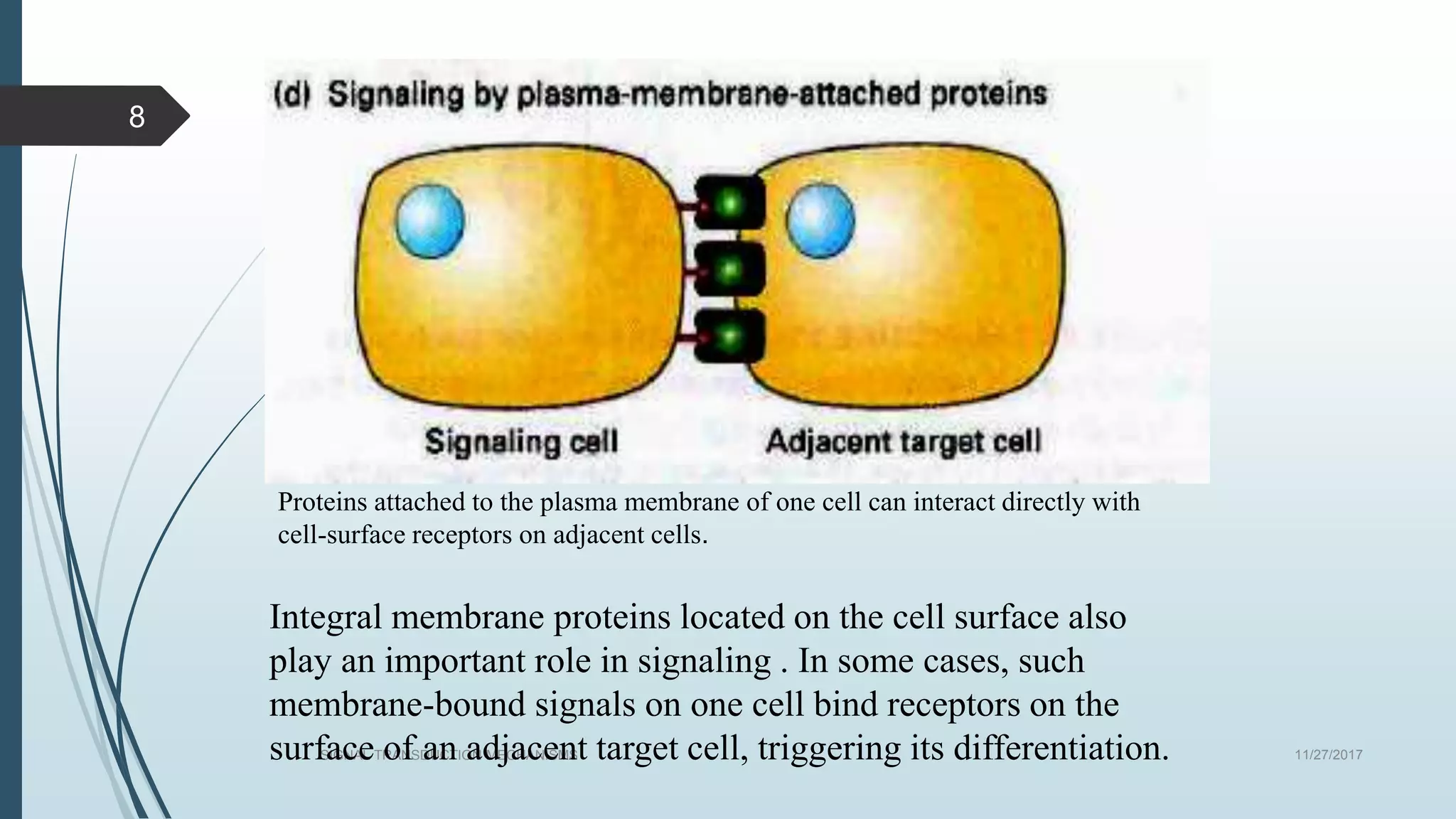
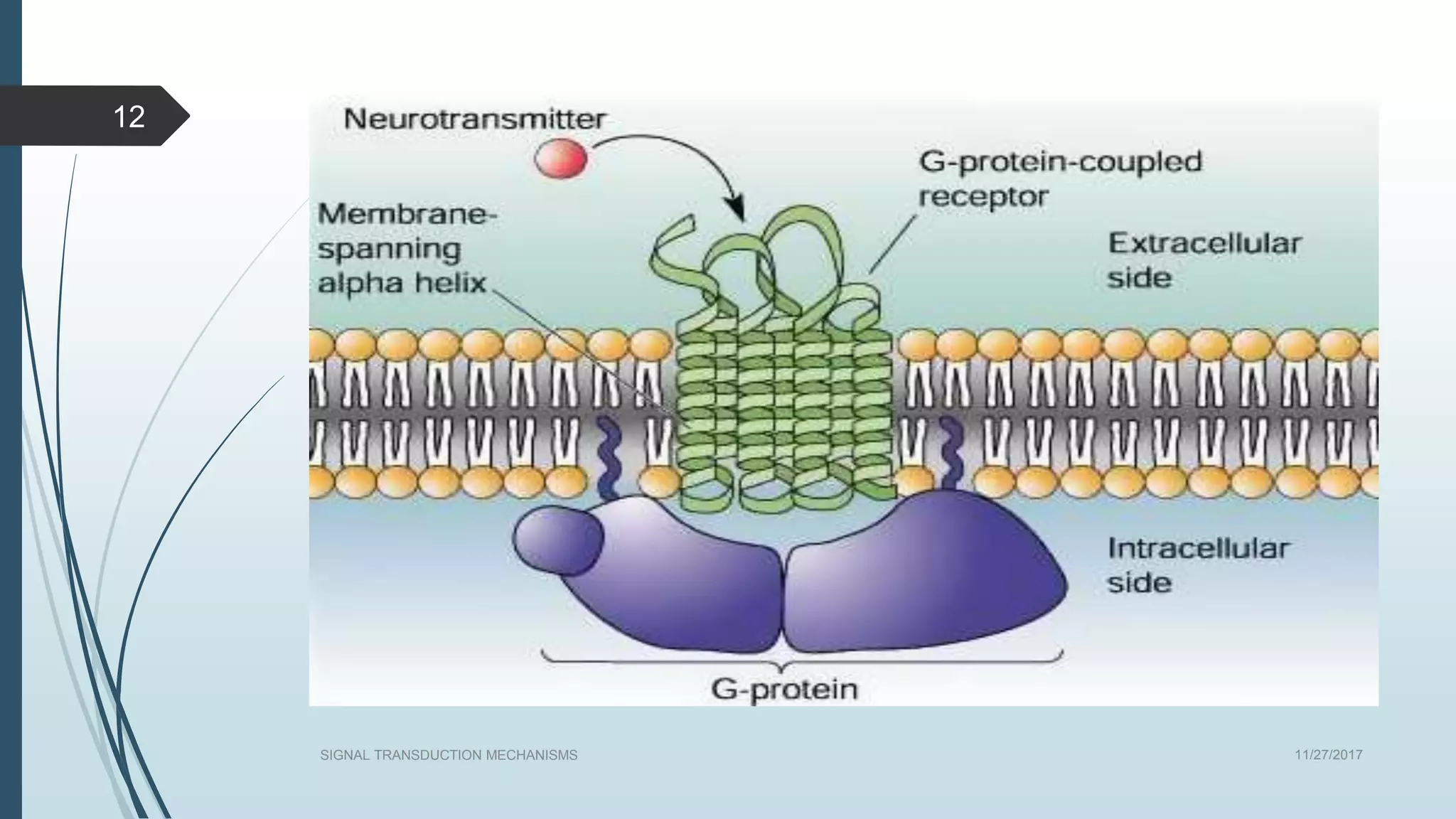
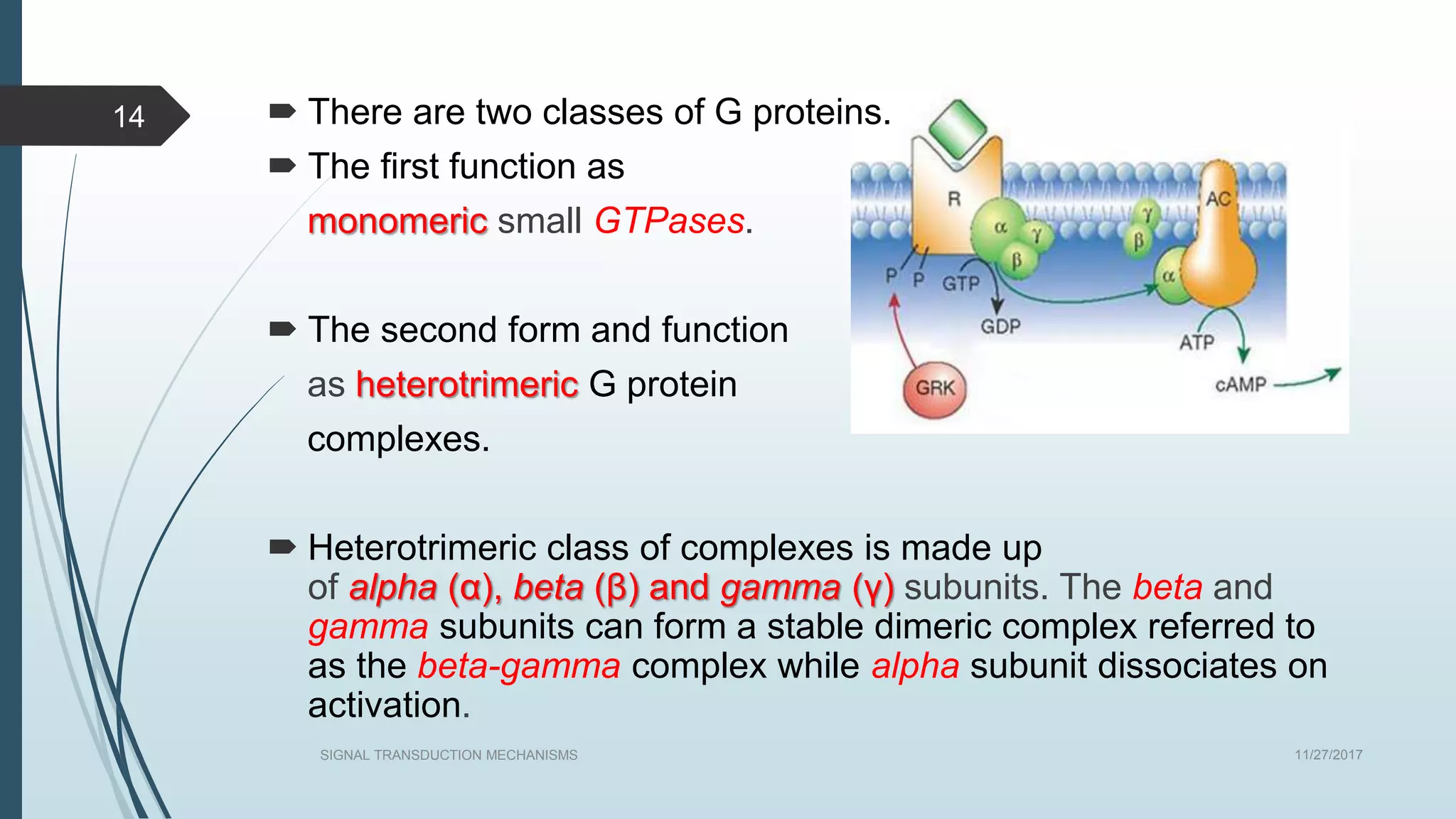
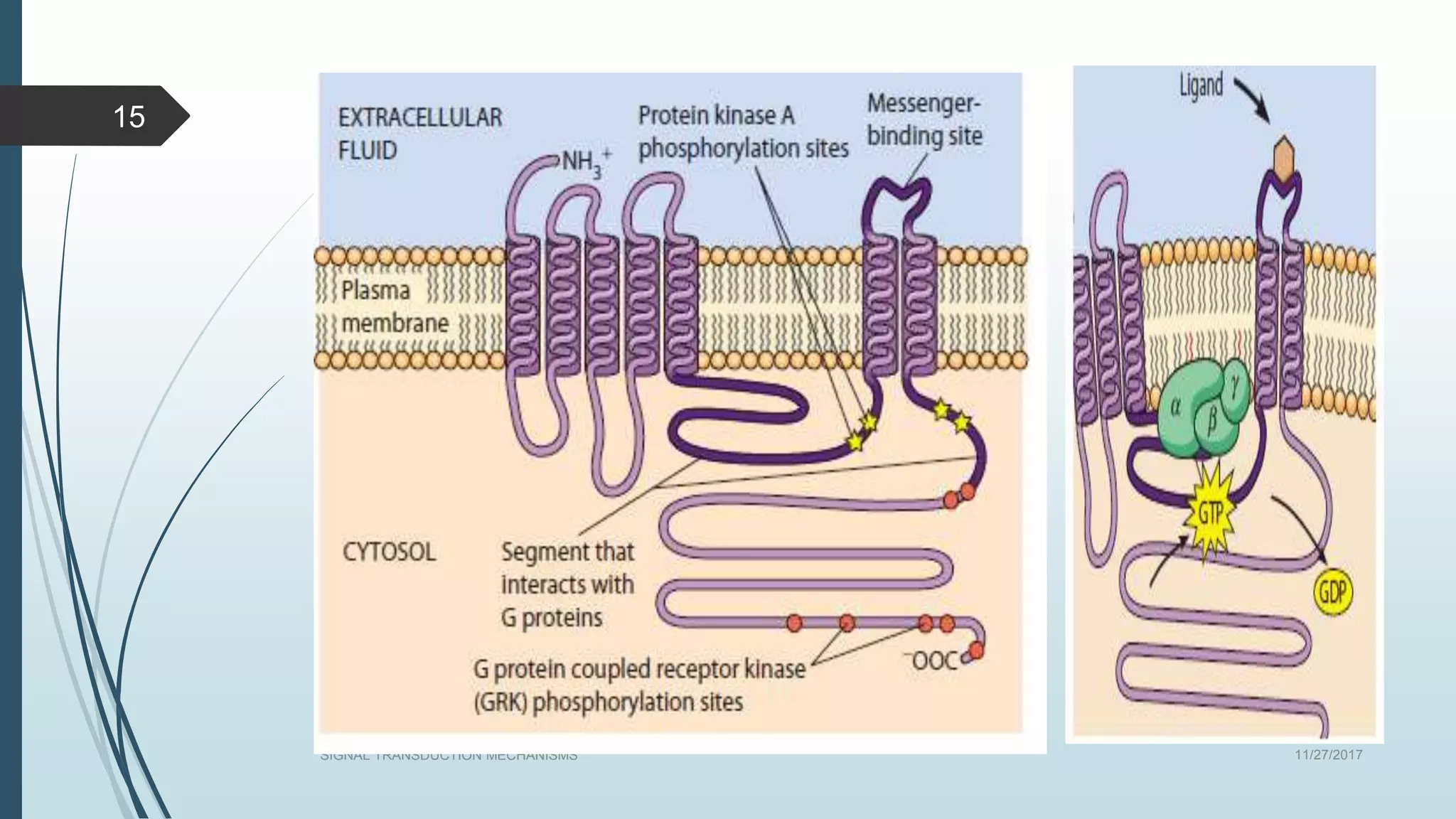
