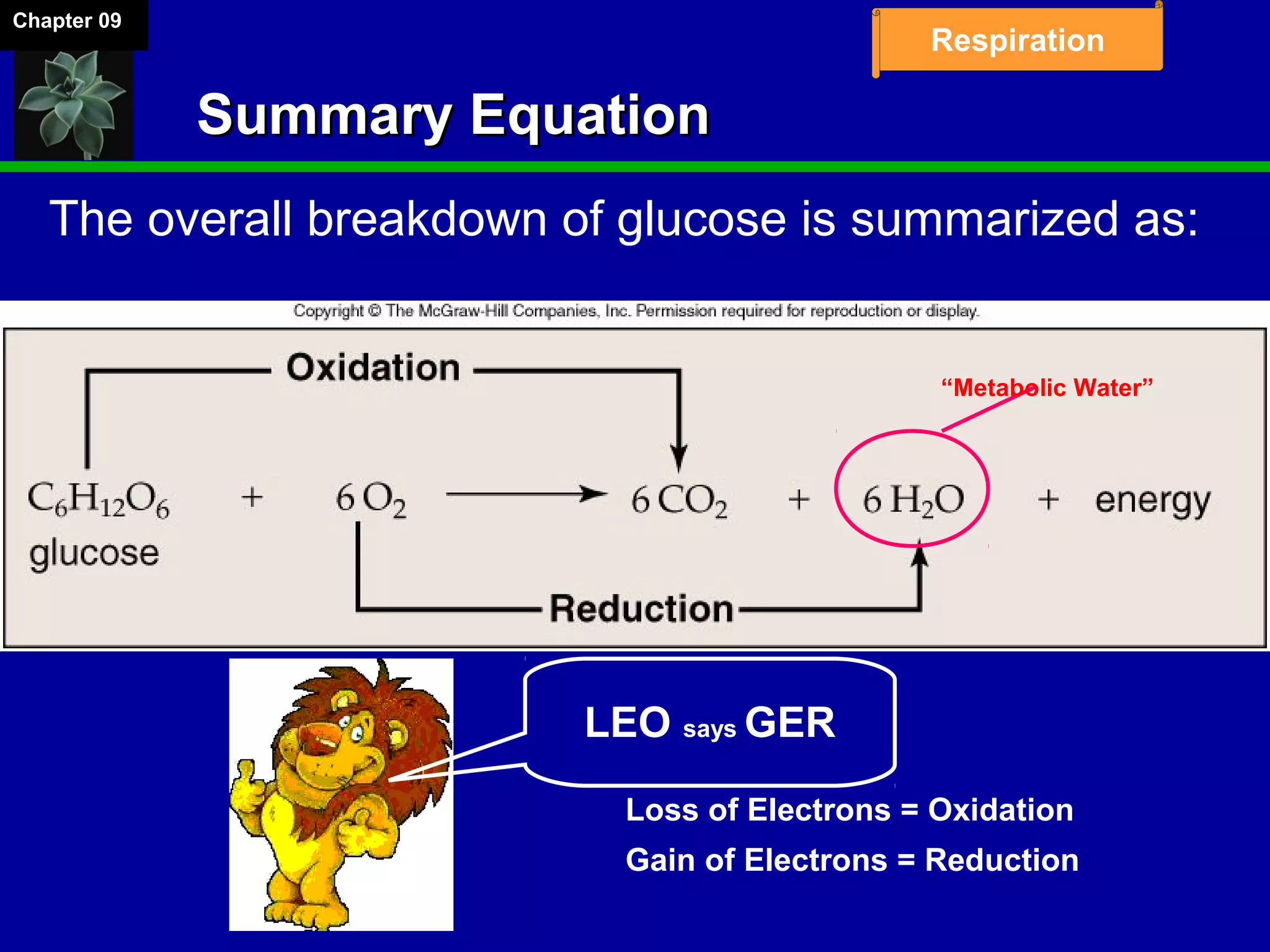
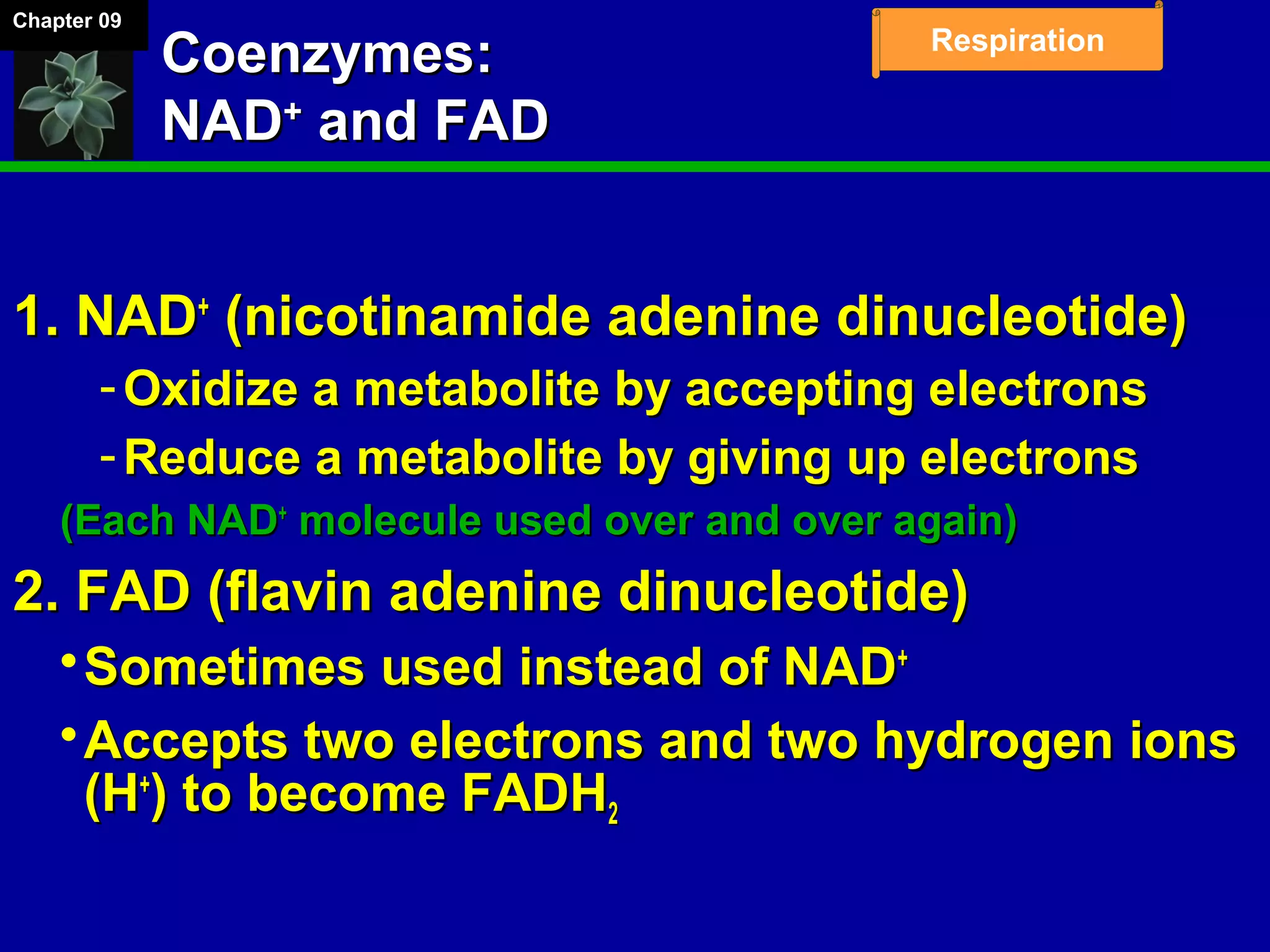
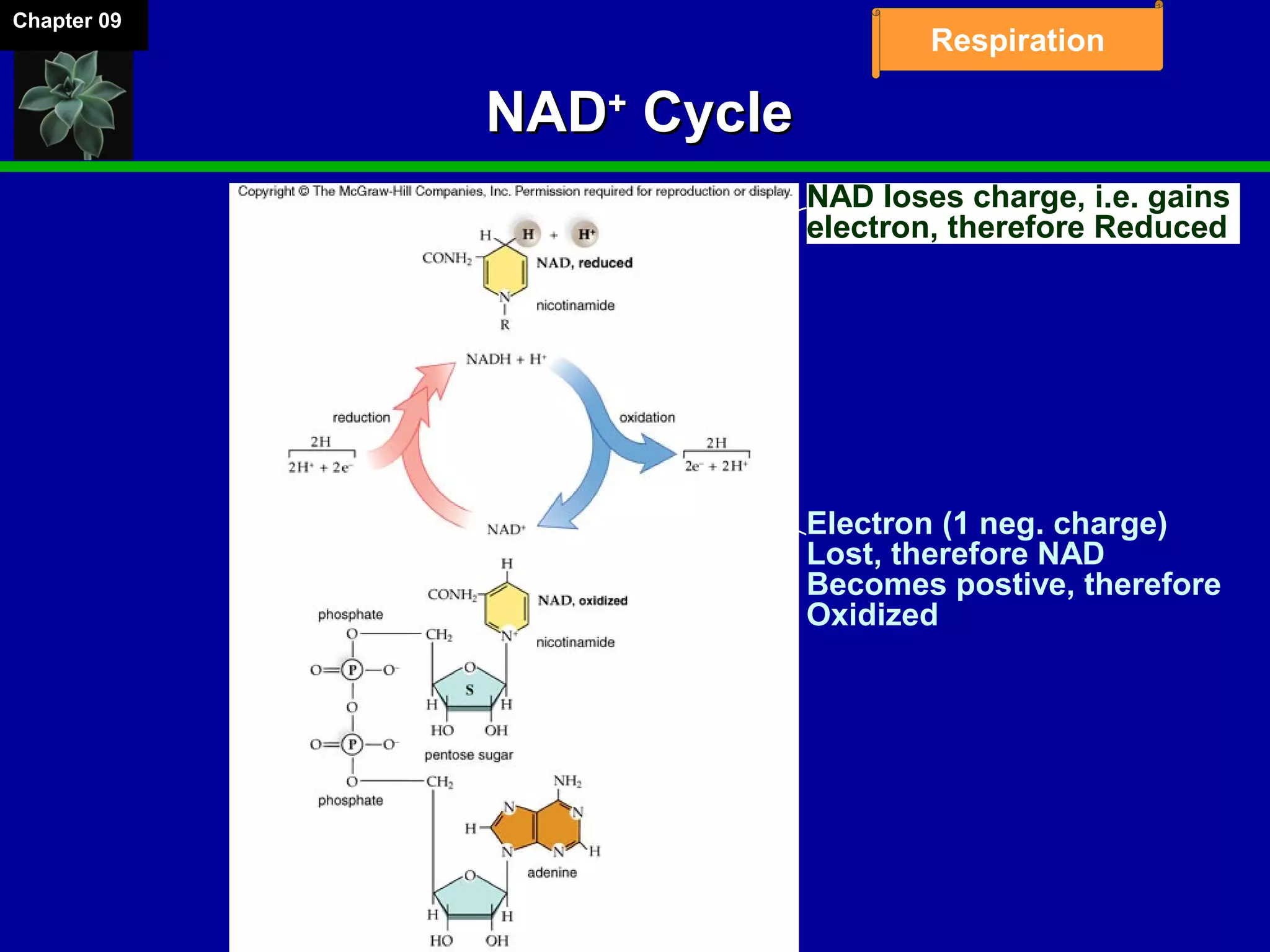
