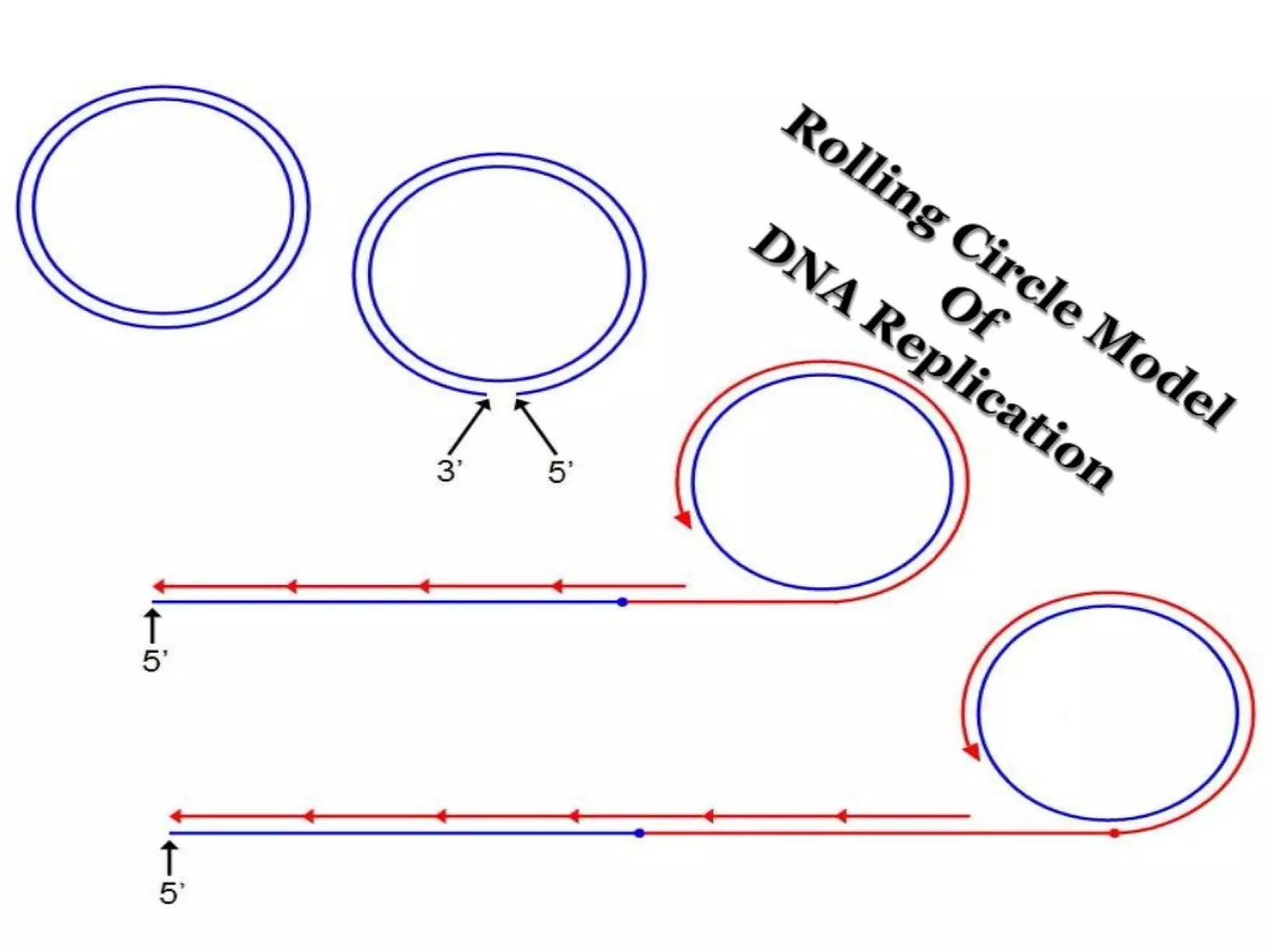
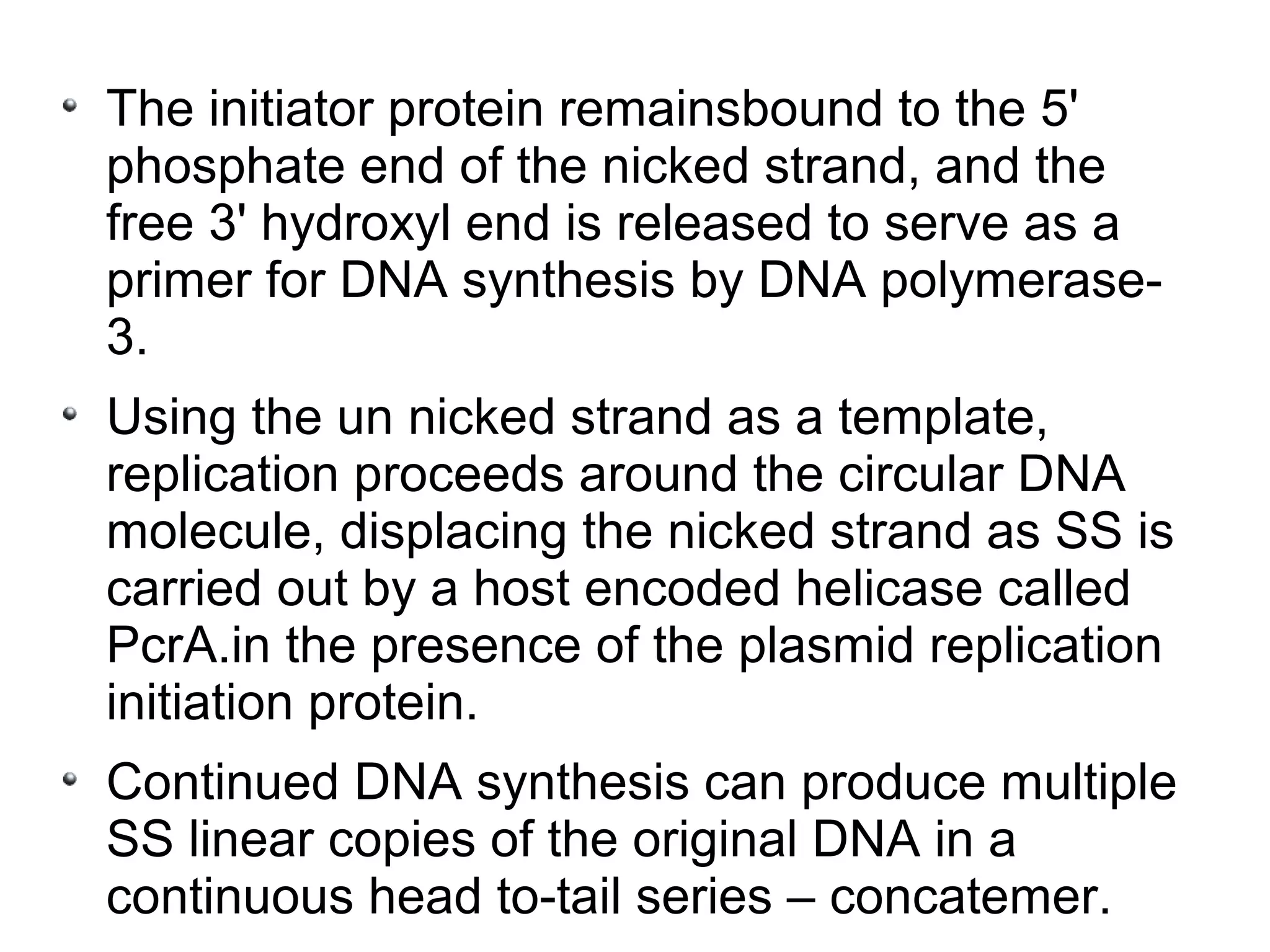
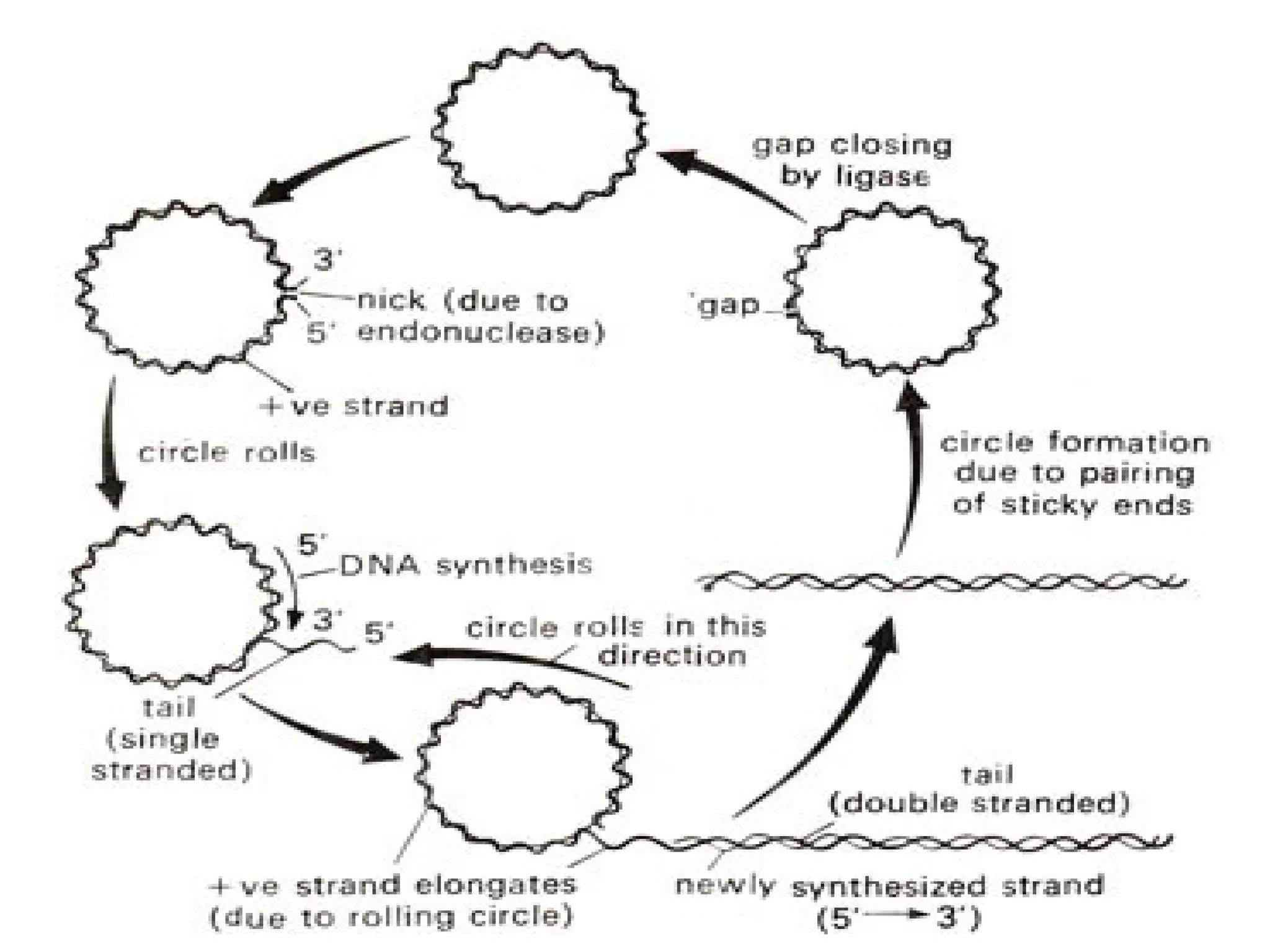
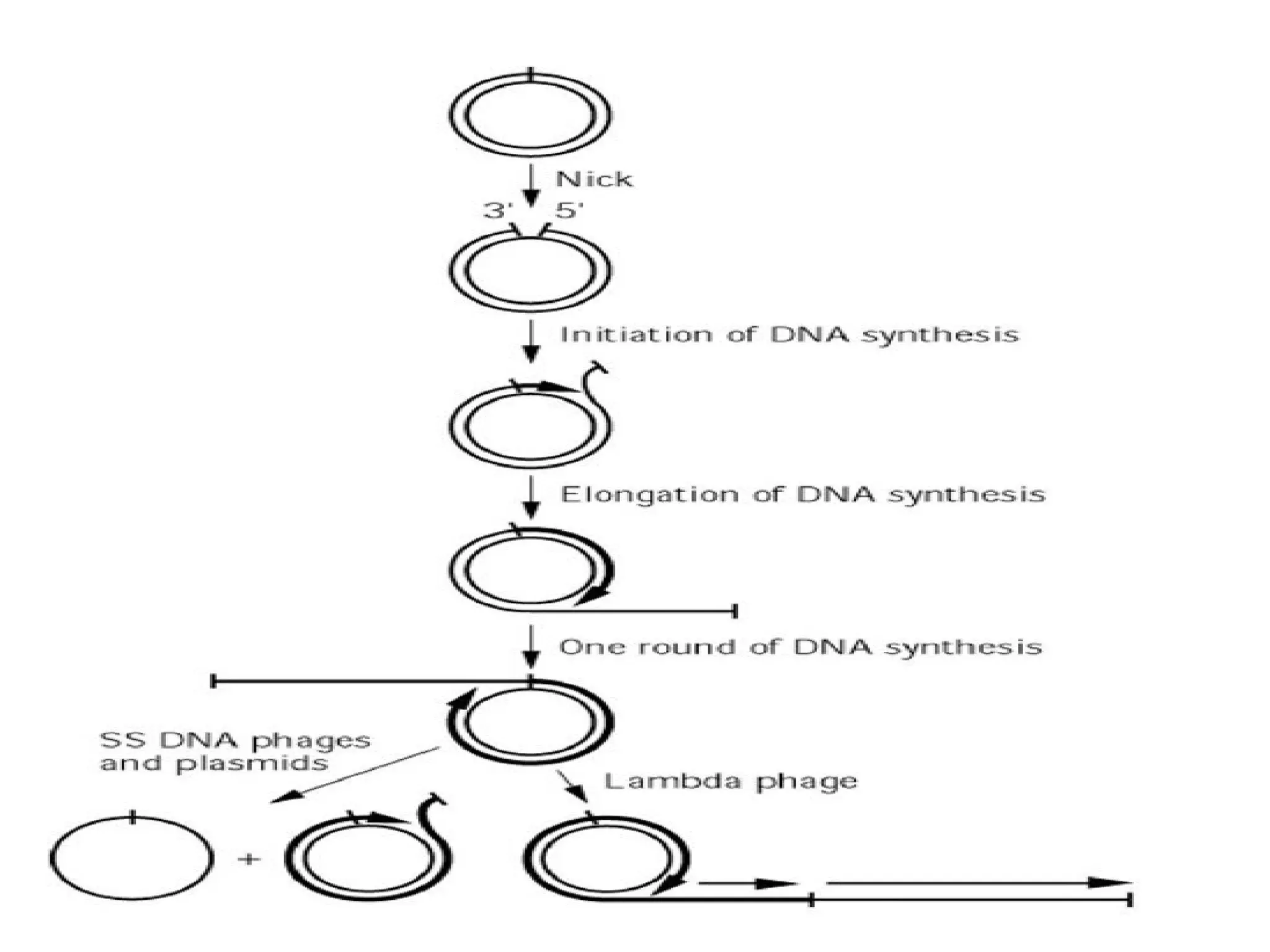
