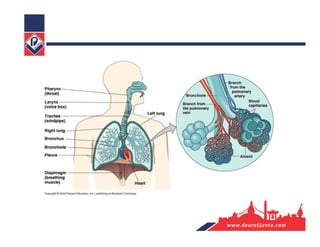
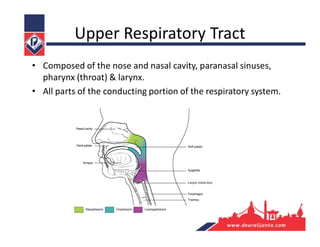
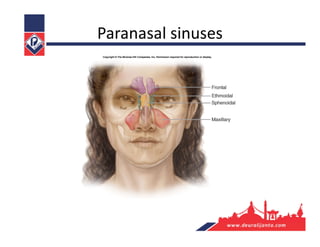
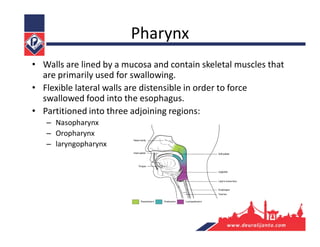
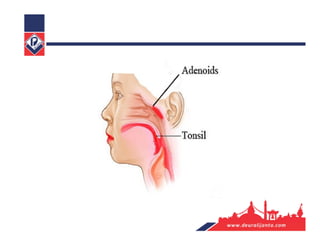
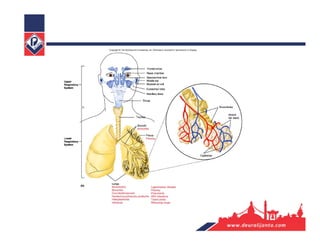
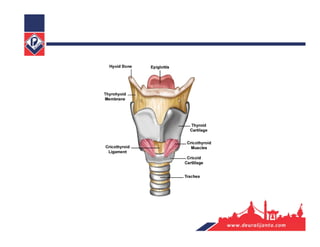
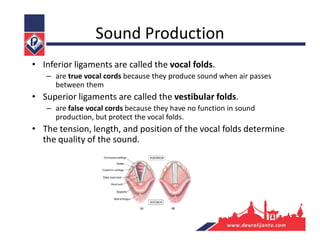
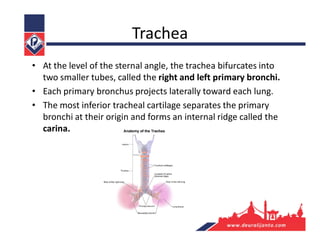
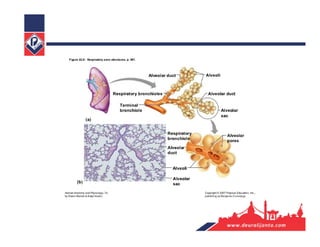
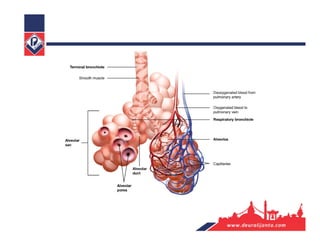
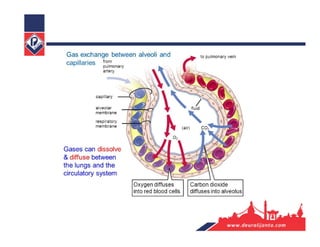
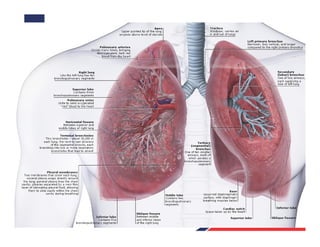
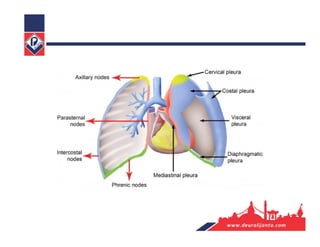
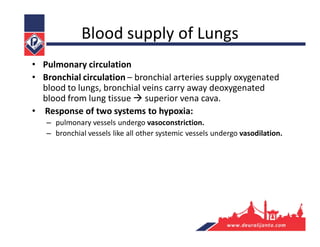
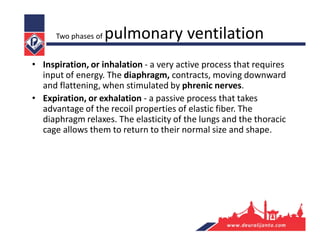
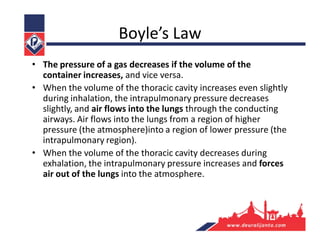
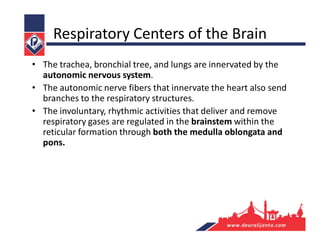
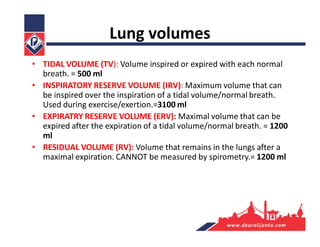
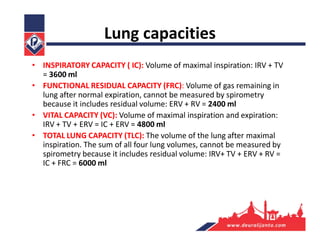
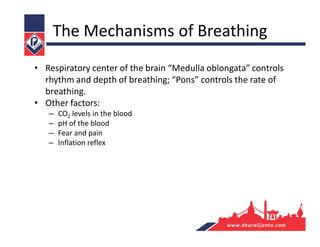
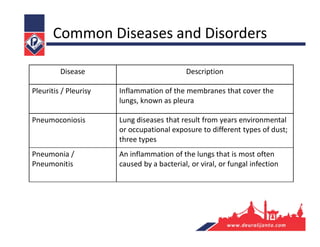
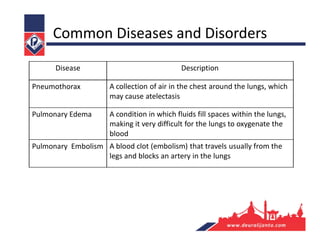
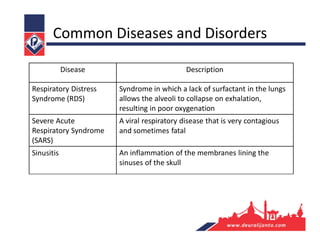
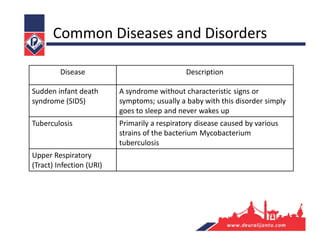
The respiratory system consists of an upper respiratory tract and lower respiratory tract. The upper tract includes the nose, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, and pharynx. The lower tract includes the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. The nose warms, moistens, and filters air and contains smell receptors. The lungs contain alveoli where gas exchange occurs between air in alveoli and blood in capillaries. Breathing involves inhalation that draws air into the lungs and exhalation that forces air out.