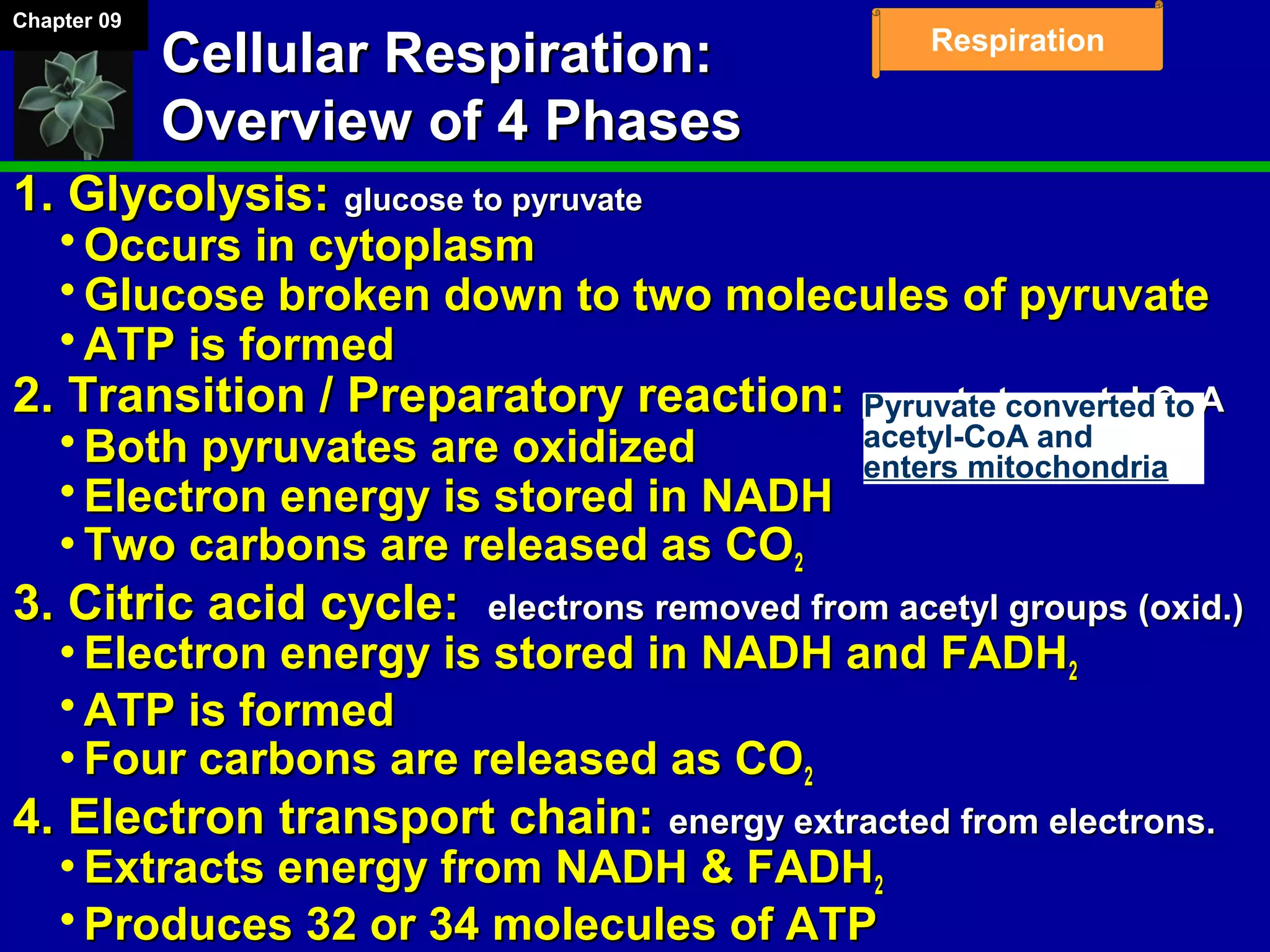
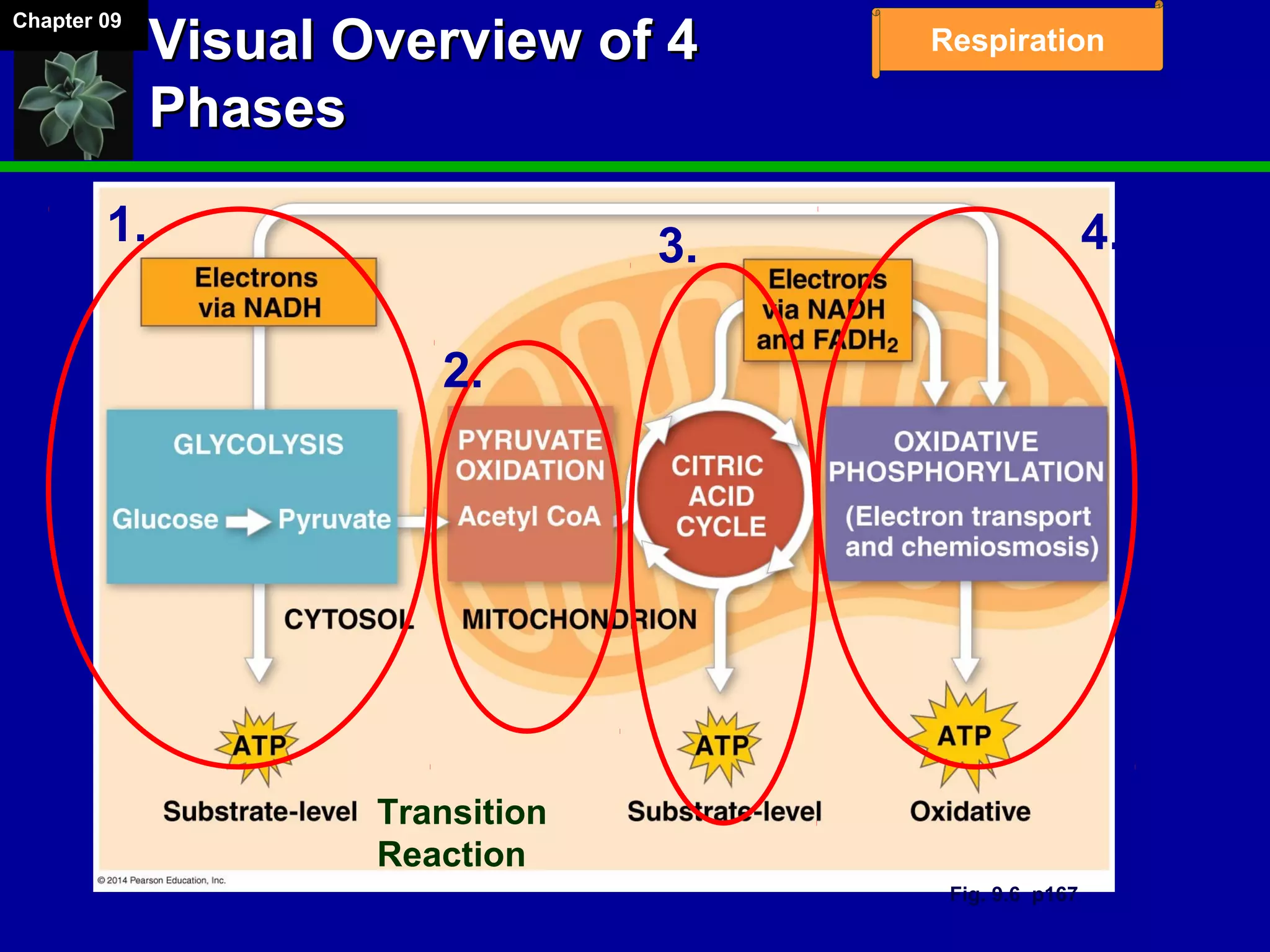
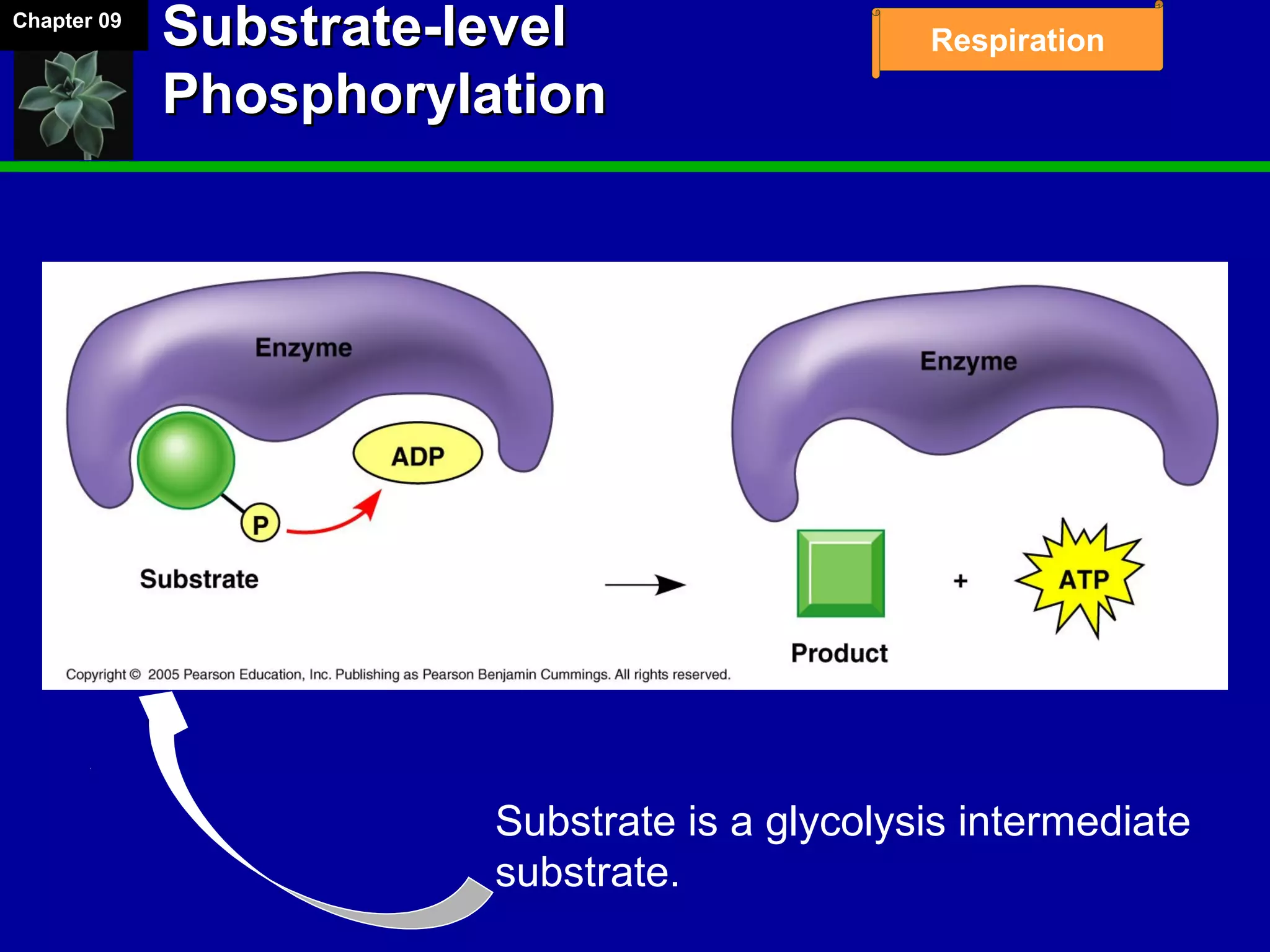