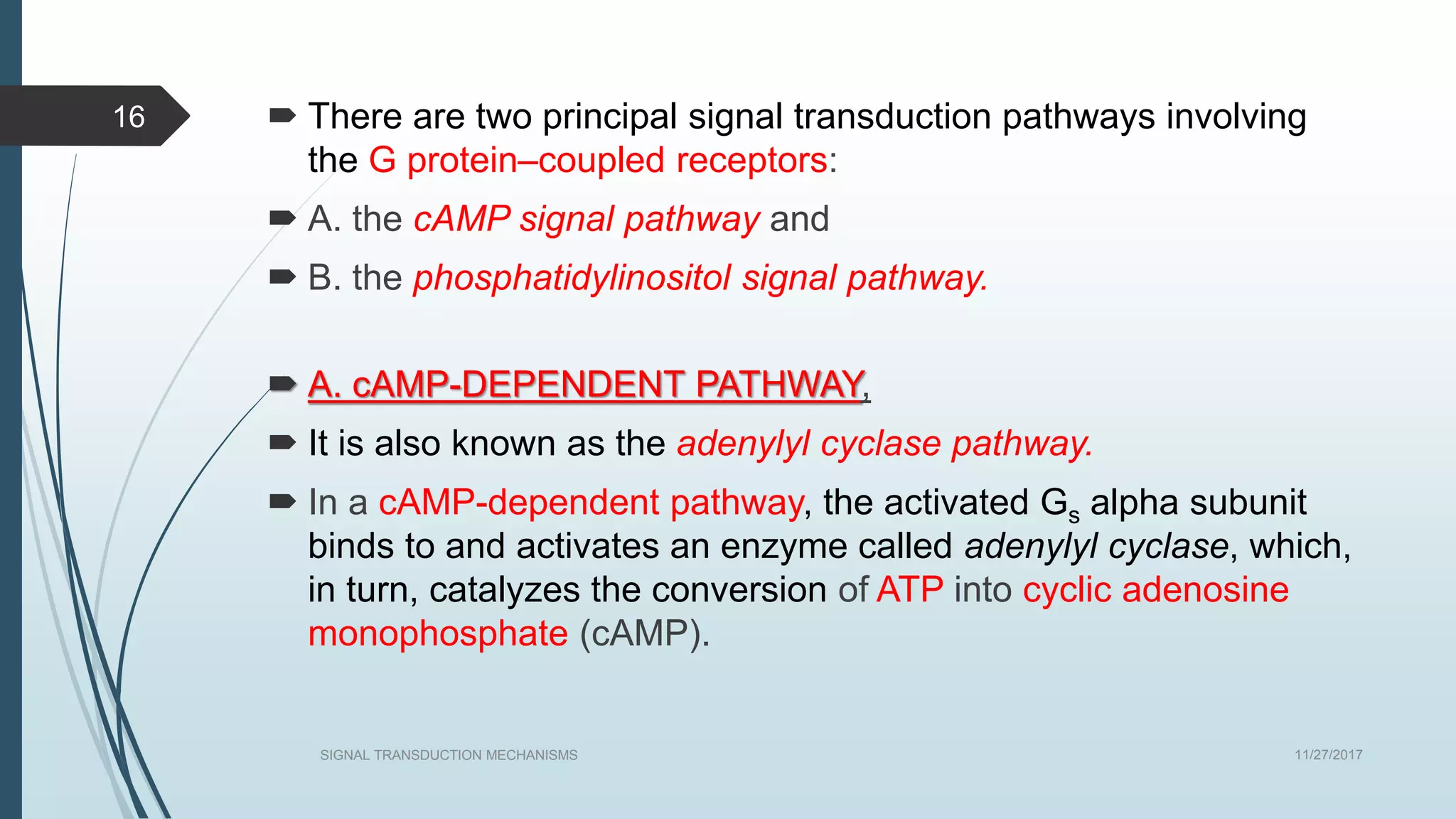
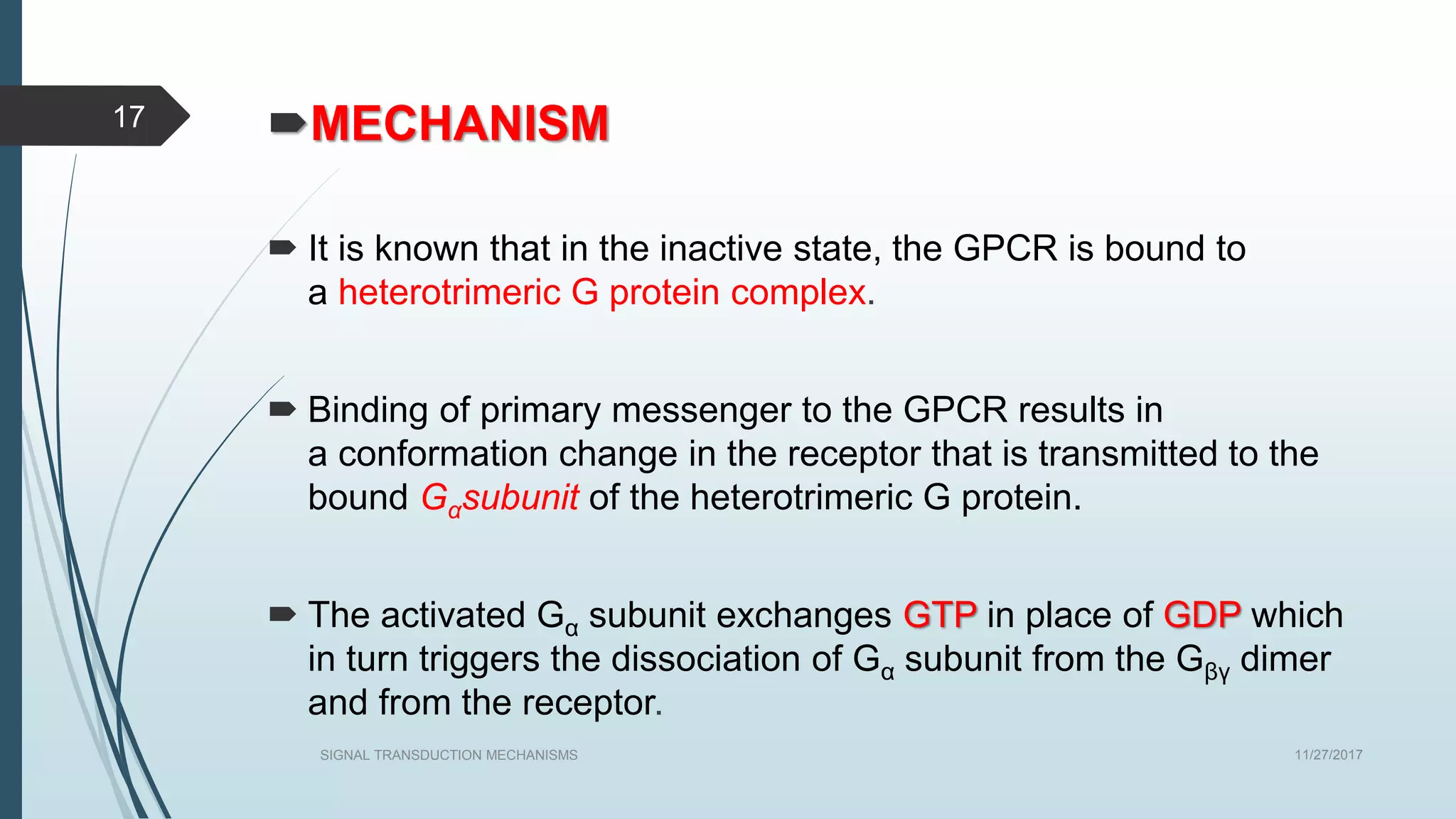
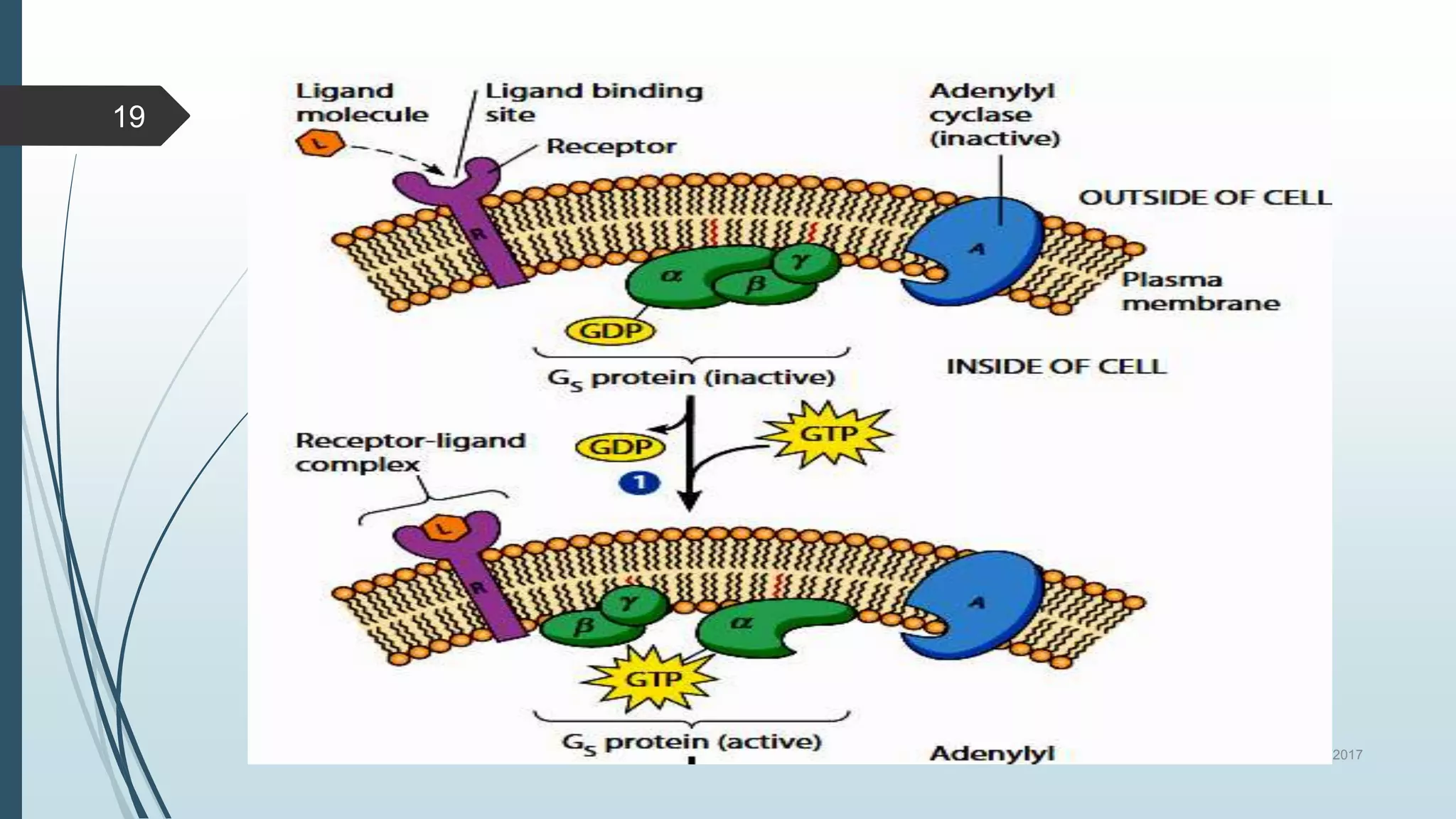
