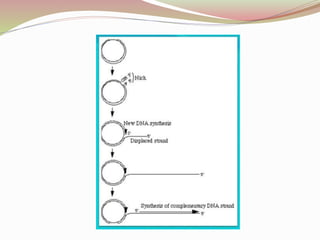
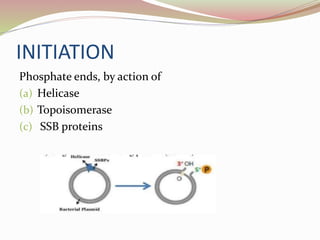
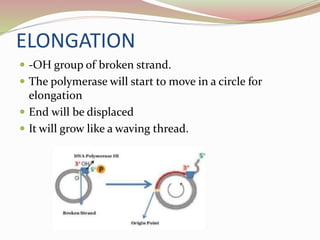
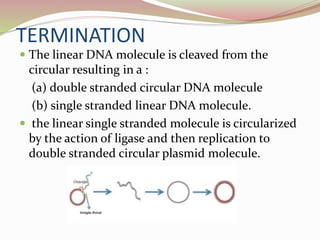
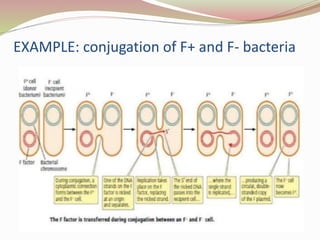
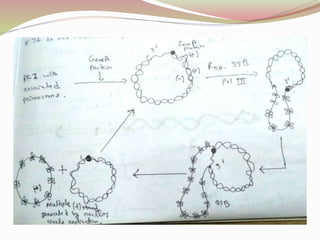
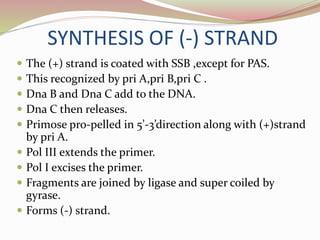
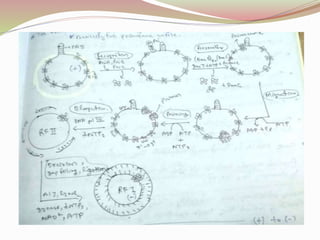
The rolling circle model describes DNA replication in circular DNA. It involves three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. In initiation, the circular DNA is nicked by helicase and topoisomerase. In elongation, the leading strand is elongated continuously while the lagging strand is displaced and replicated in fragments. In termination, the linear DNA molecule is cleaved from the circular DNA, resulting in a double stranded circular DNA molecule and a single stranded linear DNA molecule that is then circularized by ligase.