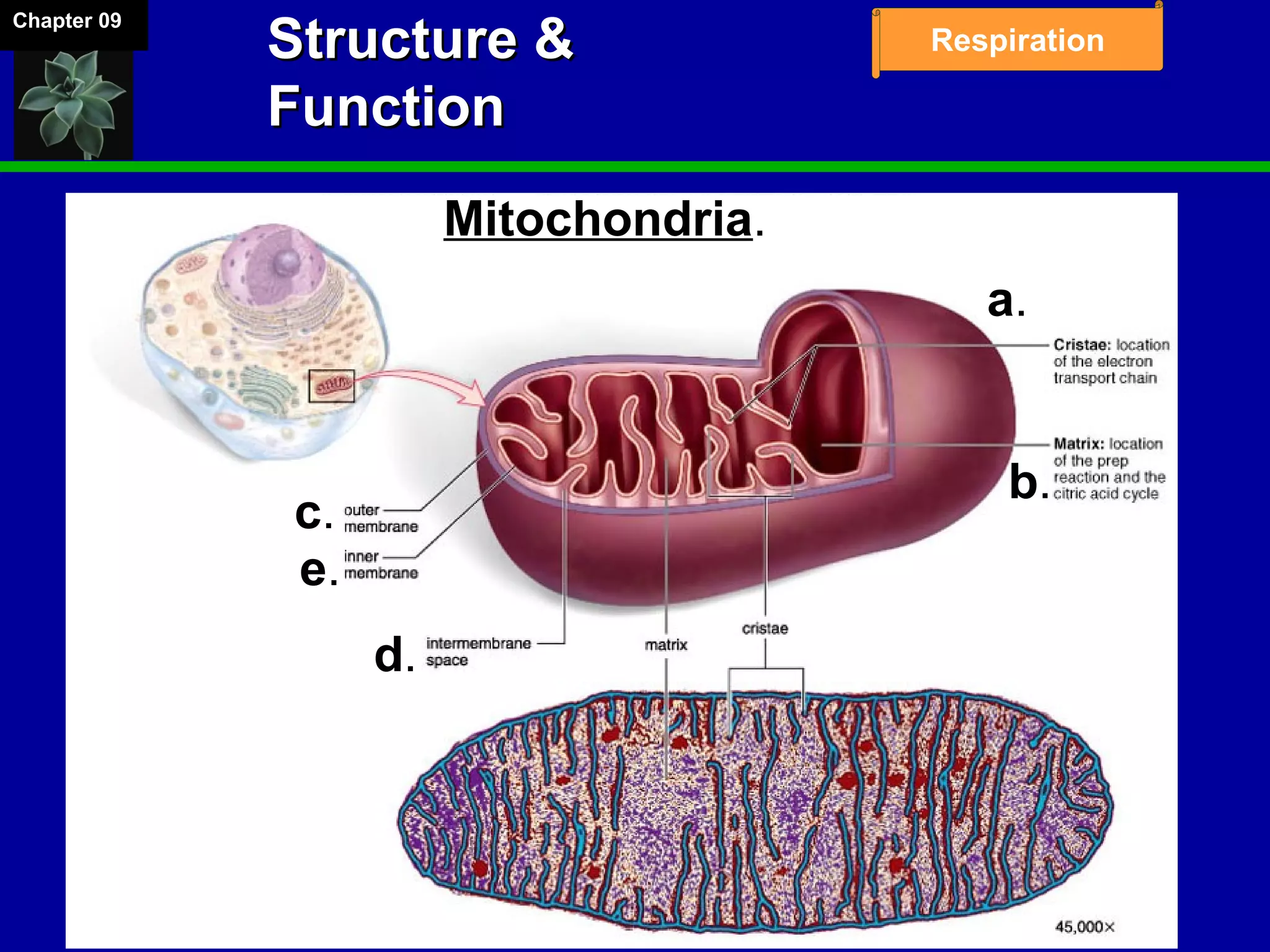
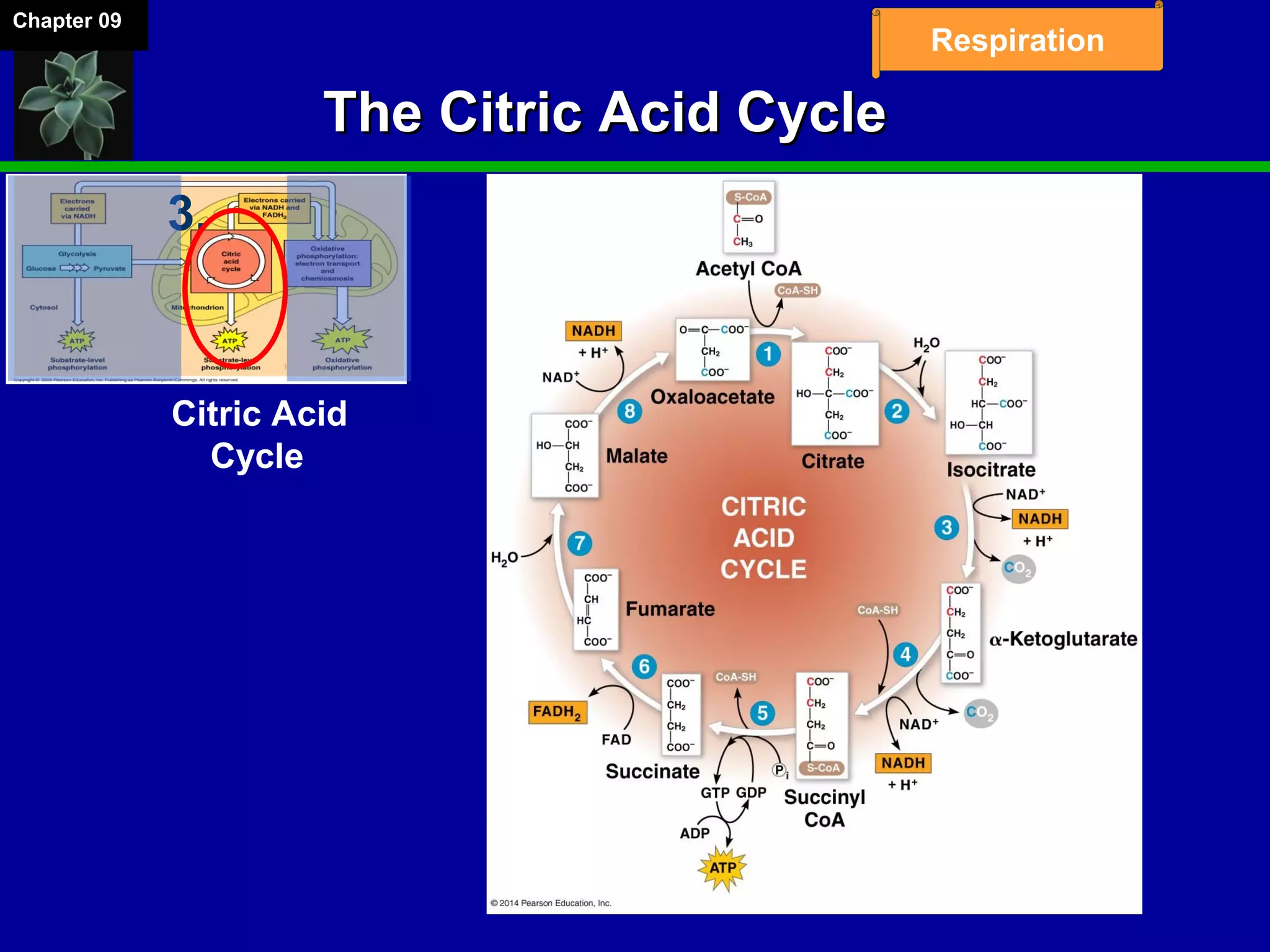
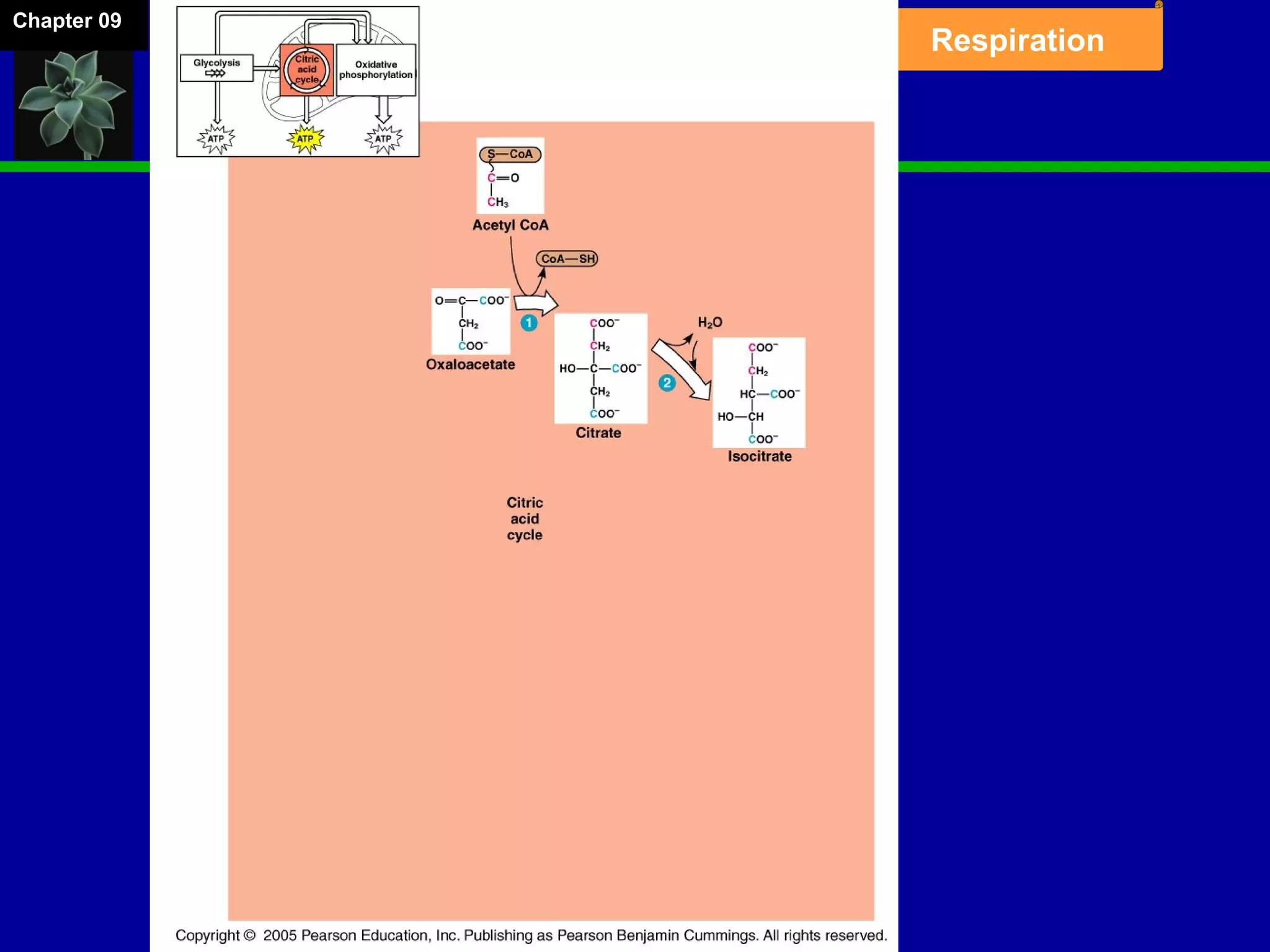
