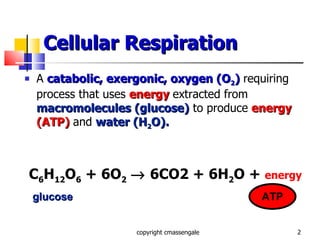
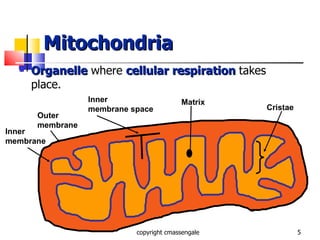
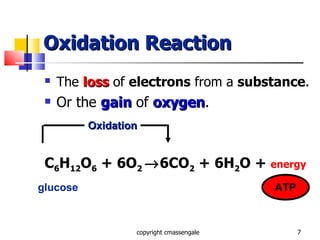
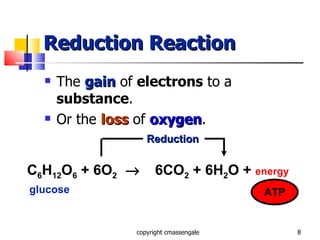
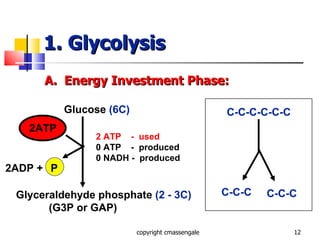
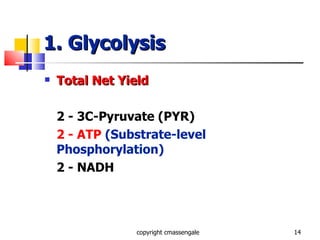
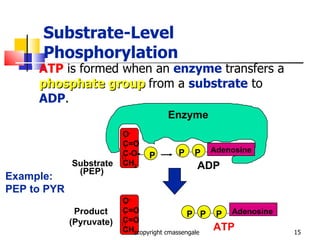
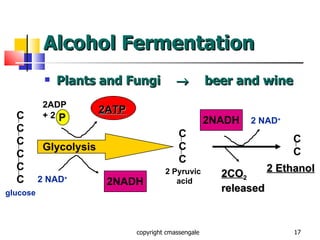
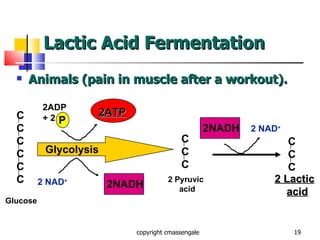
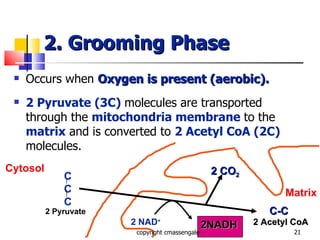
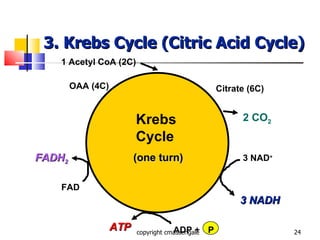
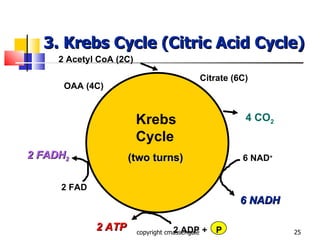
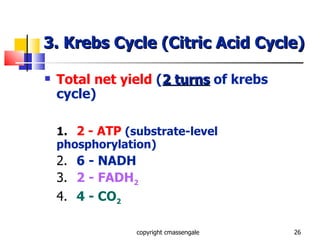
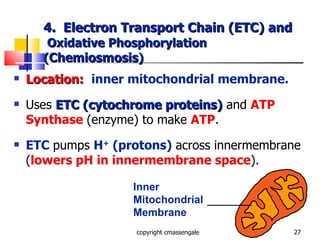
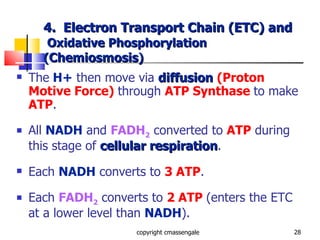
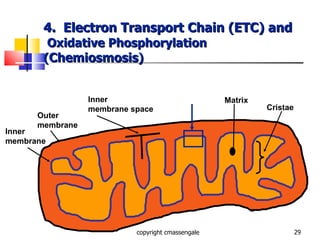
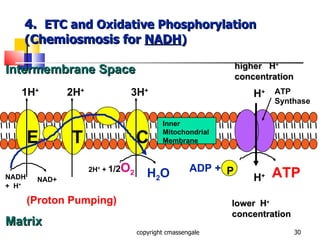
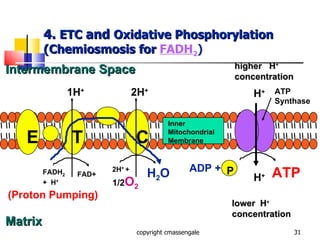
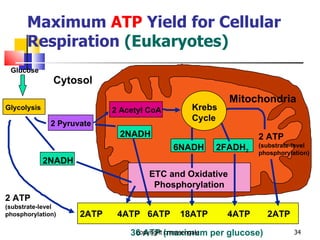
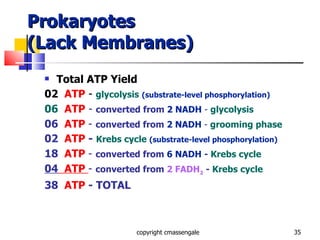
Cellular respiration is a catabolic process that occurs in the mitochondria of plants and animals. It uses oxygen to break down glucose and other food molecules to extract energy in the form of ATP. The process involves four main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation. This releases energy to produce up to 38 ATP per glucose molecule.