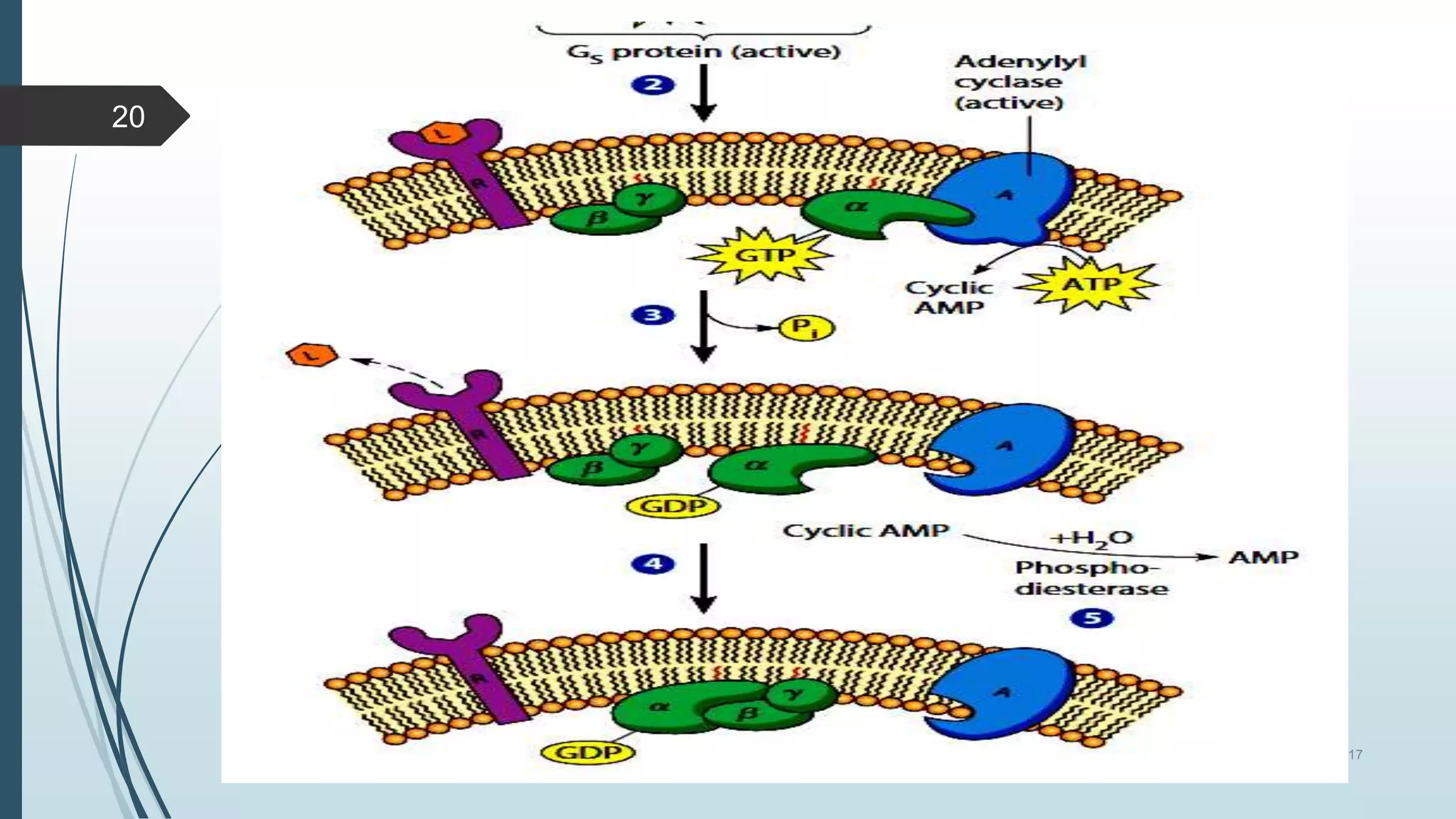
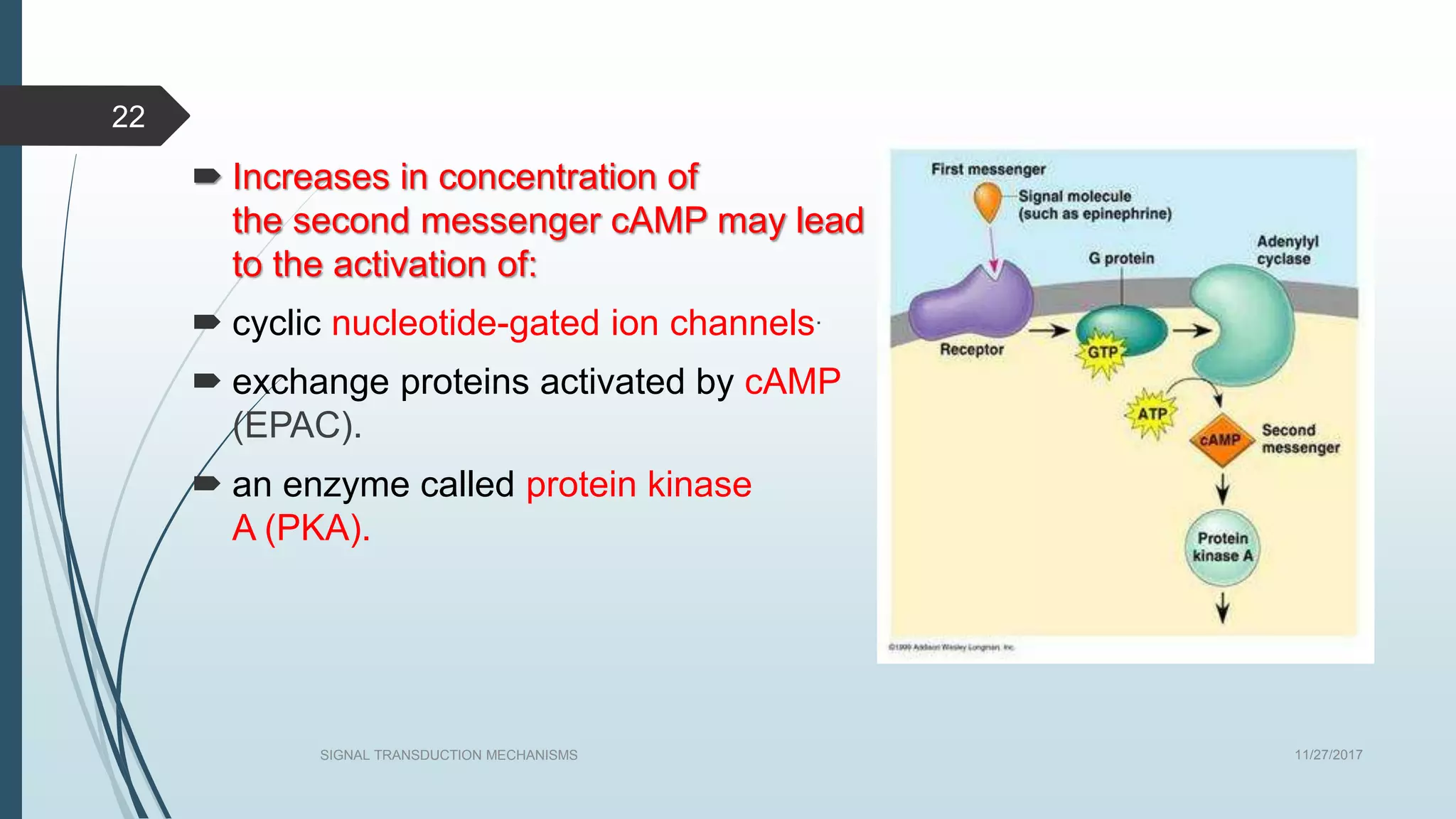
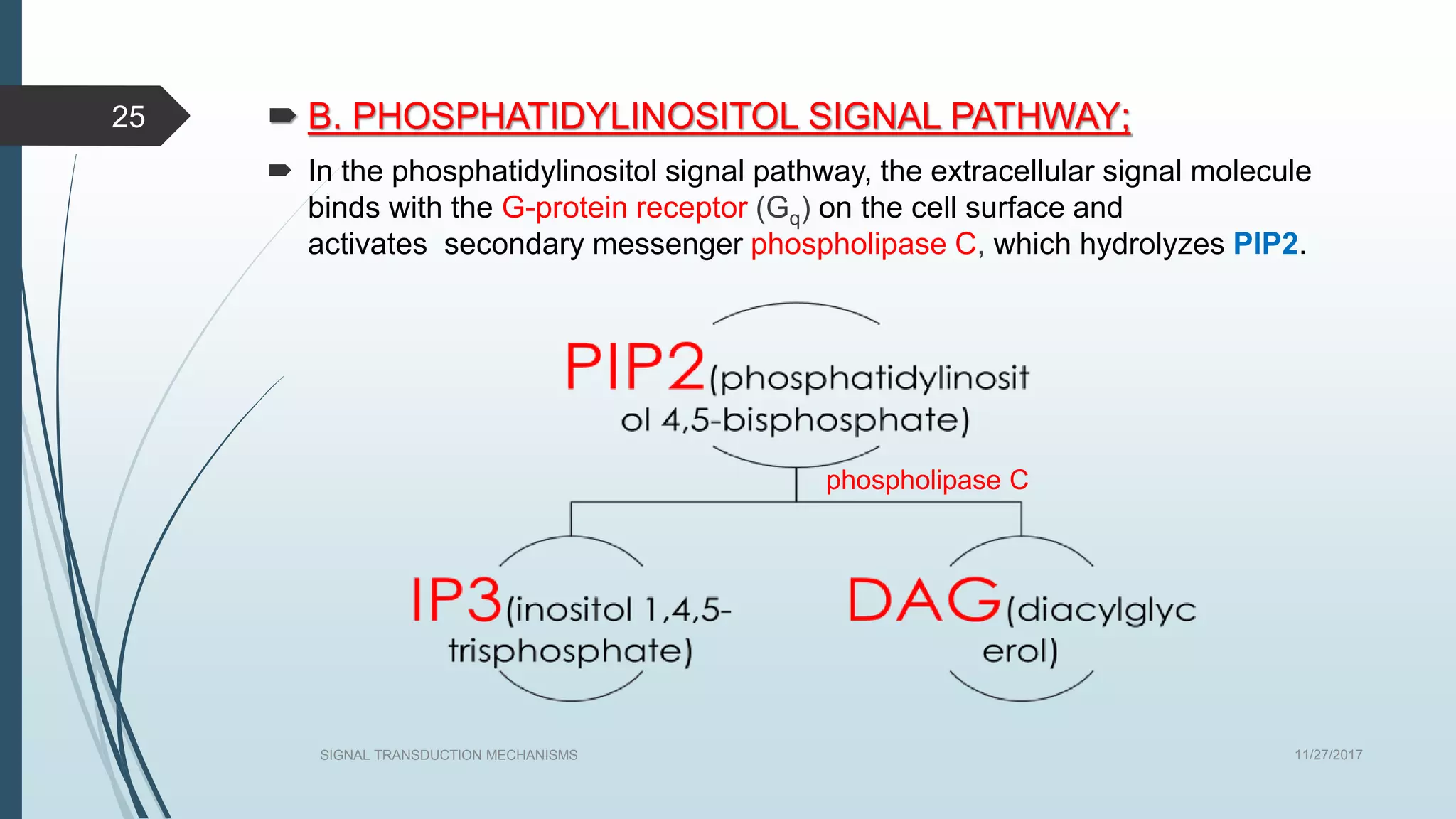
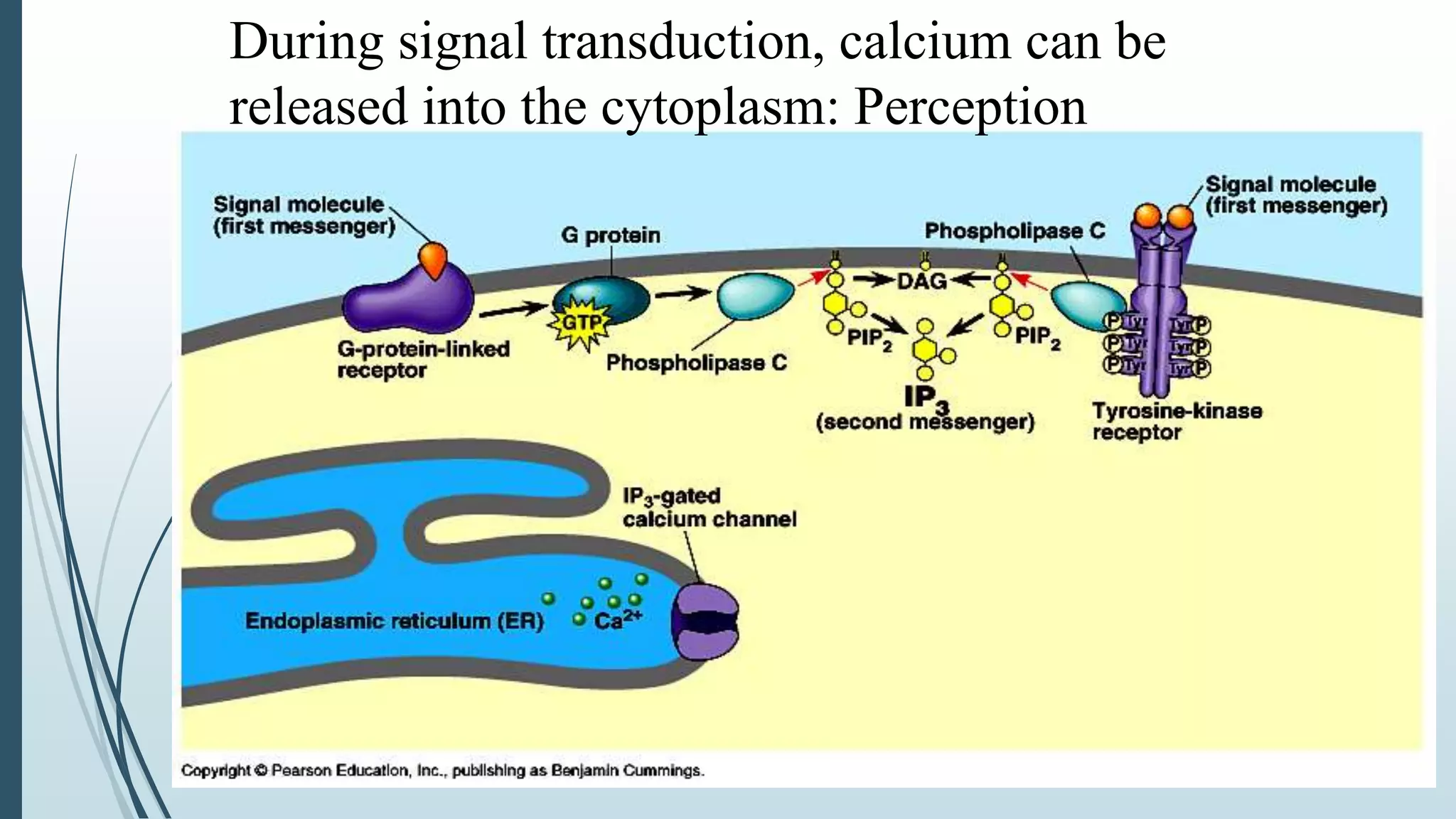