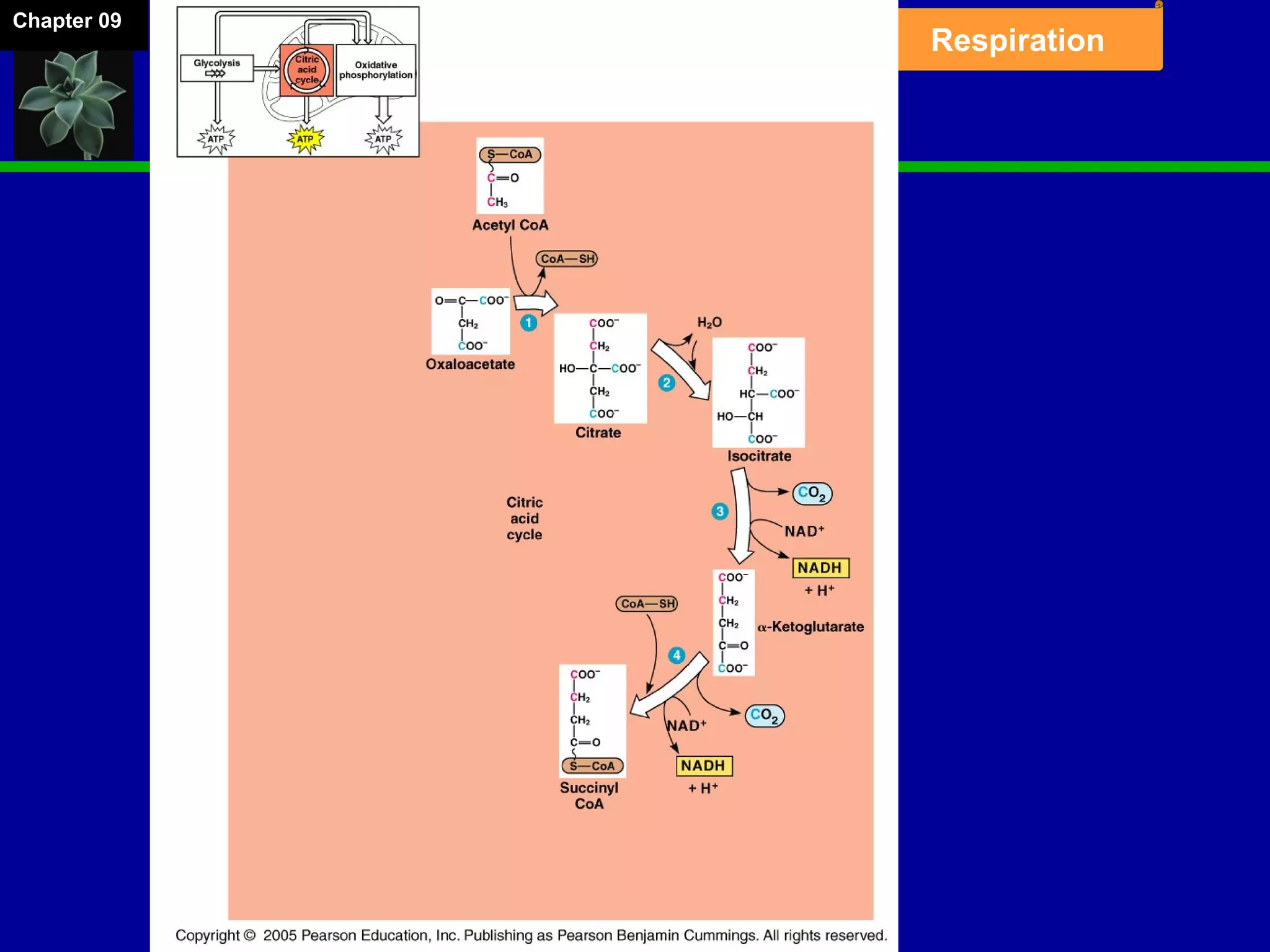
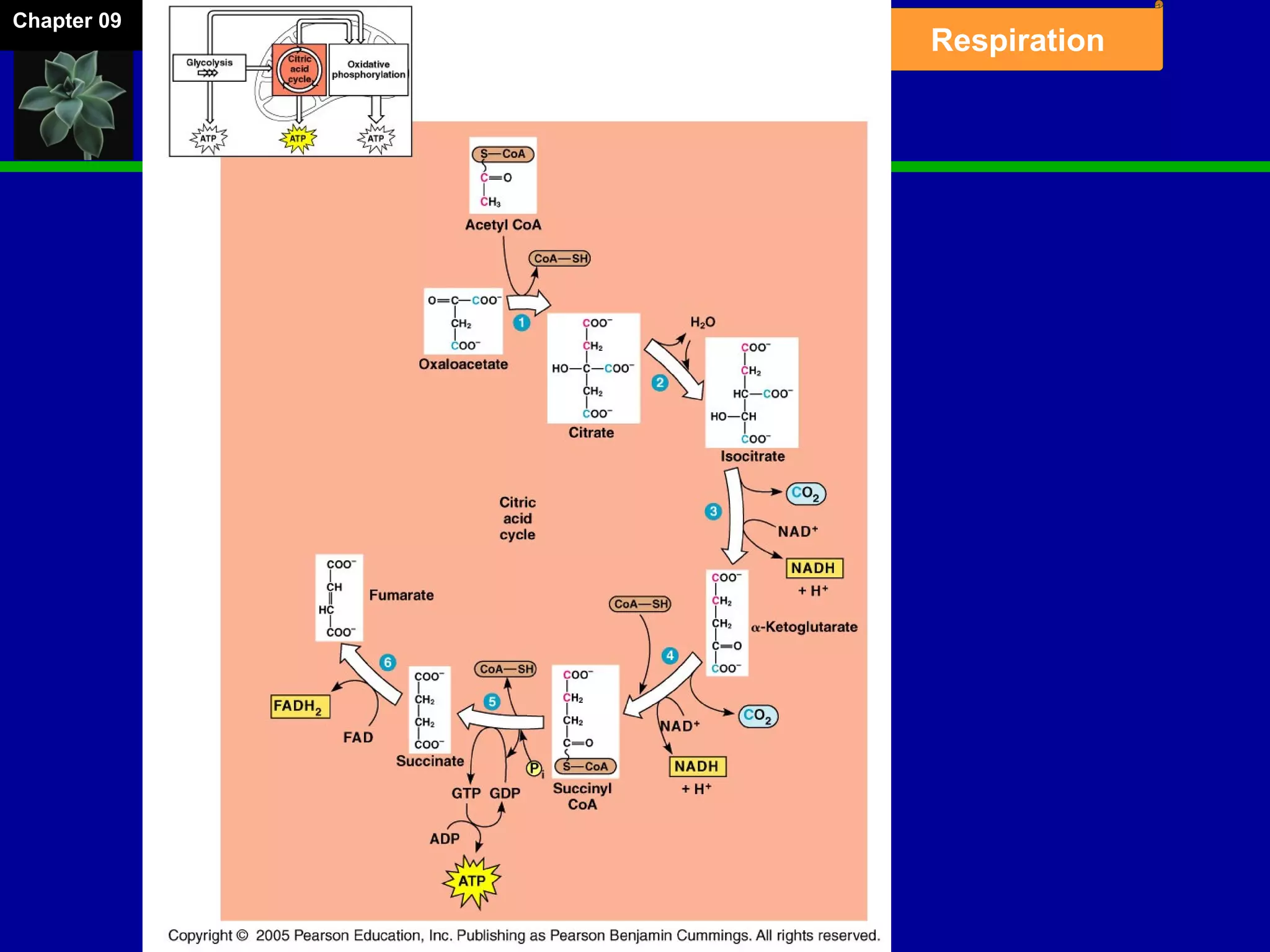
