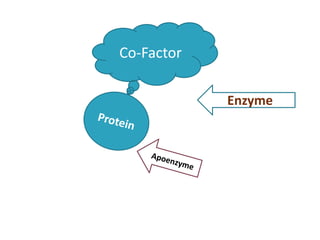
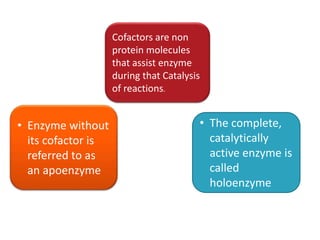
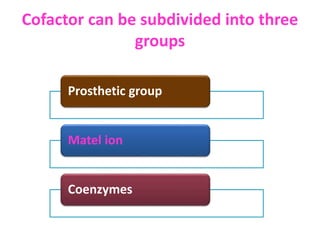
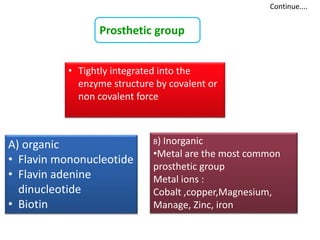
Cofactors are non-protein molecules that assist enzymes during catalysis. There are three main types of cofactors: prosthetic groups, metal ions, and coenzymes. Prosthetic groups are tightly bound organic or inorganic molecules that are integrated into the enzyme structure. Metal ions are commonly bound prosthetic groups that facilitate substrate binding and reactions. Coenzymes serve as recyclable carriers that transport substrates between where they are generated and utilized in reactions.