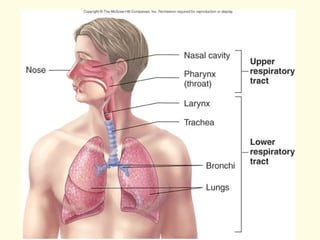
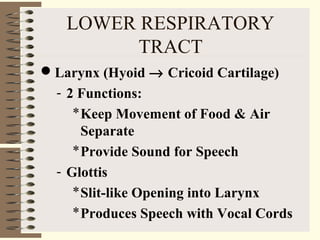
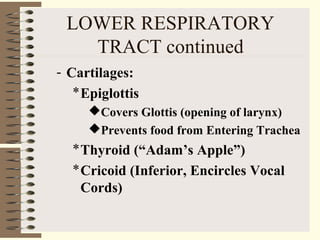
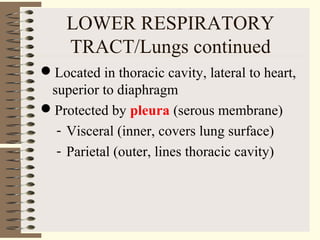
The respiratory system functions to oxygenate the blood and remove carbon dioxide through gas exchange that occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. It is organized into an upper respiratory tract including the nose and pharynx, and a lower respiratory tract including the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. The lungs are paired organs located in the thoracic cavity that contain alveoli which are the sites of gas exchange between the respiratory and circulatory systems.