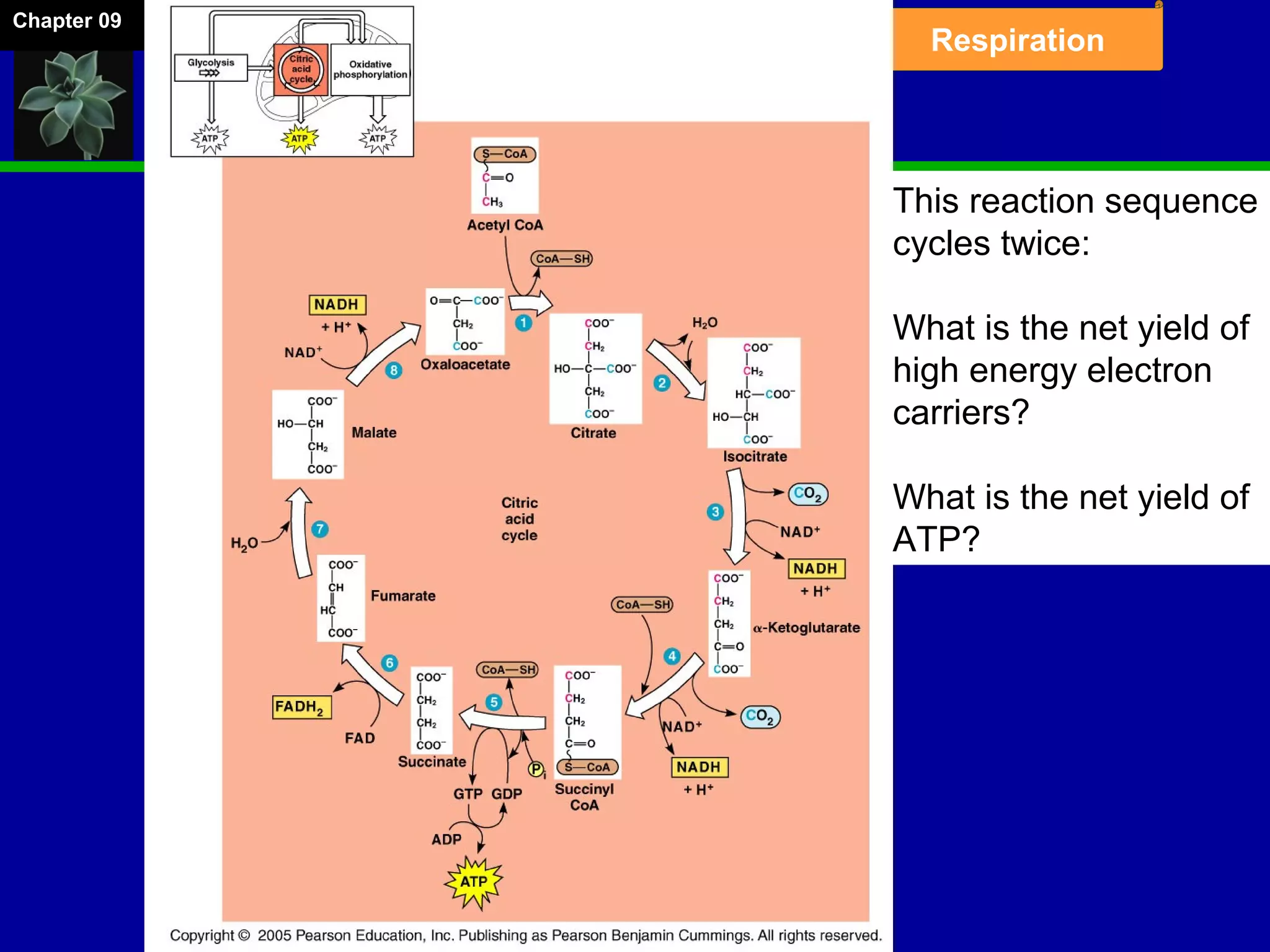
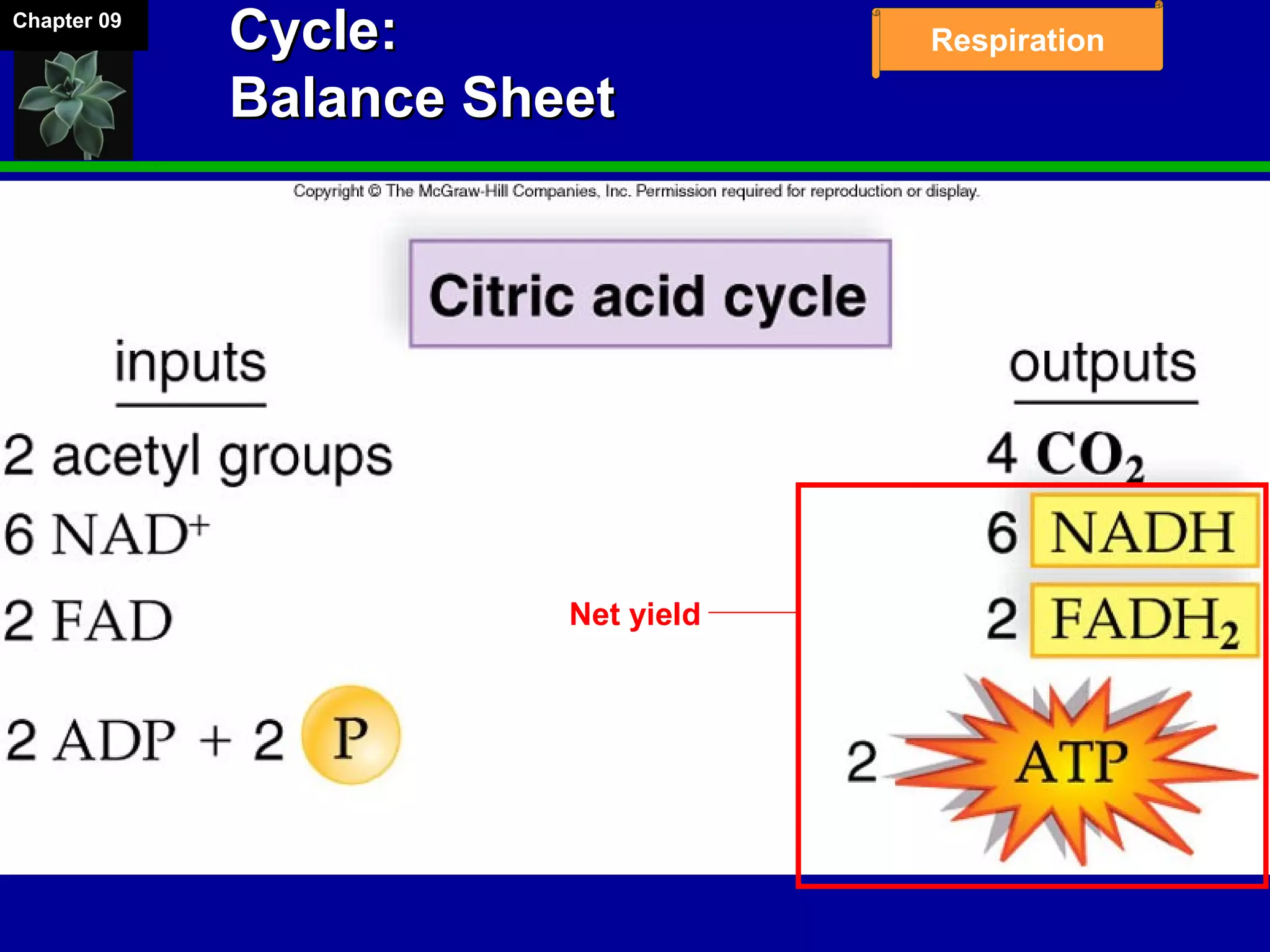
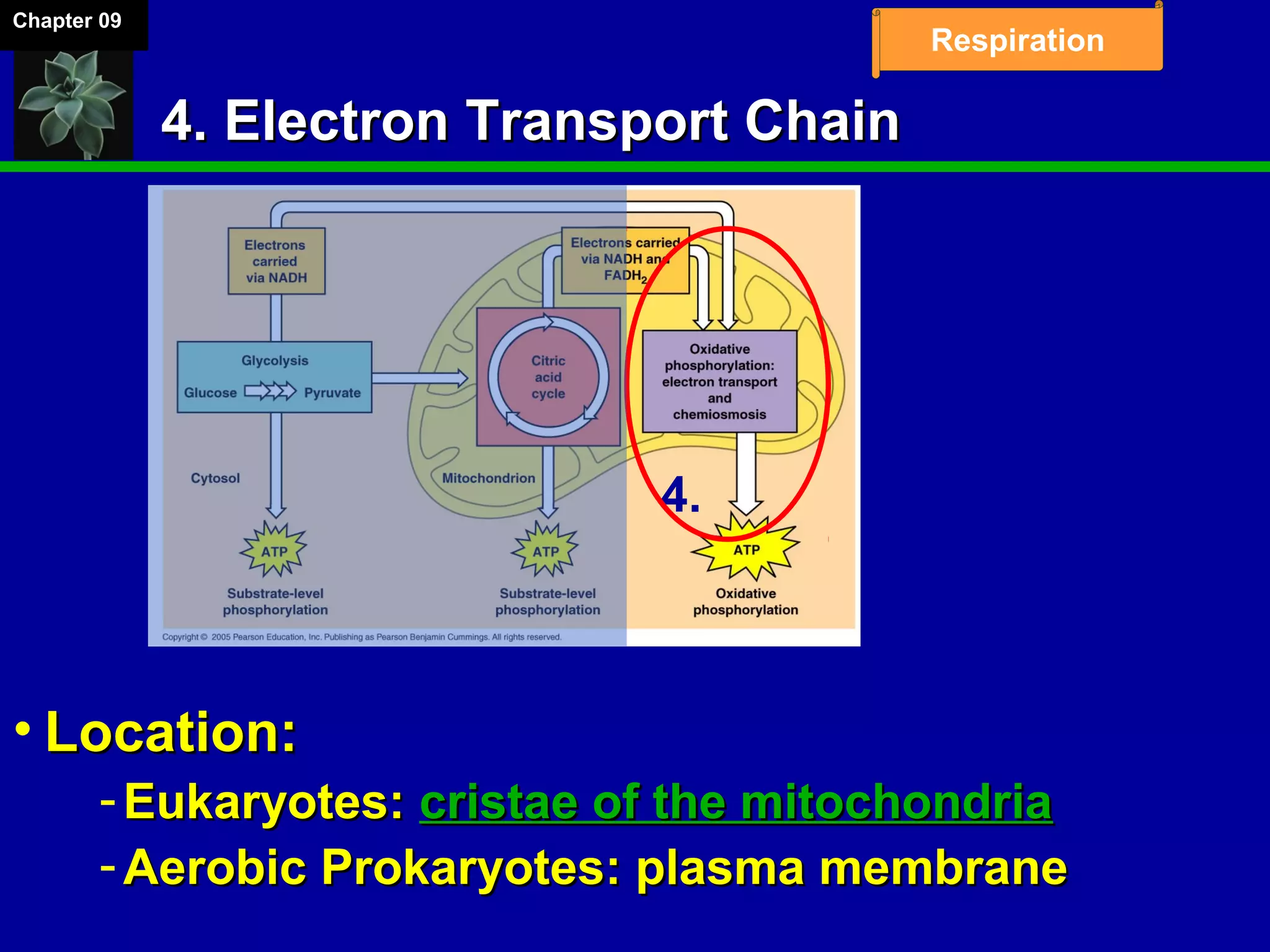
