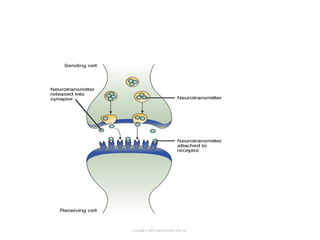
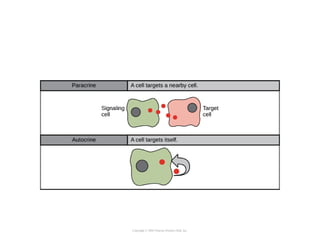
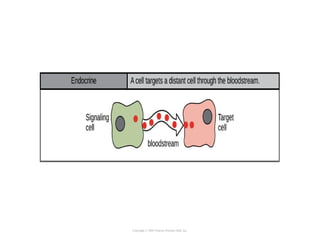
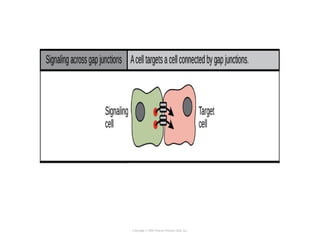
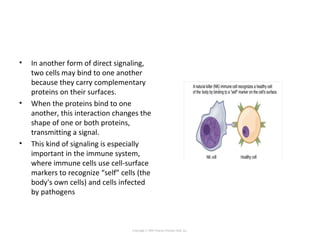
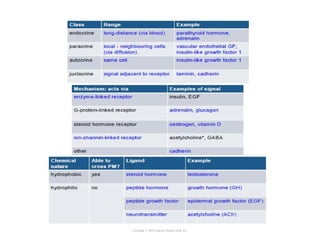
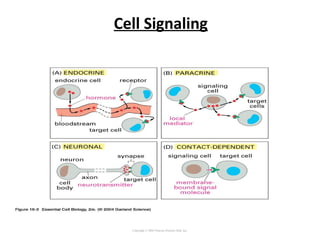
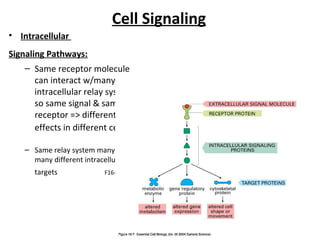
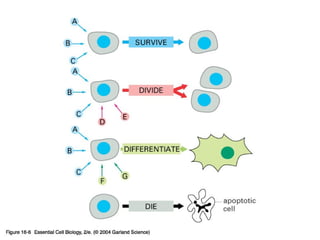
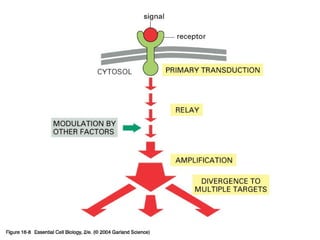
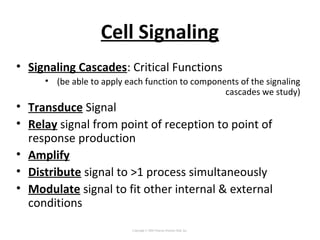
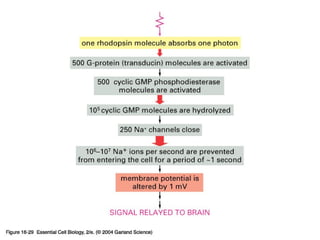
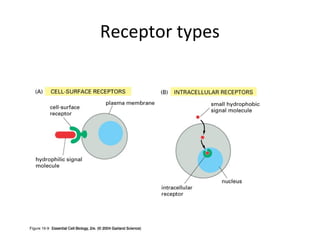
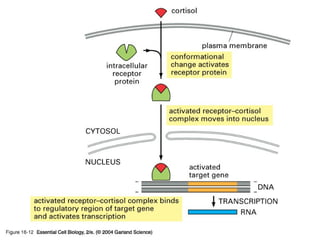
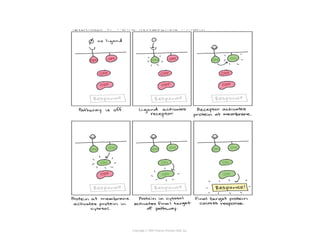
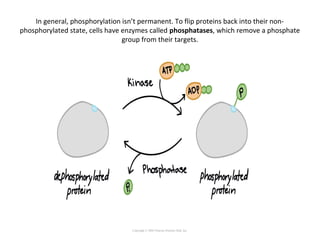
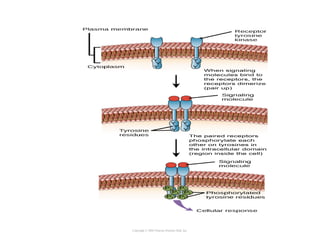