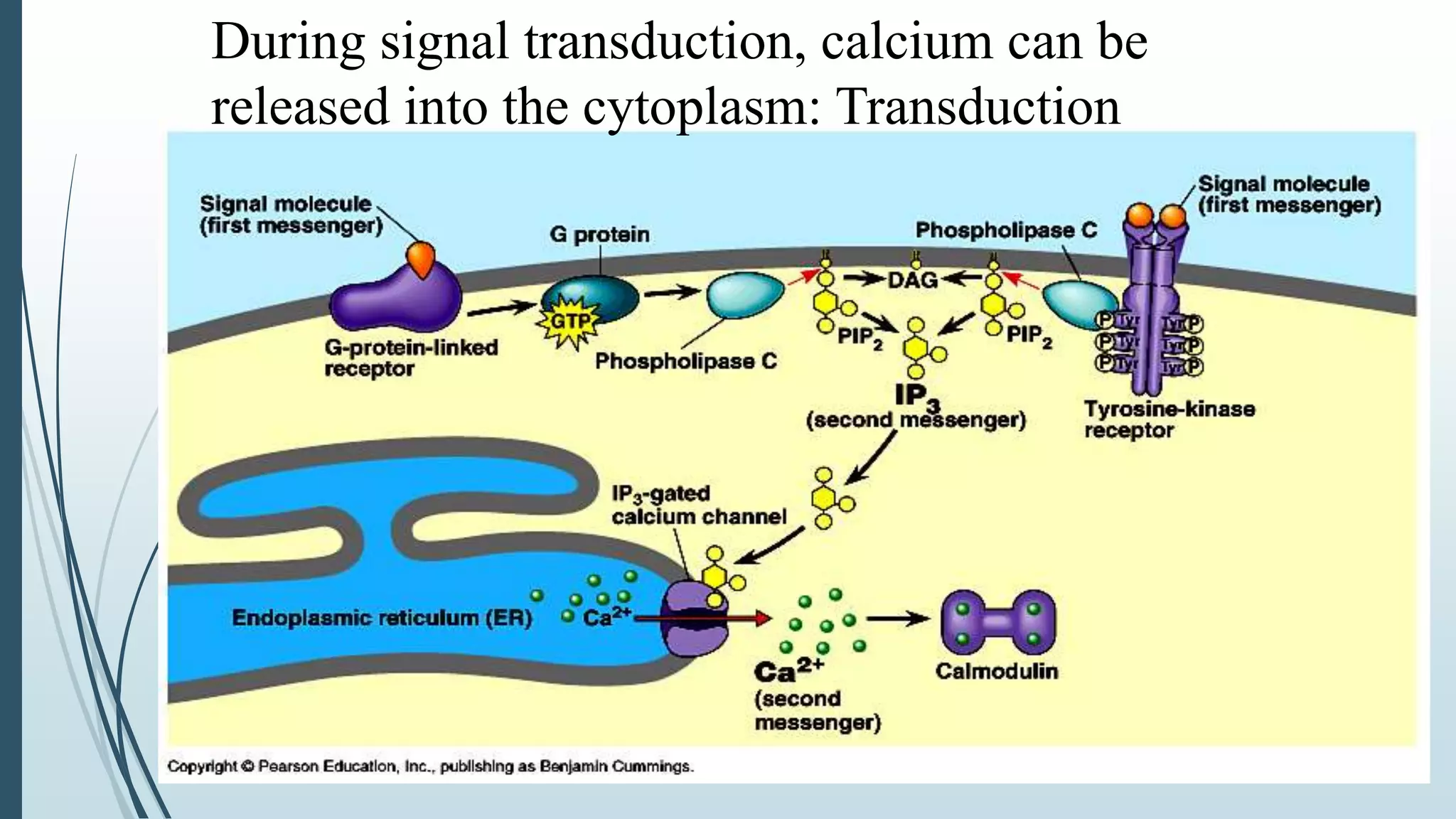
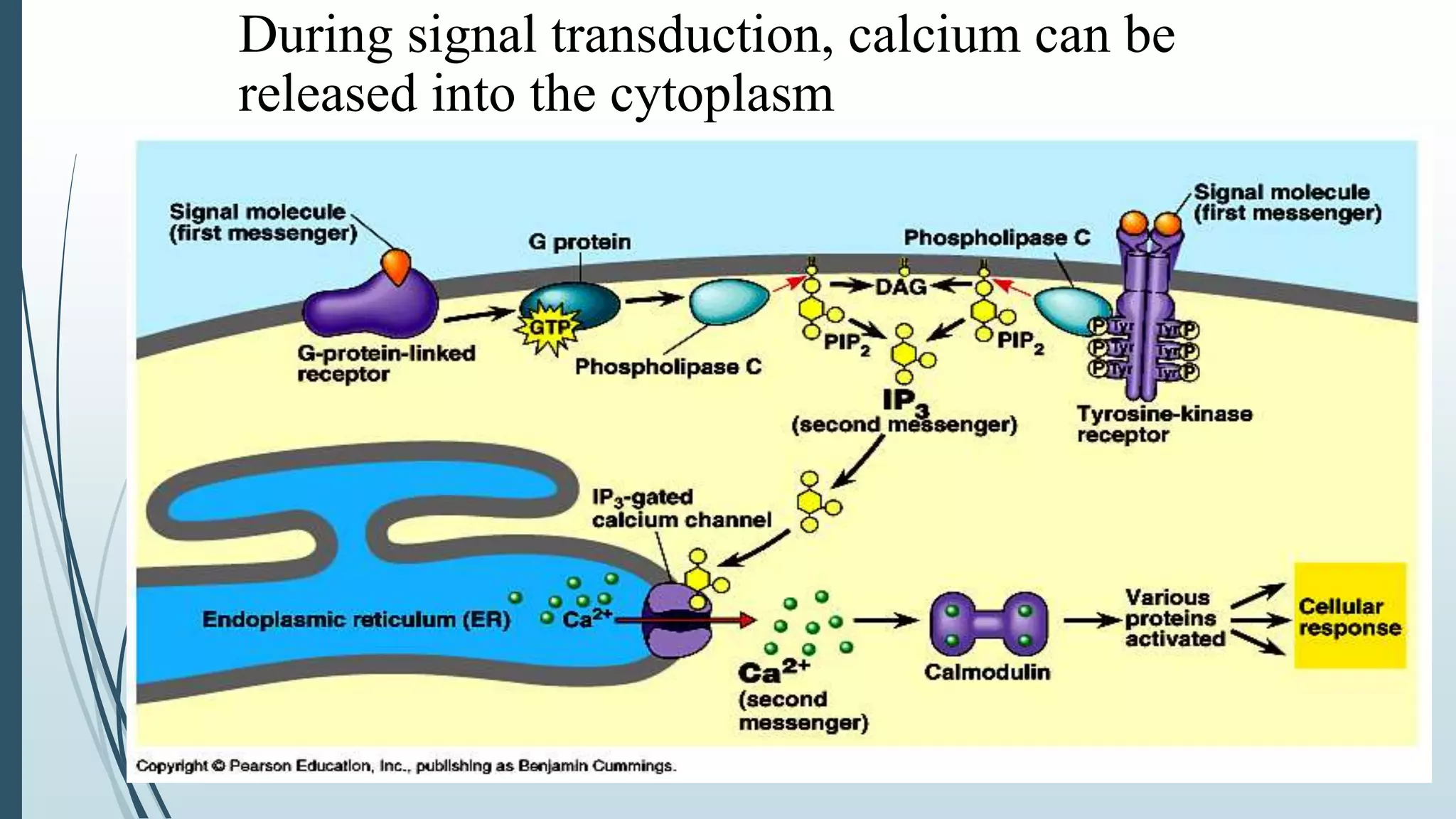
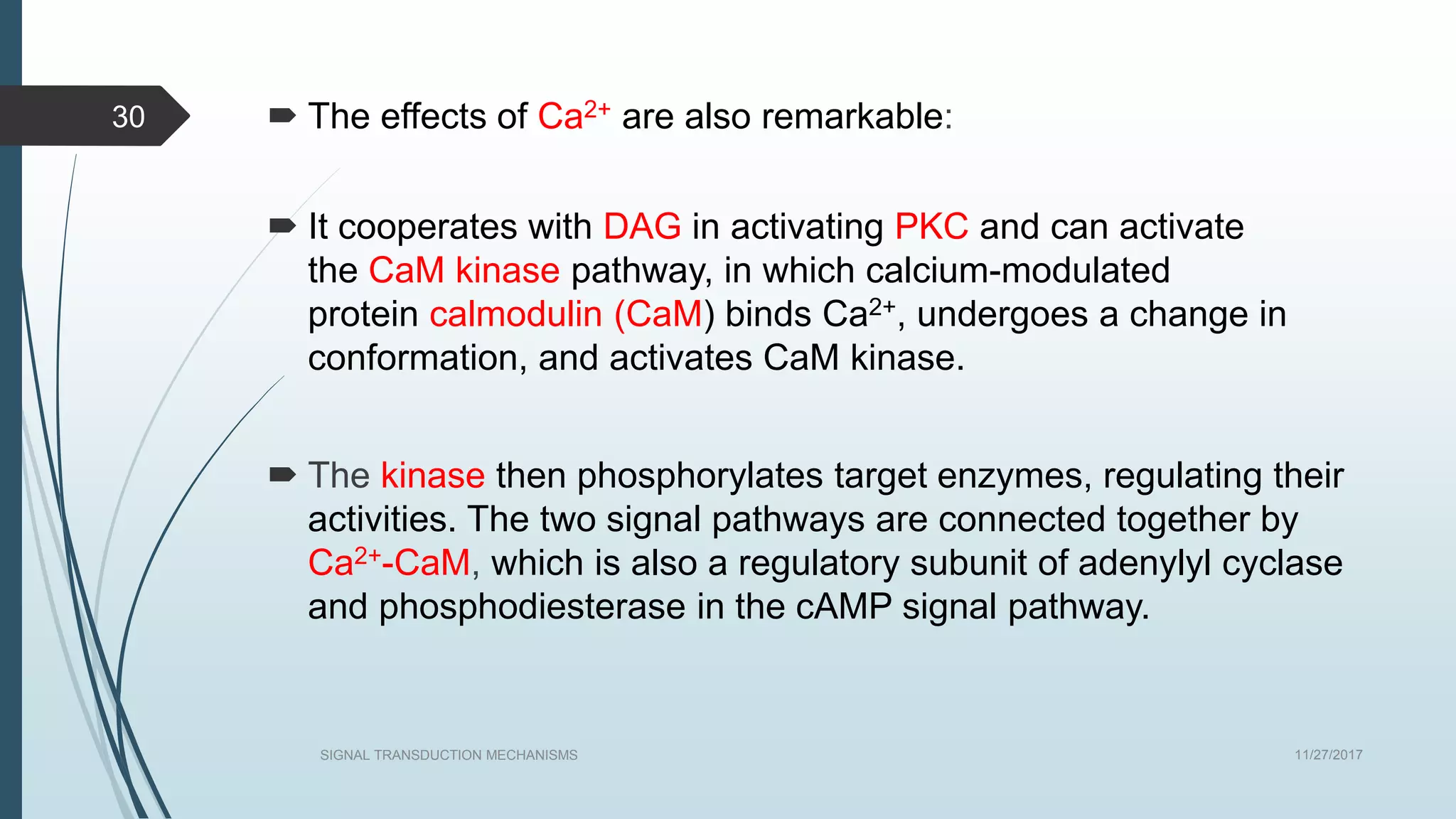
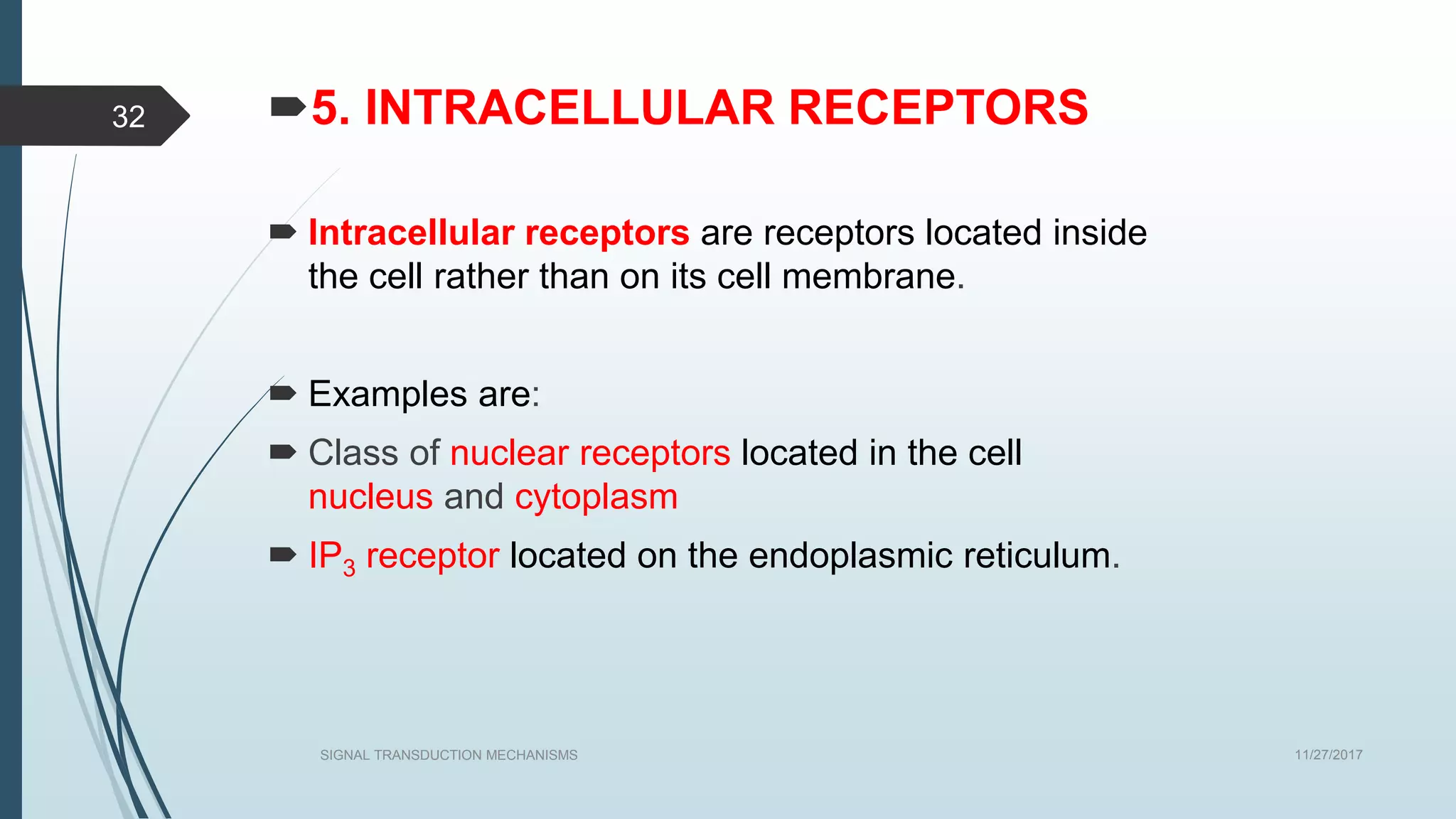
Signal transduction begins with ligand binding to a receptor on the cell surface. This triggers a series of molecular events within the cell through second messengers like cAMP or IP3. These second messengers activate intracellular pathways that ultimately result in changes in cell function or gene expression. The two major pathways are the cAMP pathway which activates protein kinase A, and the phosphatidylinositol pathway which activates protein kinase C through IP3 and calcium release. These second messenger systems allow cells to respond appropriately to signals from other cells.