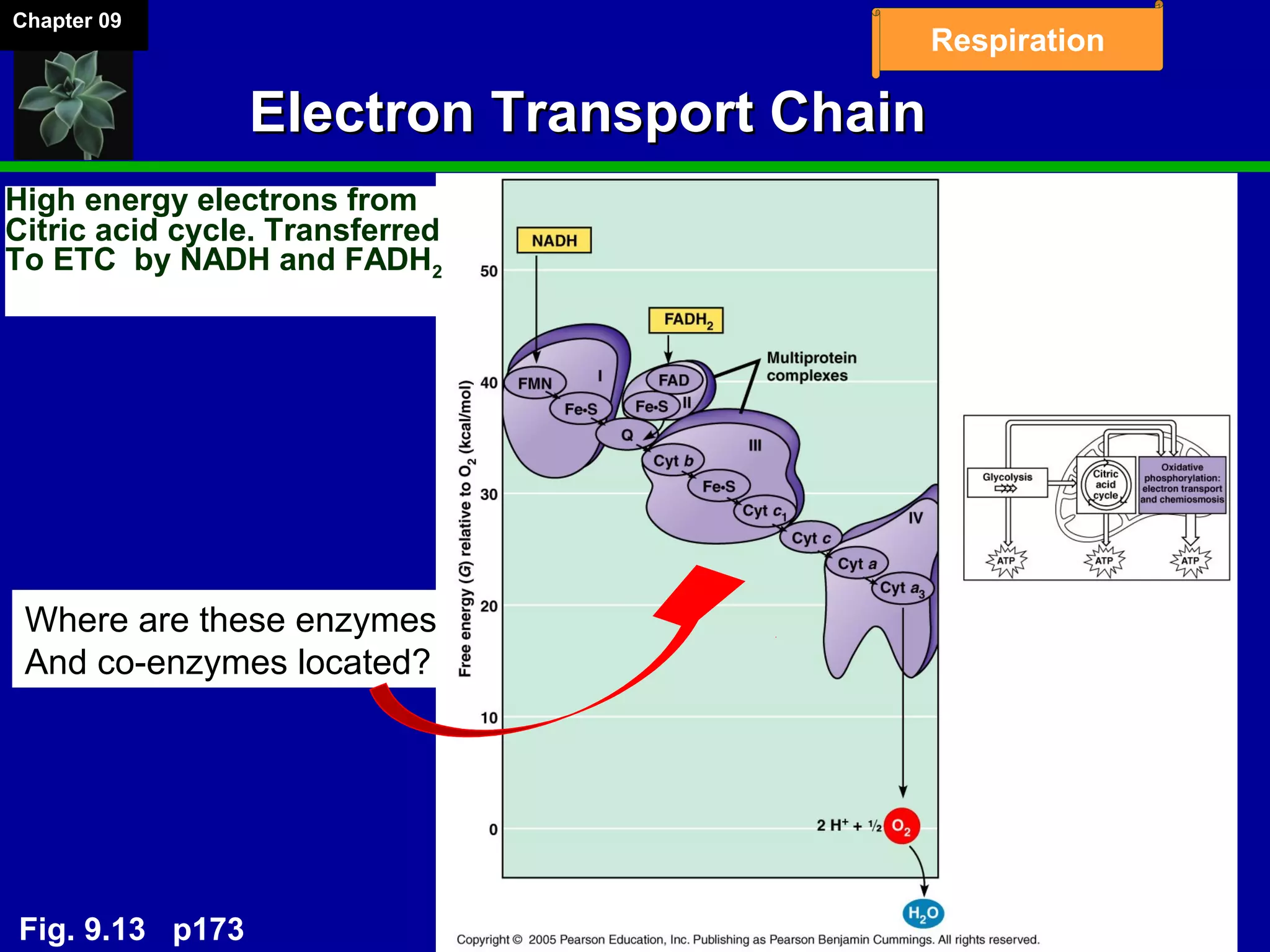
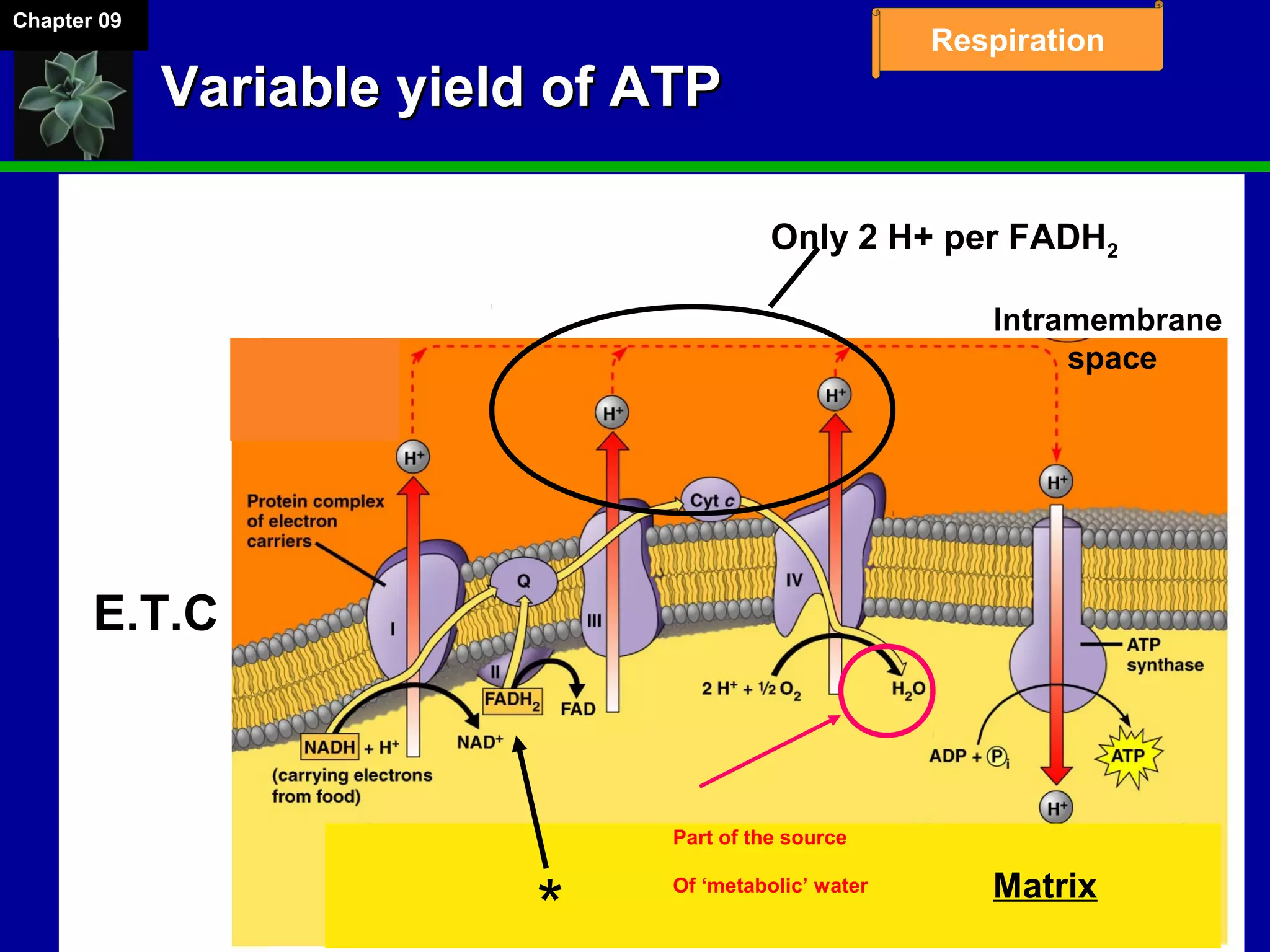
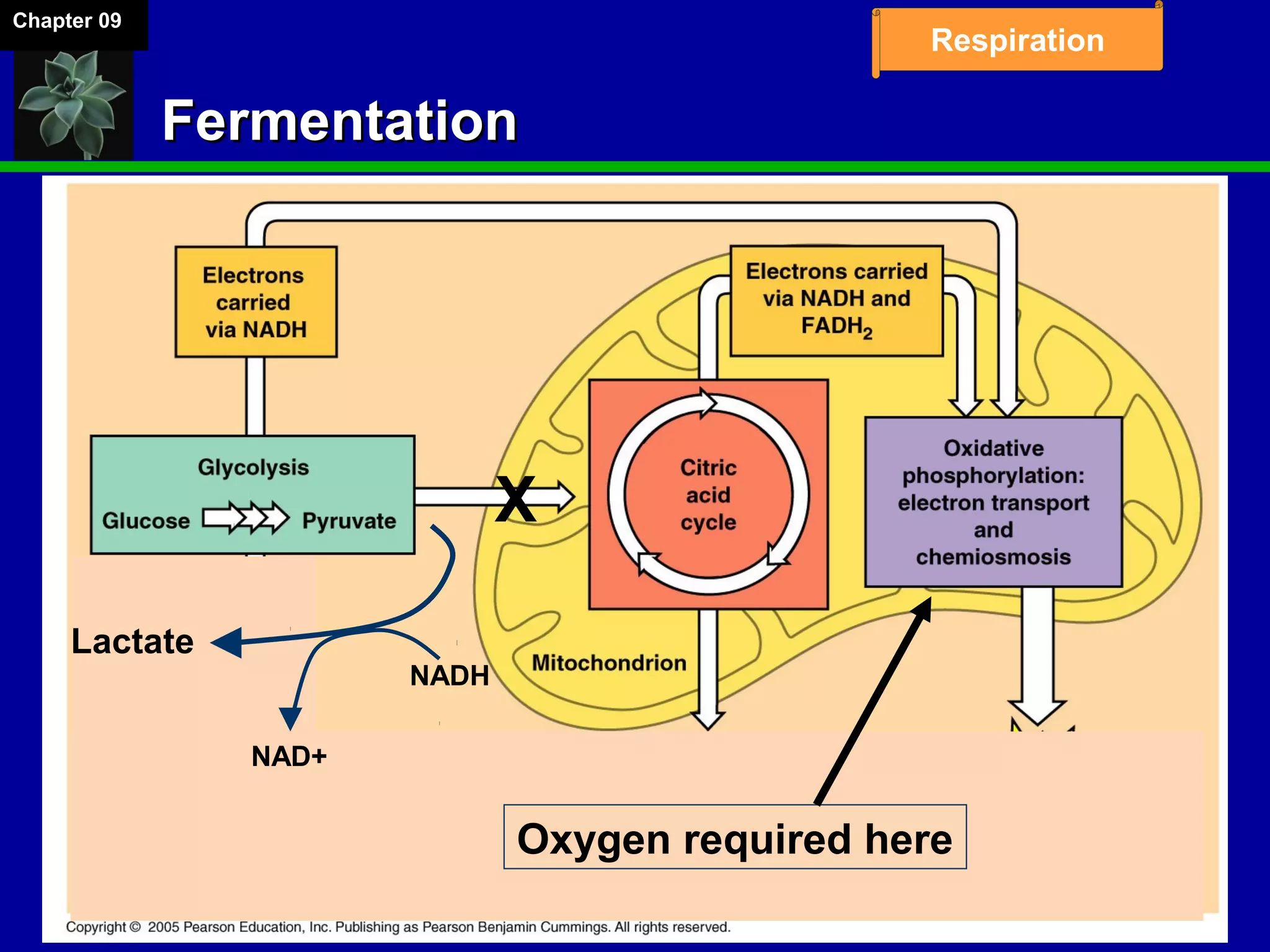