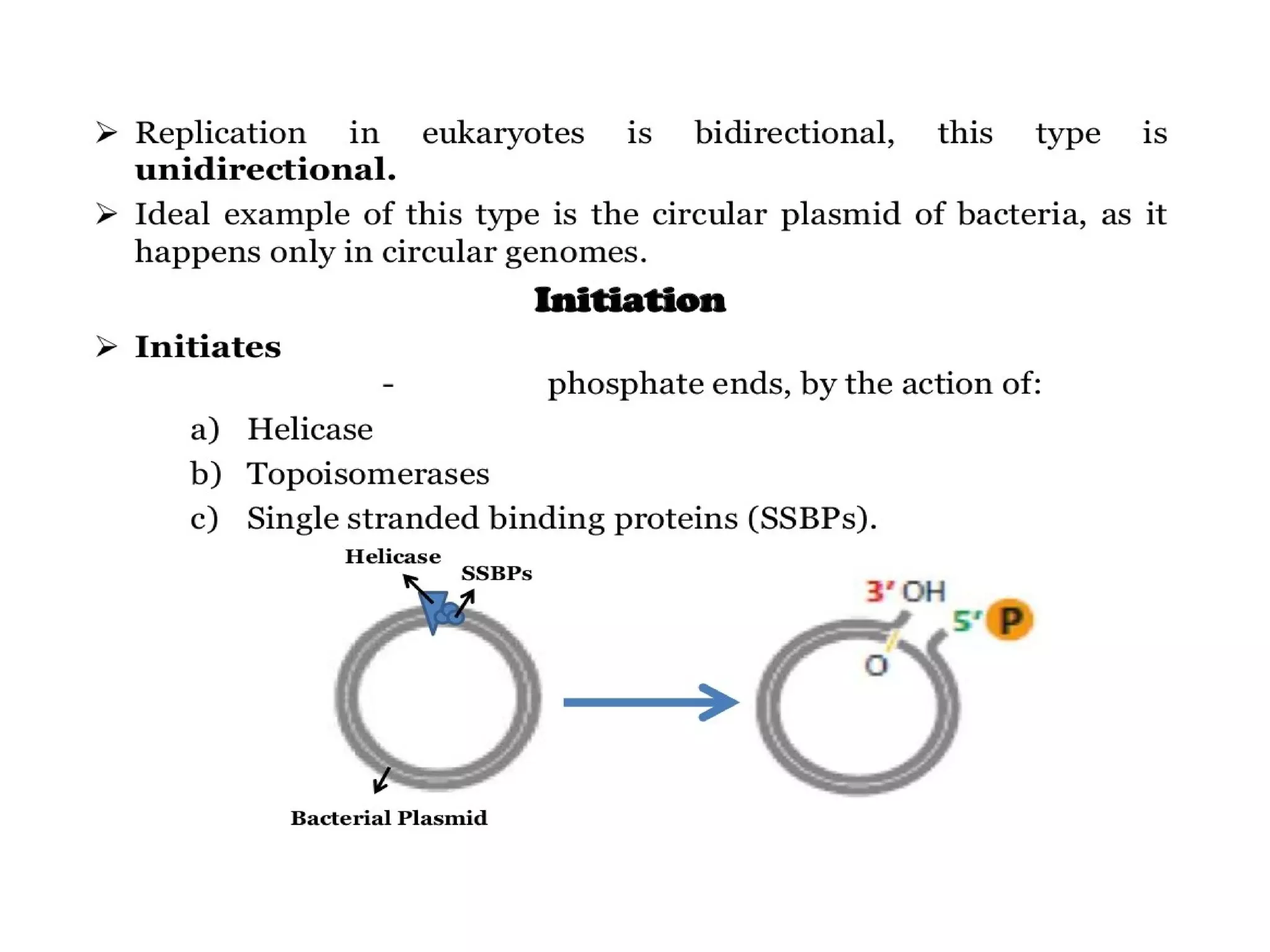
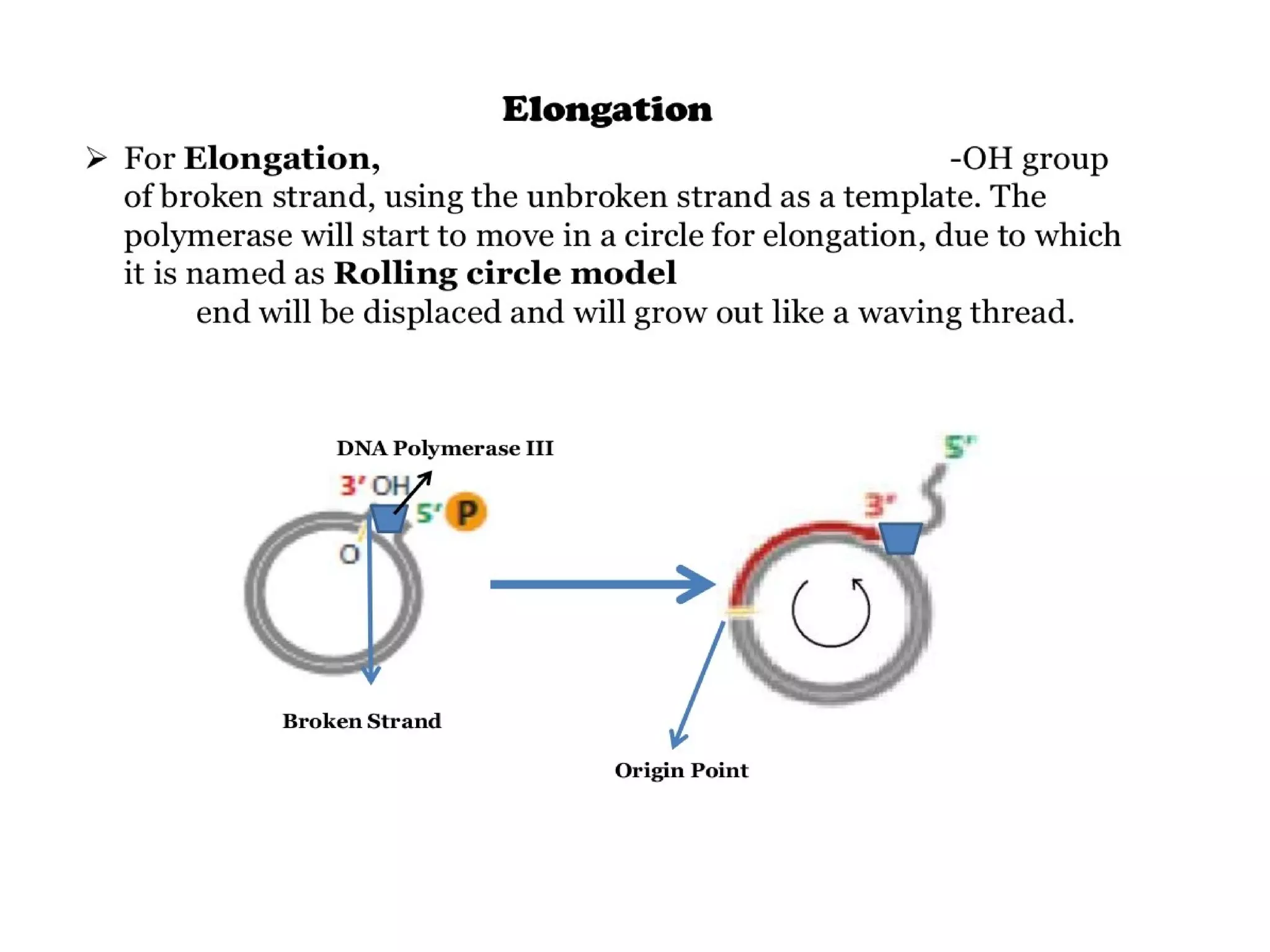
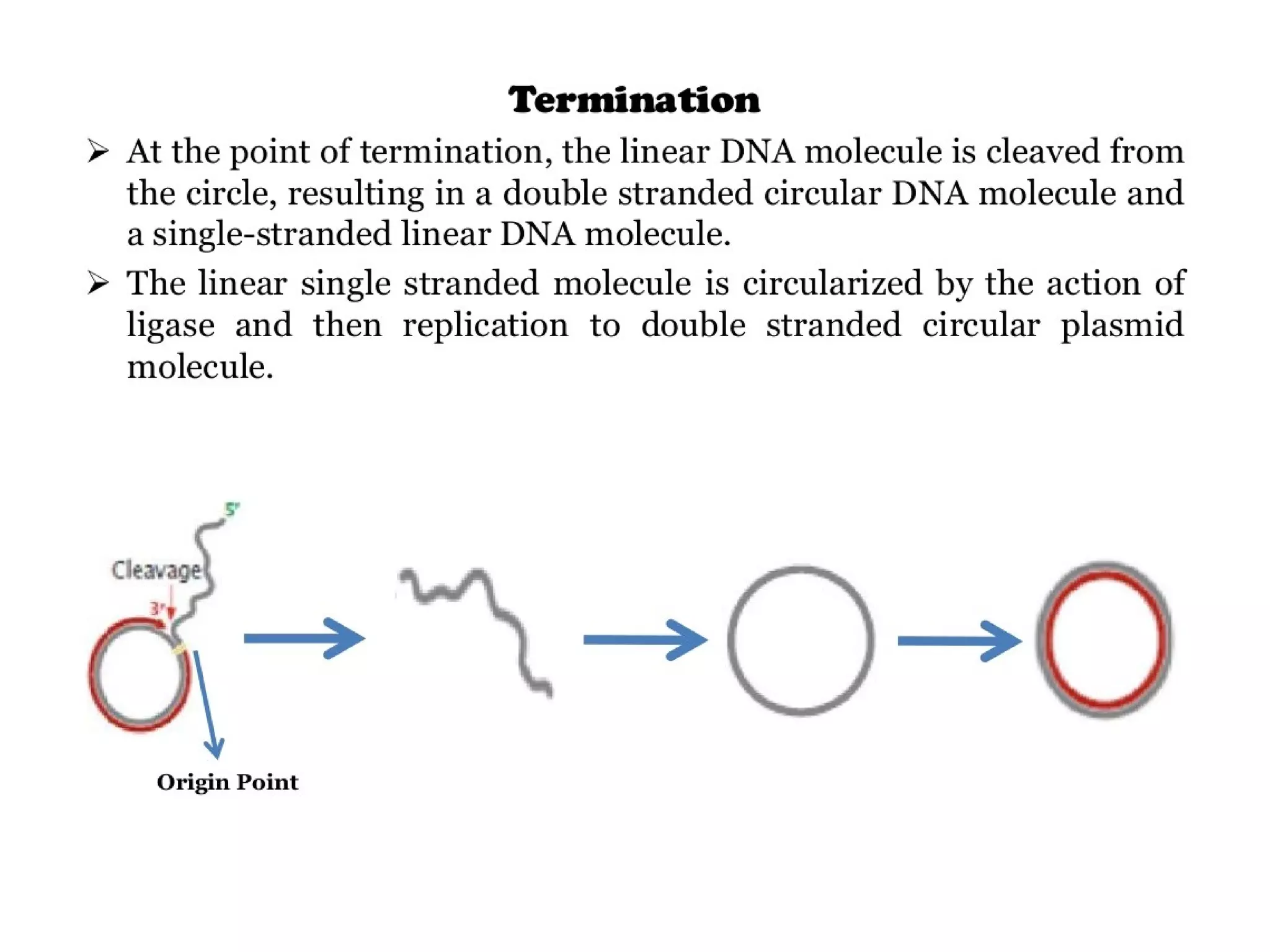
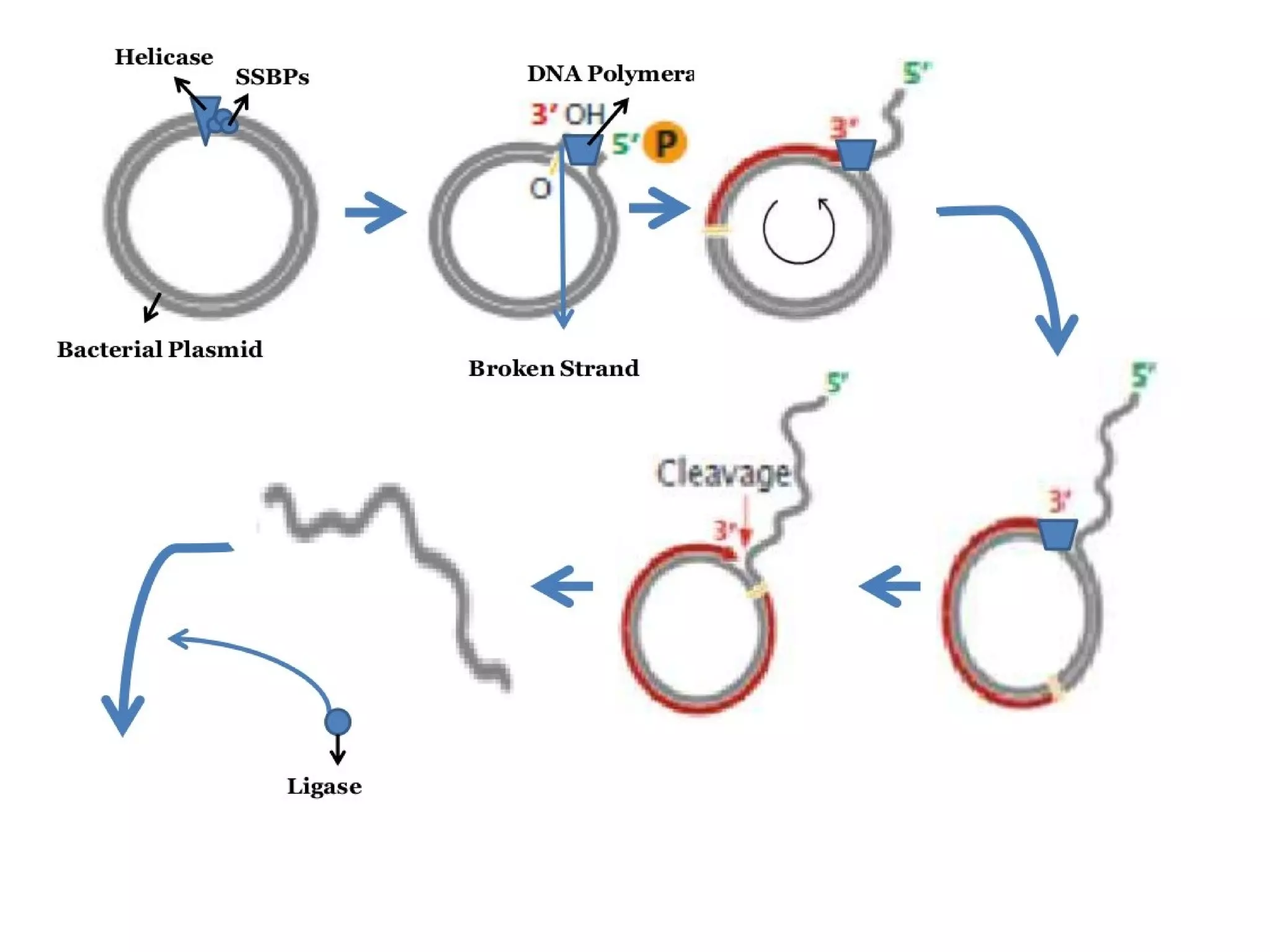
