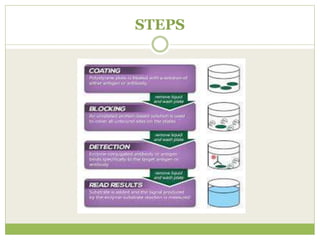
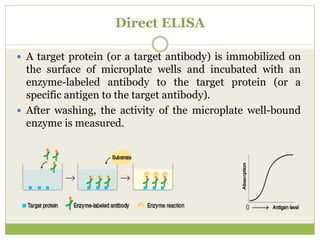
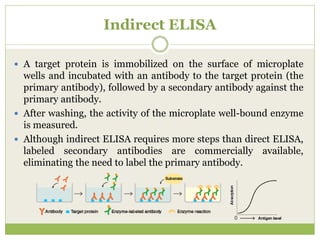
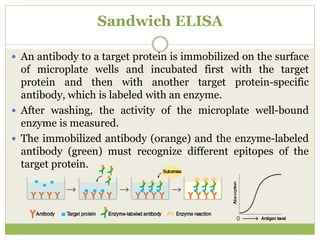
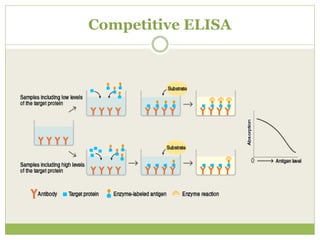
The document describes the ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) technique for detecting and quantifying substances. ELISA uses an antigen immobilized on a plate that complexes with an antibody linked to an enzyme. Detection involves measuring the activity of the conjugated enzyme after incubation with a substrate. There are four main types of ELISA - direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive - which differ in their antibody and antigen binding steps. ELISA has advantages like high sensitivity, specificity, and throughput, making it widely used in research and clinical applications.