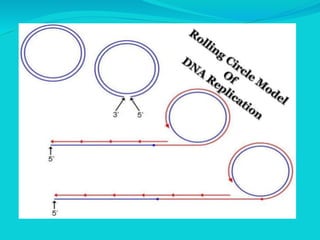
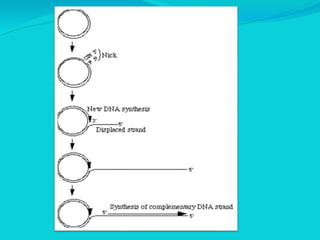
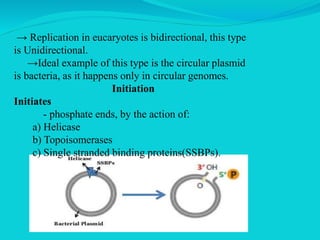
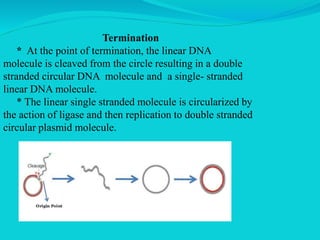
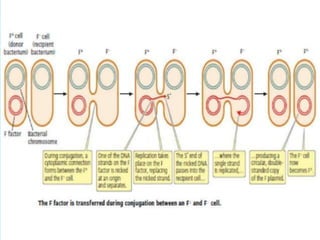
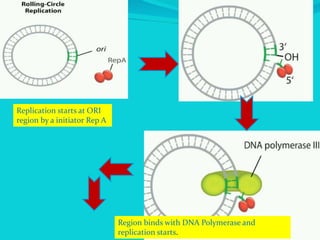
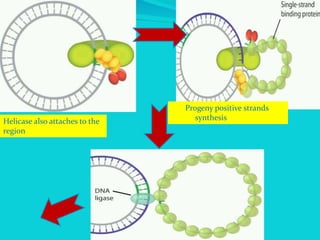
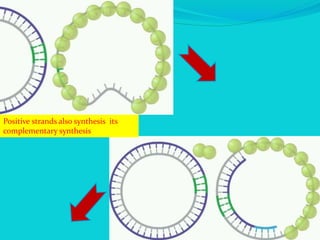
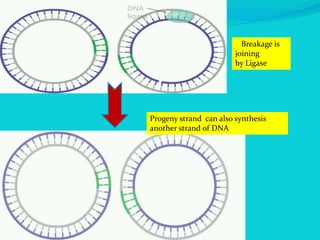
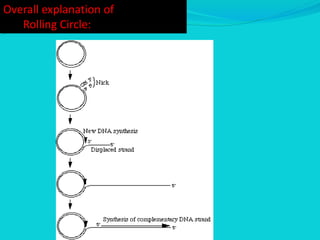
Rolling circle replication is a process of unidirectional nucleic acid replication that can rapidly synthesize multiple copies of circular DNA or RNA molecules such as plasmids. It involves nicking a circular double-stranded DNA molecule, elongating the 3' end to form the leading strand while displacing the 5' end to form the lagging strand of Okazaki fragments. The displaced single-stranded DNA then circulates and synthesizes its own complementary strand, resulting in replication of both the original nicked and displaced strands in a rolling motion. Examples include replication of circular plasmids in bacteria and certain viruses like herpesvirus, papillomavirus, and geminivirus.