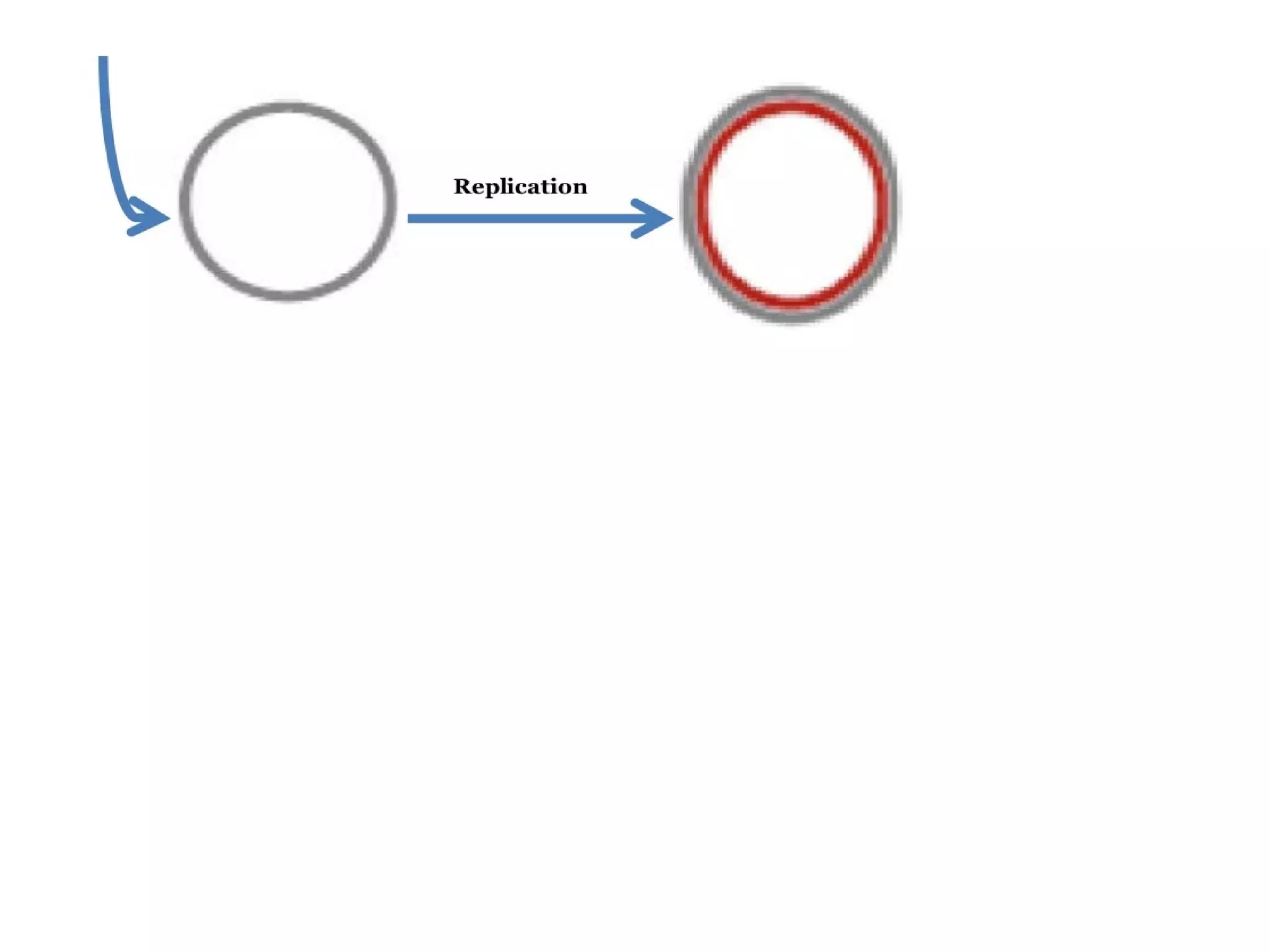
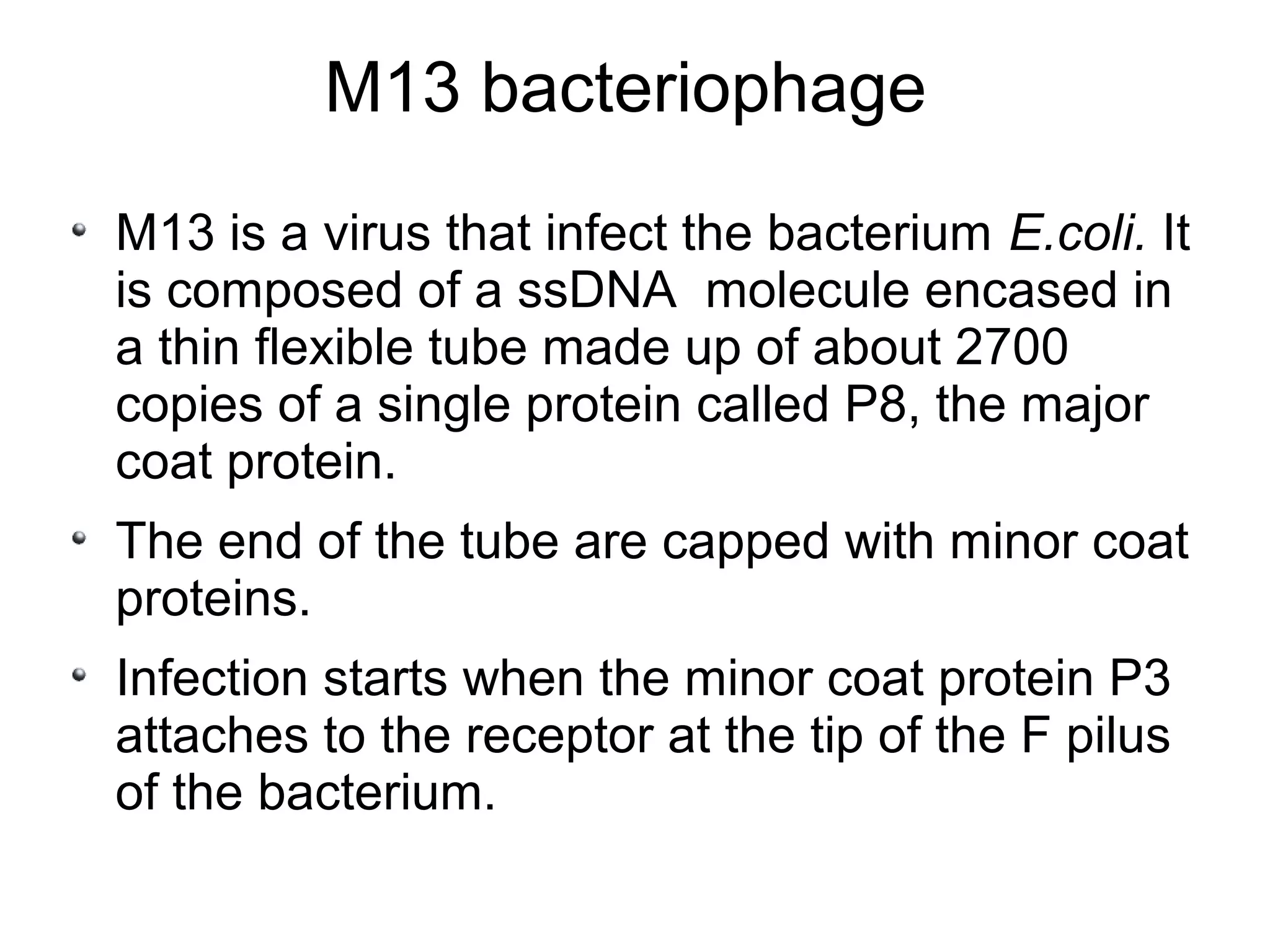
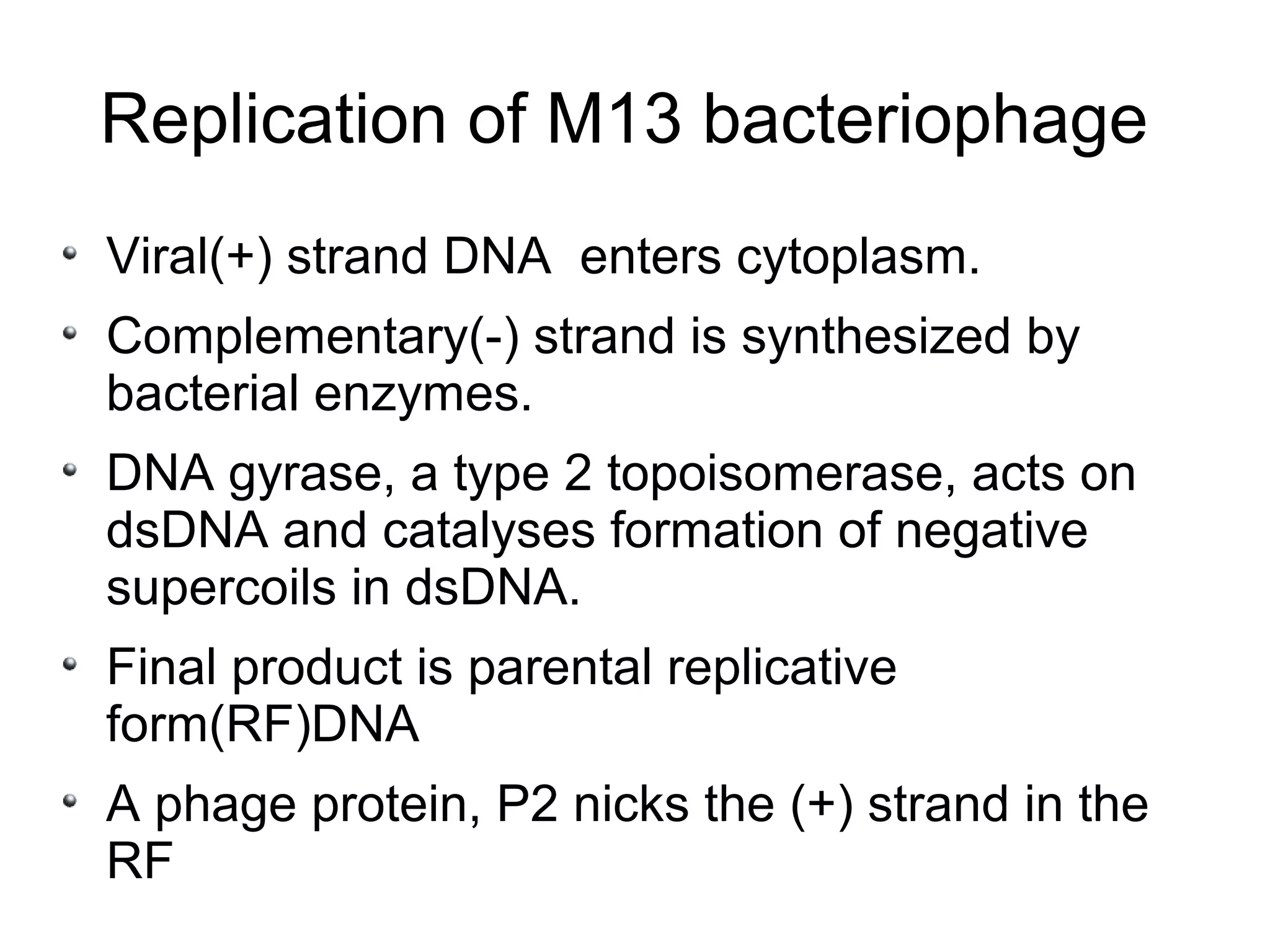
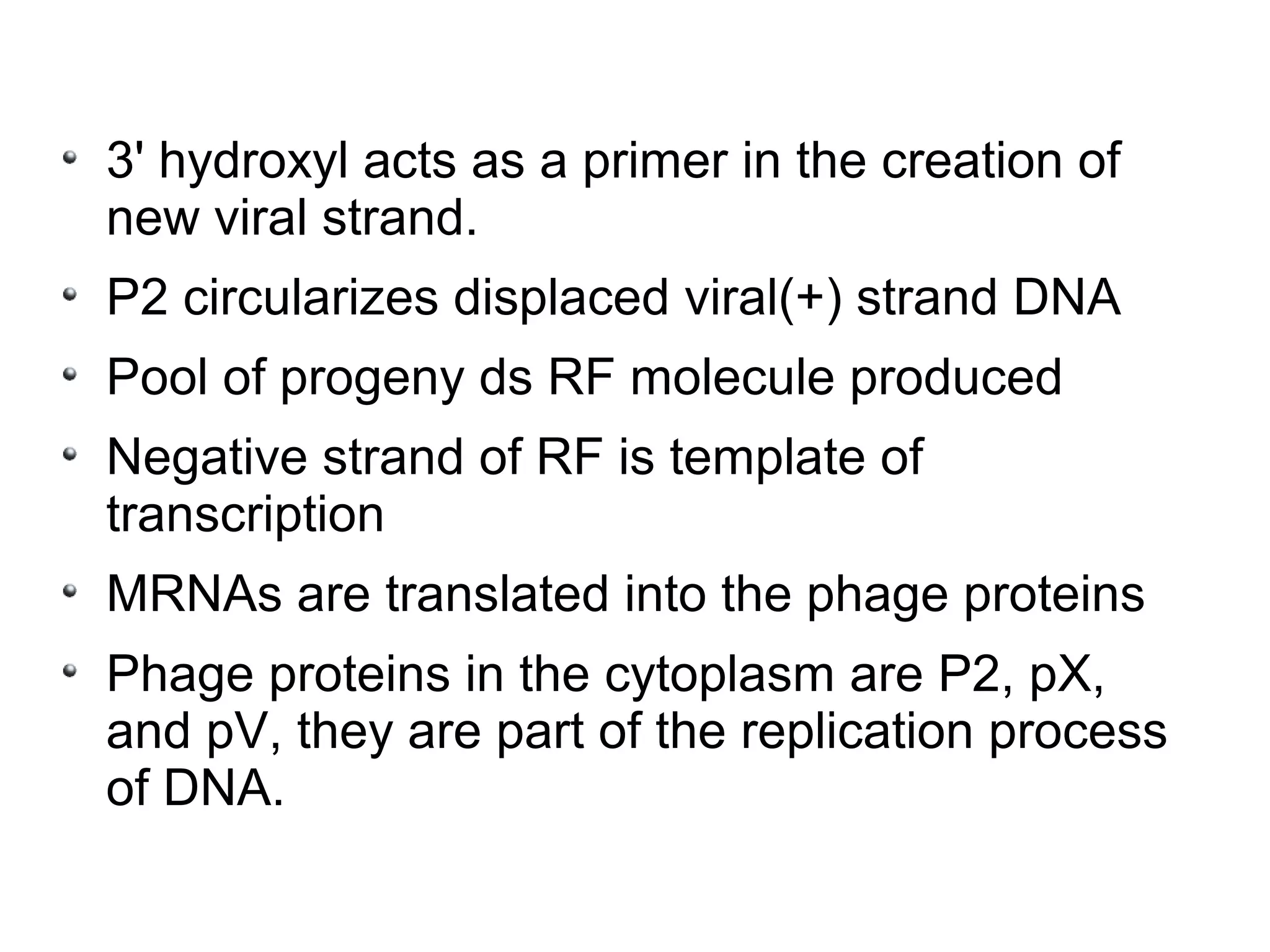