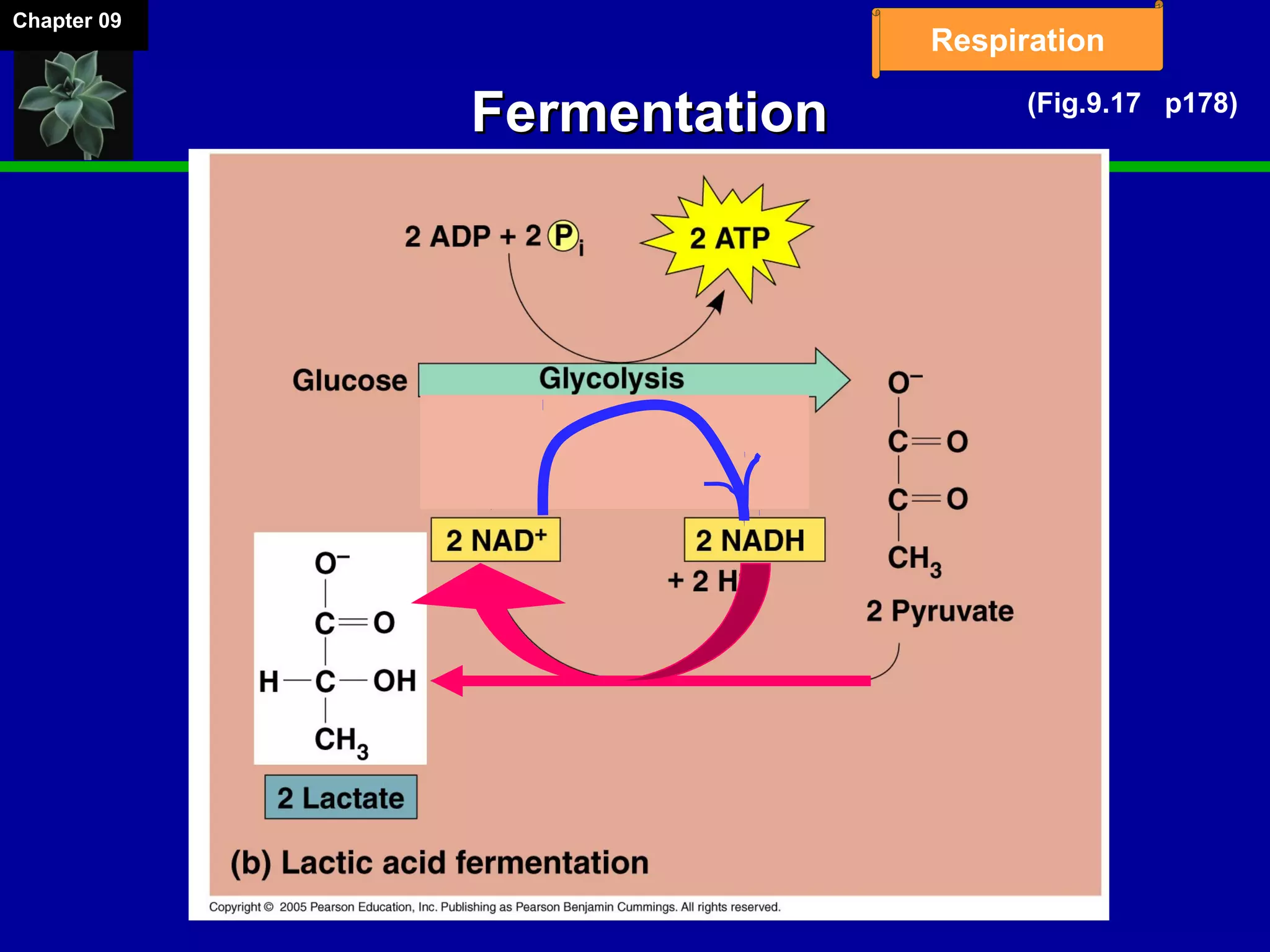
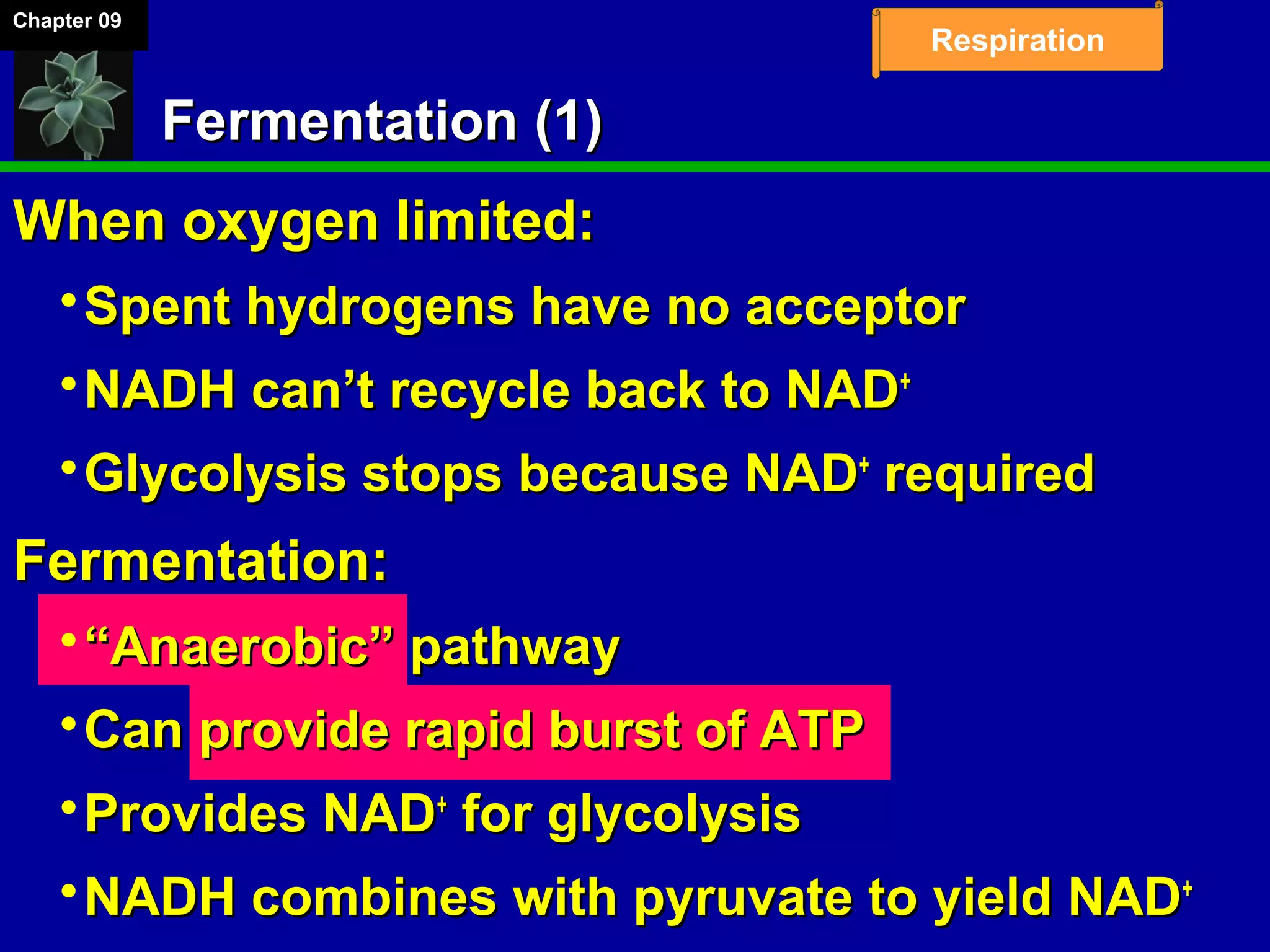
1. Cellular respiration involves the breakdown