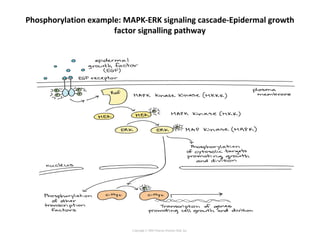
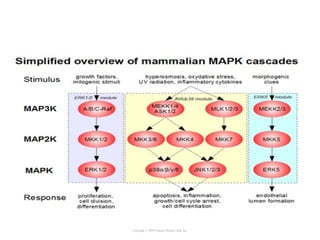
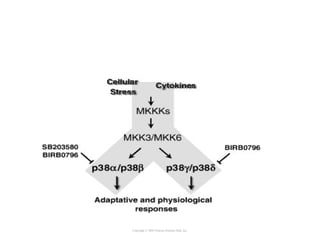
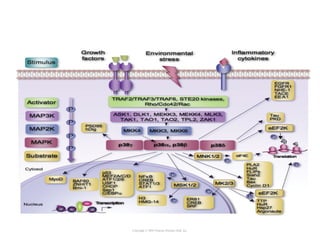
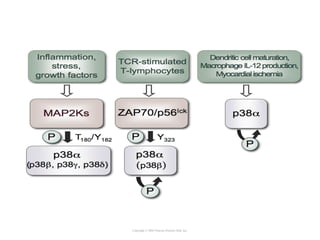
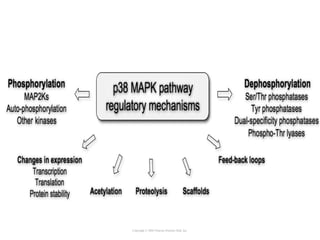
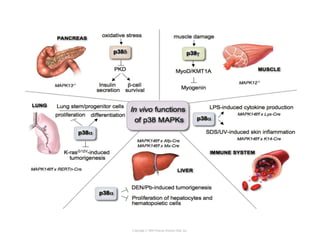
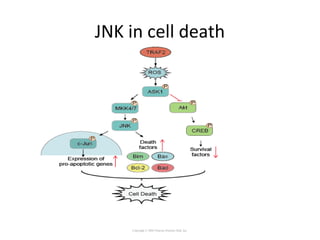
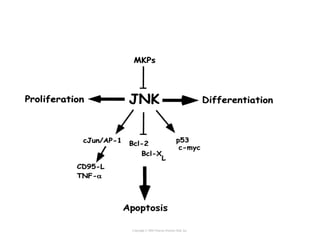
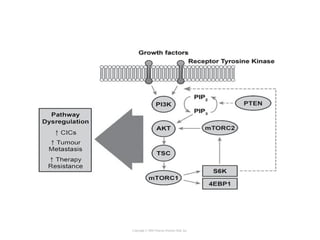
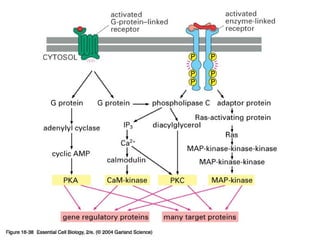
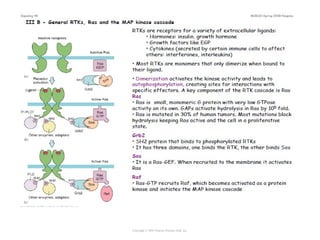
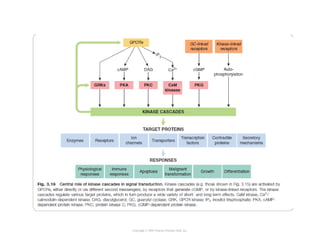
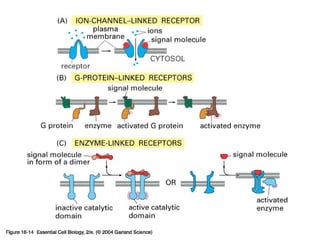
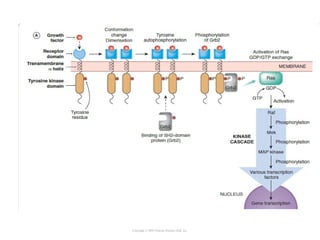
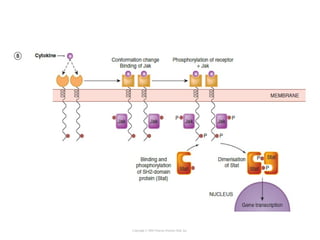
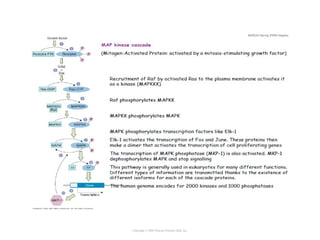
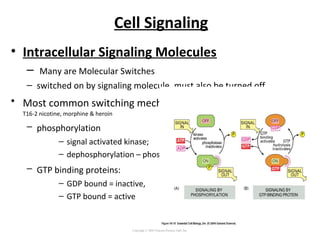