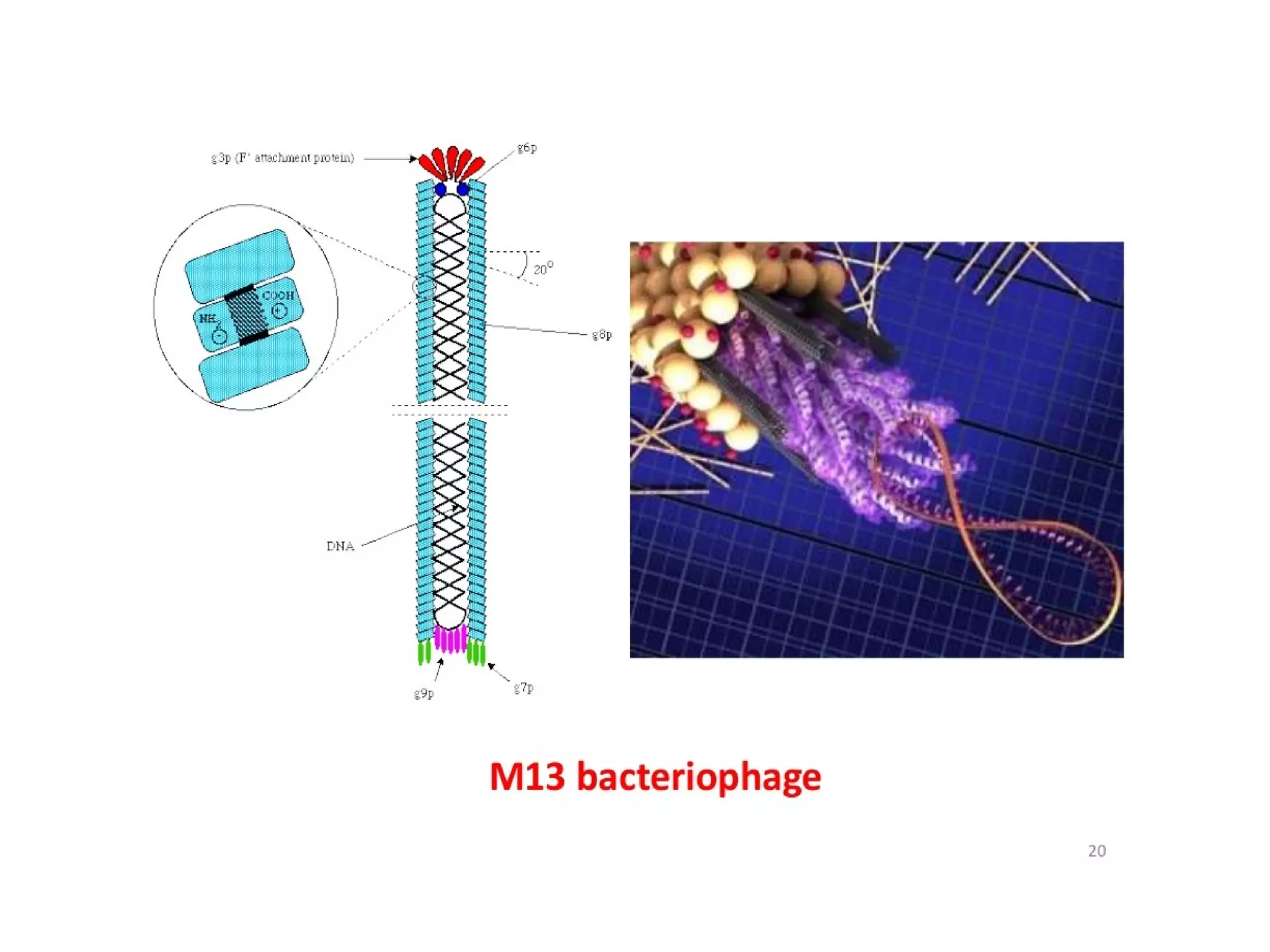
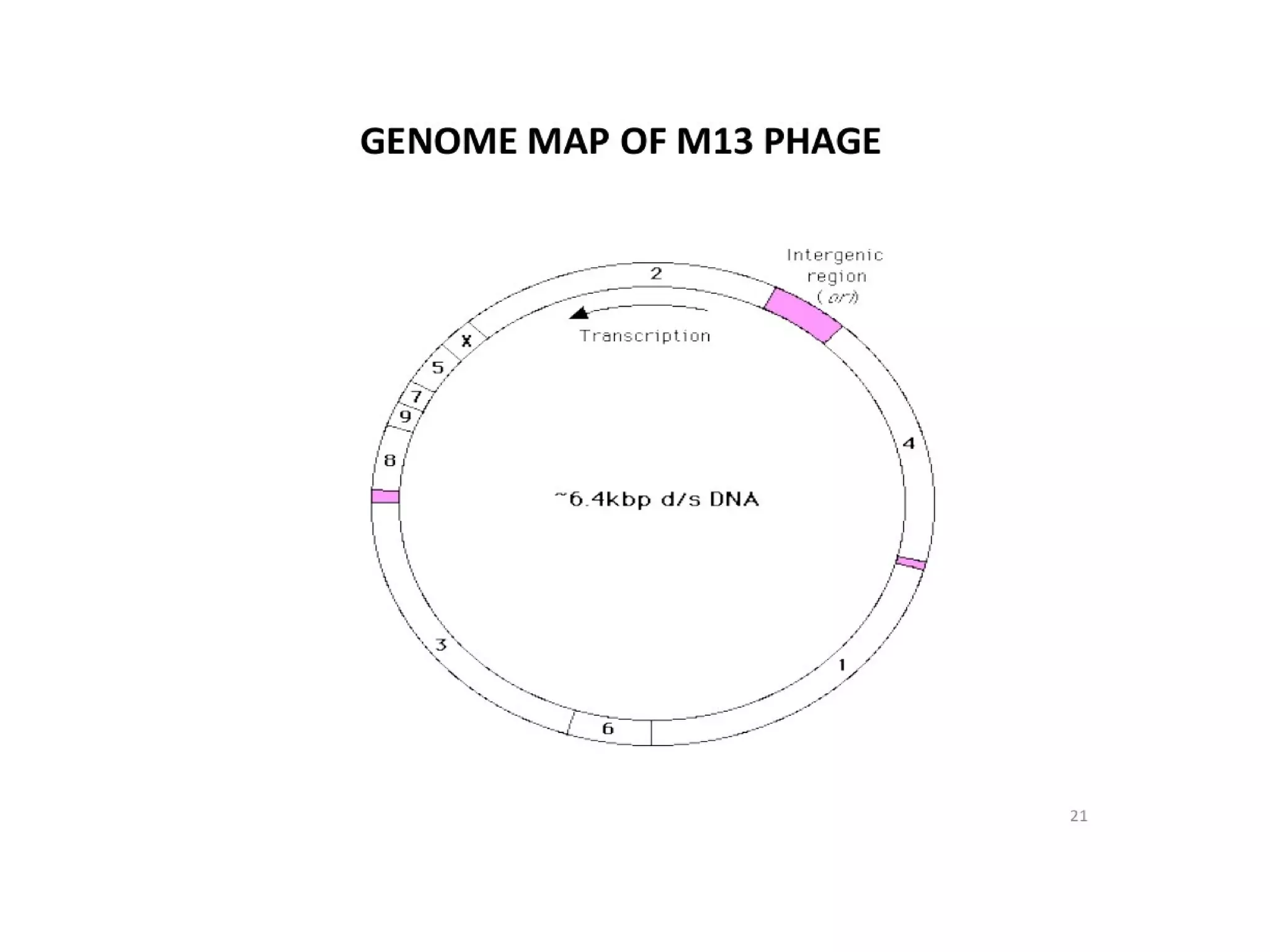
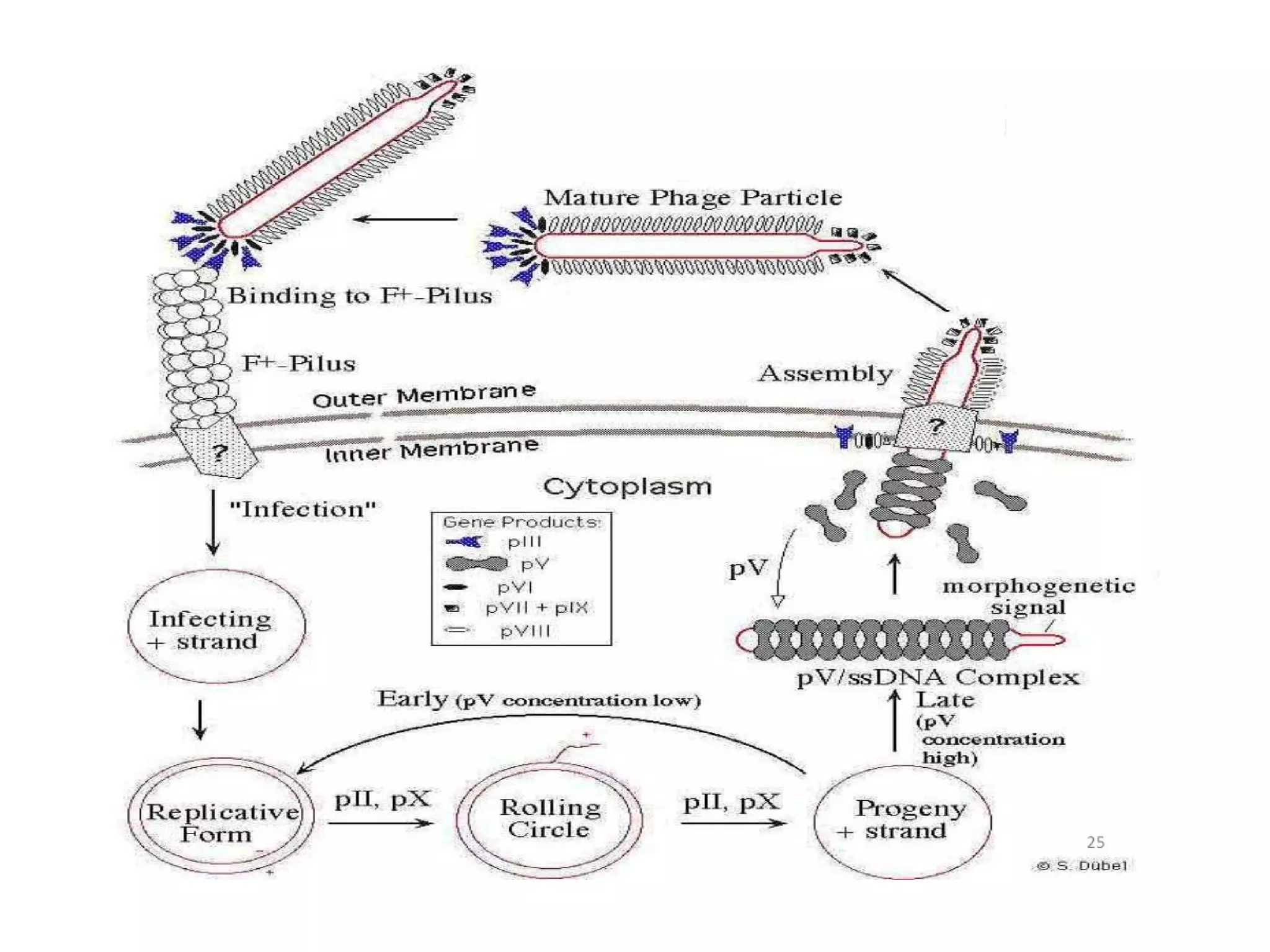
This document summarizes rolling circle replication and the replication of M13 bacteriophage. Rolling circle replication involves the nicking of one strand of circular DNA by an initiator protein. DNA polymerase then uses the unnicked strand as a template to synthesize multiple copies of the DNA in a continuous head-to-tail series. These linear copies can then be converted to circular DNA molecules through additional processing. Replication of M13 bacteriophage involves its single-stranded DNA entering an E. coli cell and being converted to double-stranded replicative form DNA. A phage protein then nicks the viral DNA to allow replication and production of progeny phage genomes and assembly of new viral particles.