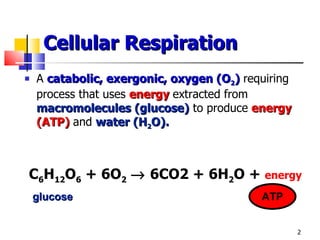
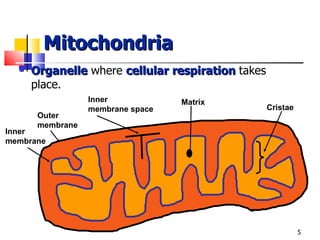
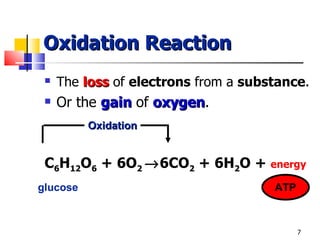
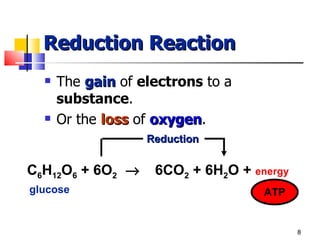
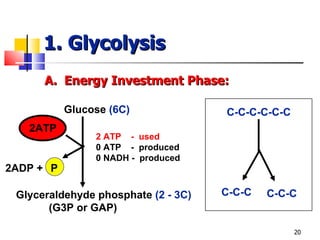
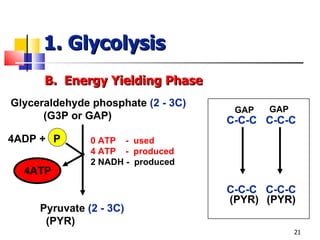
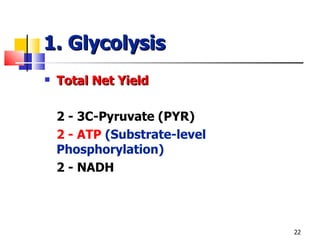
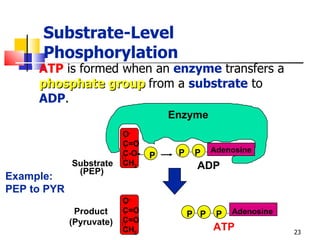
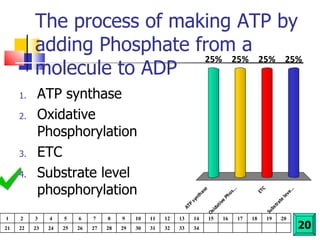
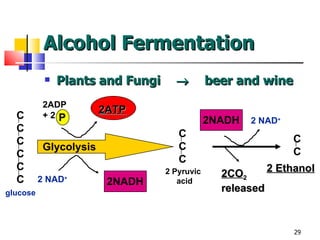
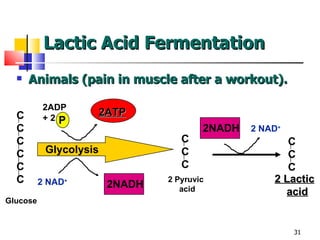
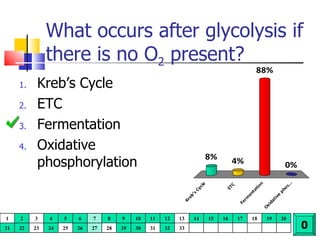
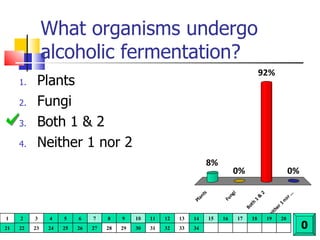
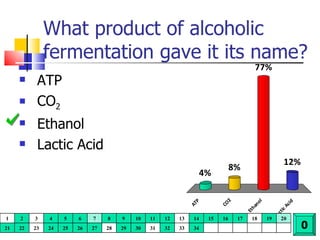
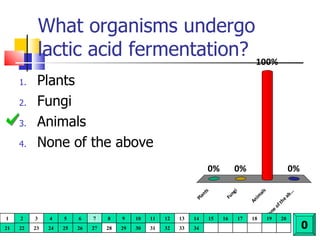
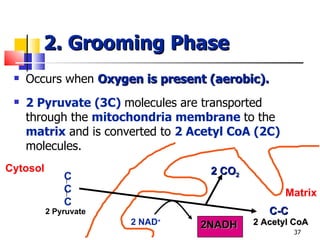
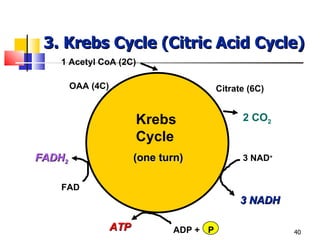
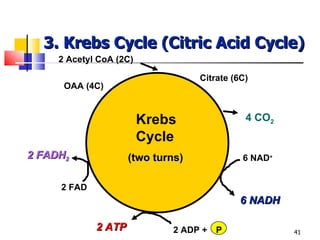
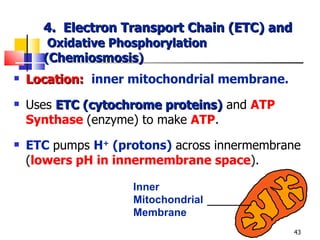
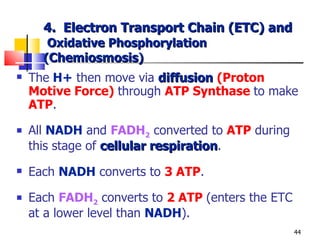
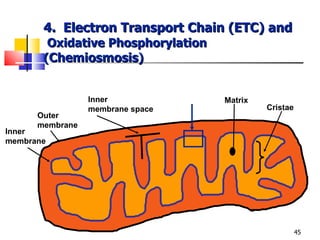
