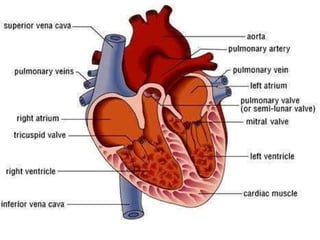
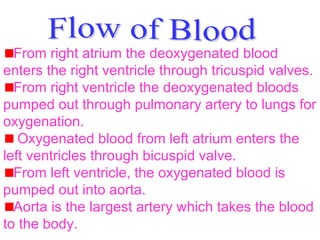
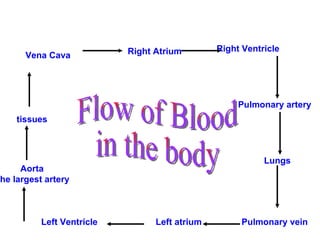
The heart is a pumping organ located in the chest that continuously circulates blood through the body. It has four chambers - the two upper chambers are the atria and the two lower chambers are the ventricles. The septum separates the chambers and prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. Blood flows from the right atrium to the right ventricle then to the lungs, returns oxygenated to the left atrium and left ventricle, then is pumped through the aorta to the rest of the body in a continuous cycle.