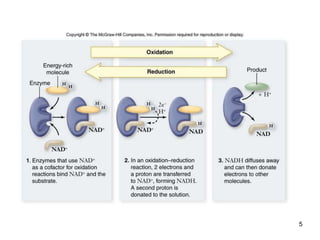
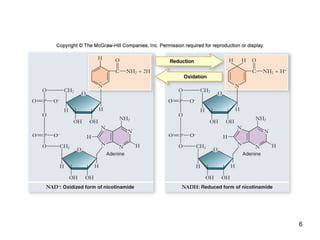
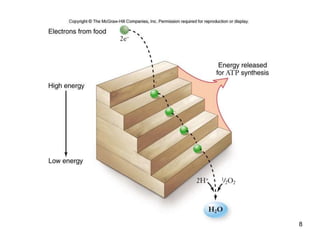
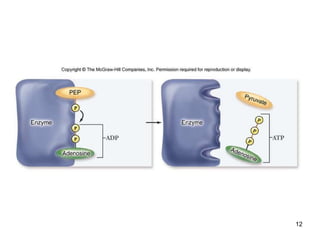
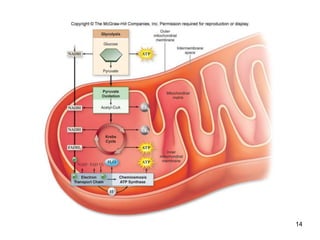
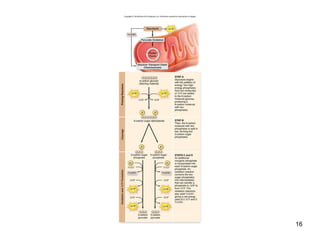
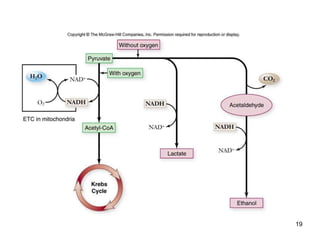
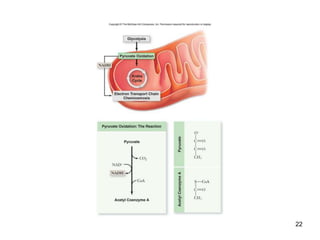
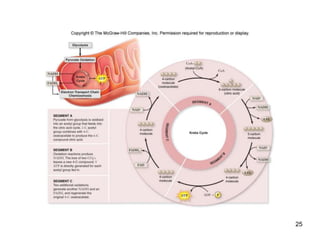
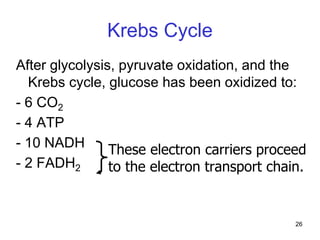
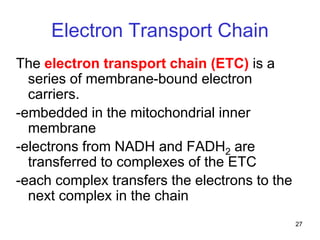
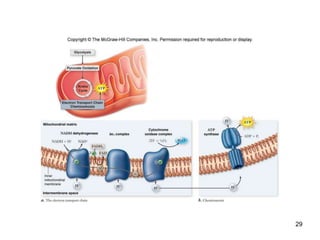
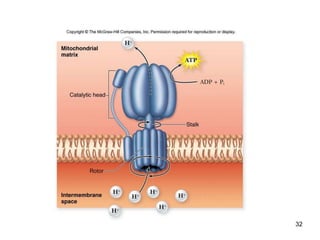
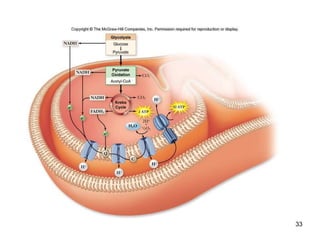
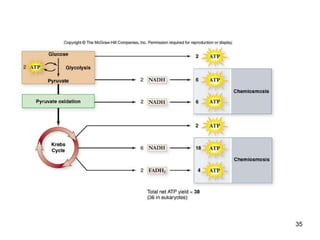
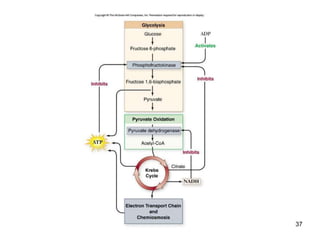
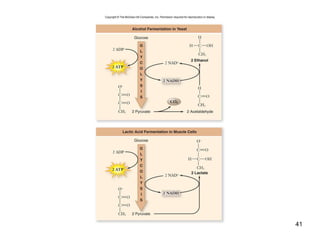
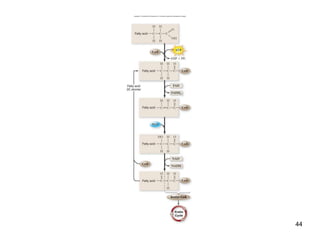
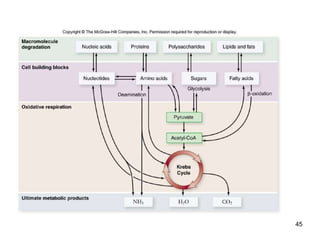
Cellular respiration extracts energy from organic molecules like glucose in three stages: glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the Krebs cycle. This releases electrons that are transferred via electron carriers like NADH to the electron transport chain, where a proton gradient is used to synthesize ATP via oxidative phosphorylation. Aerobic respiration fully oxidizes glucose to CO2 and H2O, yielding around 30 ATP per glucose. Without oxygen, fermentation or anaerobic respiration are used to regenerate NAD+.