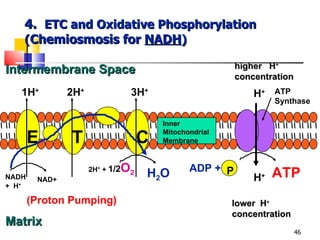
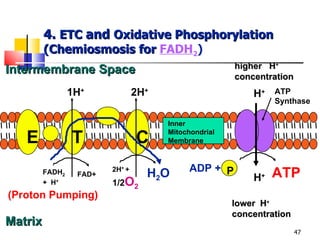
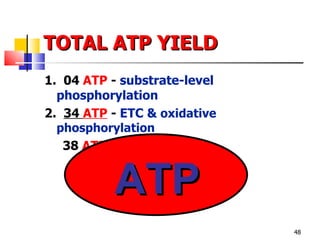
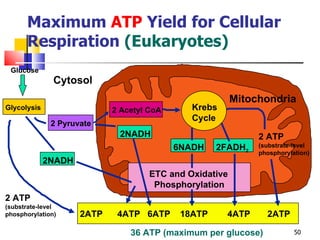
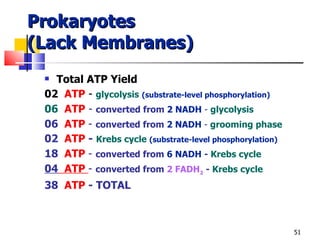
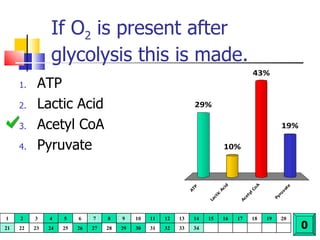
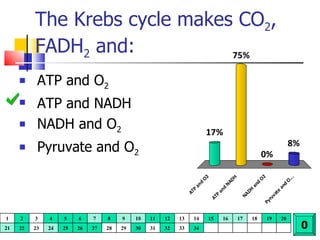
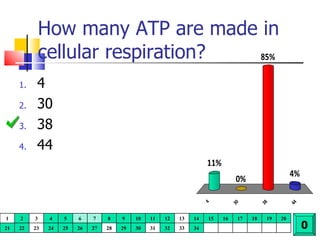
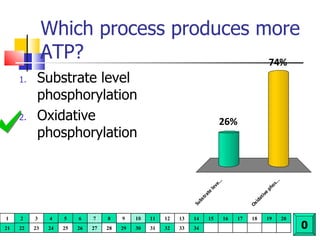
Cellular respiration is a catabolic process that uses oxygen to break down glucose and other organic molecules to extract energy in the form of ATP. It occurs in four main stages: 1) glycolysis in the cytosol, 2) transport of pyruvate into the mitochondria, 3) the Krebs cycle in the mitochondrial matrix, and 4) the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation on the inner mitochondrial membrane. The overall process produces 38 ATP molecules from complete oxidation of one glucose molecule.