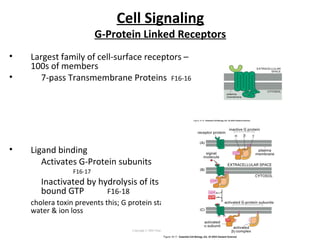
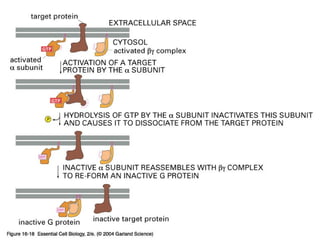
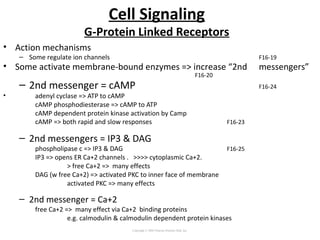
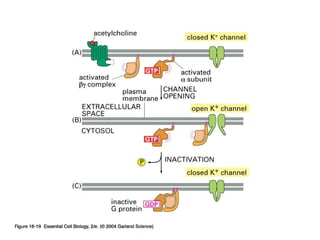
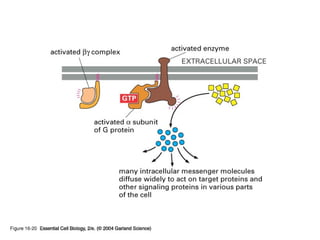
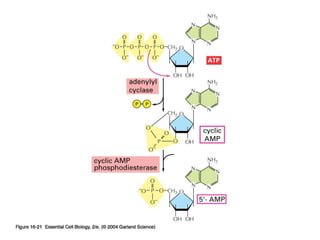
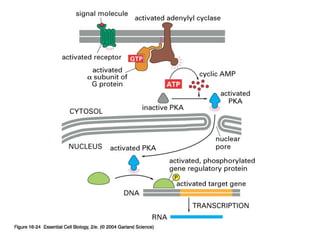
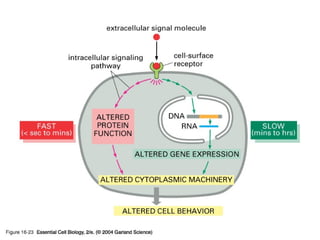
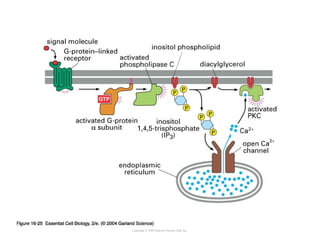
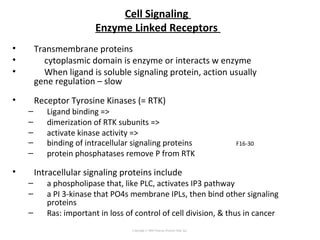
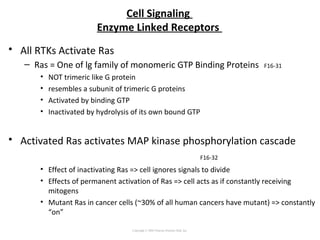
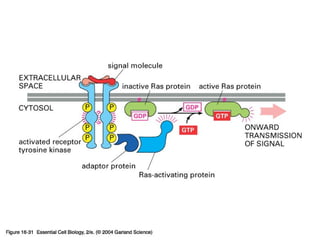
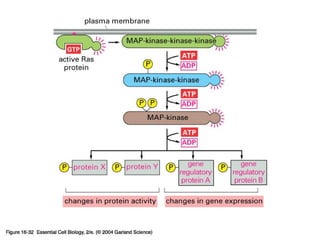
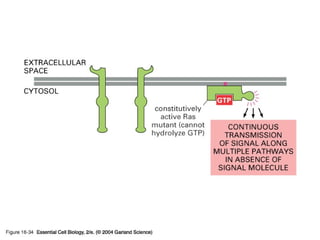
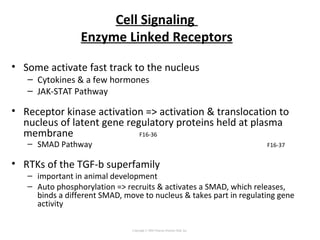
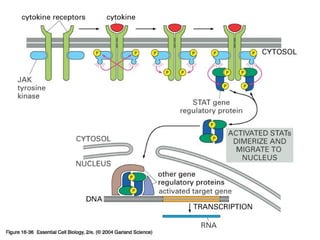
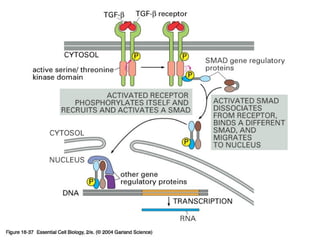
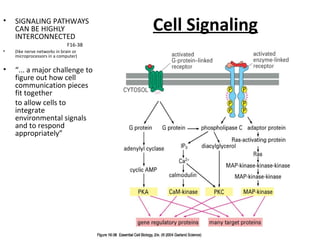
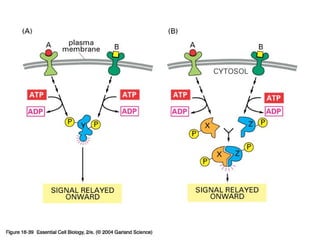
Cell signaling occurs through four main categories: paracrine, autocrine, endocrine, and direct contact. Paracrine signaling involves short-range signals between nearby cells, such as synaptic signaling between neurons. Autocrine signaling allows cells to signal to themselves. Endocrine signaling uses the circulatory system to transmit long-range hormones from endocrine glands. Direct contact signaling transfers small molecules through gap junctions between cells. Intracellular signaling pathways transmit extracellular signals through phosphorylation cascades like the MAPK, JNK, p38, and PI3K pathways, ultimately influencing cell behavior.