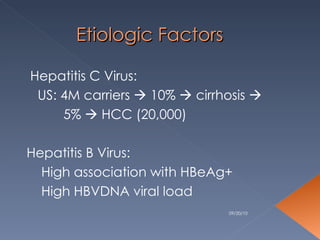
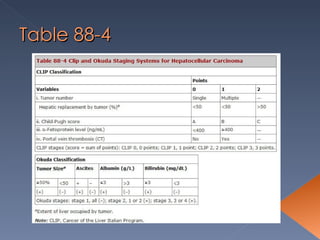
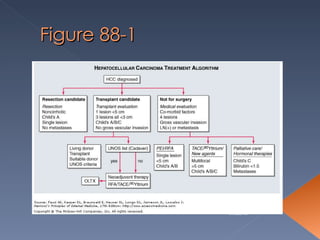
Hepatocellular carcinoma is one of the most common malignancies worldwide. Its incidence varies significantly between regions, from low rates in the United States and Africa to very high rates in parts of Asia. Major risk factors include chronic hepatitis B and C infections. Clinical features can include abdominal pain, weight loss, jaundice, and hepatomegaly. Diagnosis involves blood tests, ultrasound, CT scan, MRI and sometimes liver biopsy. High-risk groups are screened regularly through alpha-fetoprotein testing and ultrasound. Treatment options depend on the stage but may include surgical resection, ablation, chemotherapy, and transplantation.