Embed presentation
Downloaded 442 times

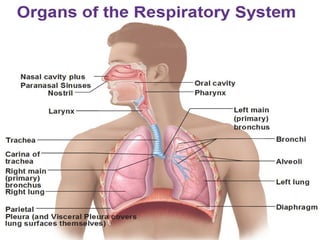




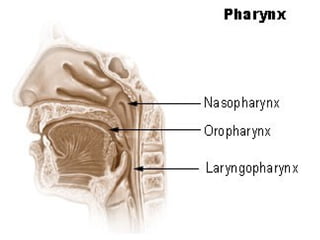

















The respiratory system allows for gas exchange in the body. It begins with the nostrils, where air enters and exits the nasal cavity to be warmed. The pharynx and larynx allow air to pass to the trachea and then bronchi, where air flows into the lungs. The lungs, located in the chest, have lobes and facilitate breathing, respiration, and protection from infection. Inhalation draws oxygen into the lungs through muscle contraction and exhalation removes carbon dioxide as a waste product.
