of glucose to extract energy through redox reactions in the mitochondria.
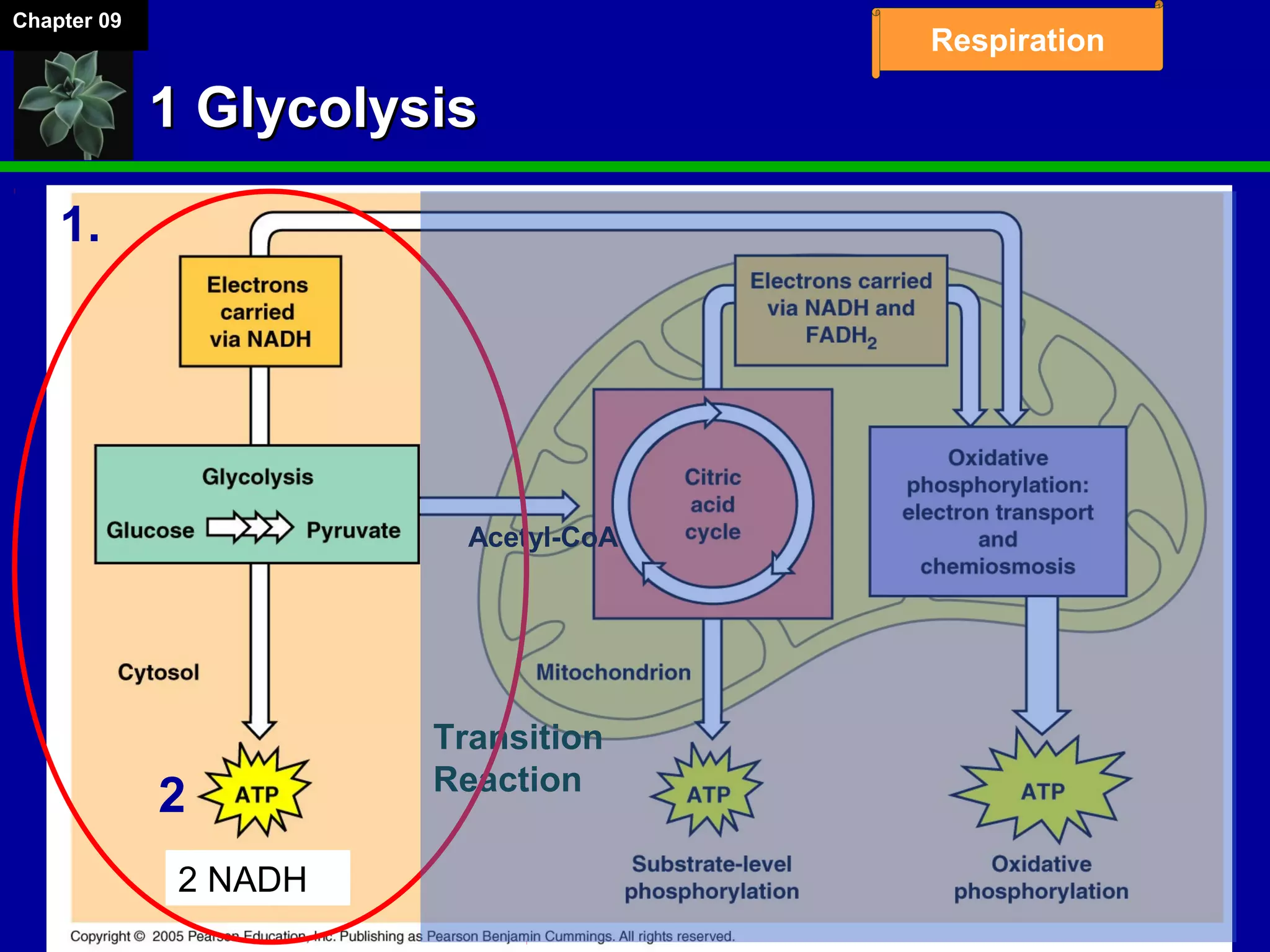
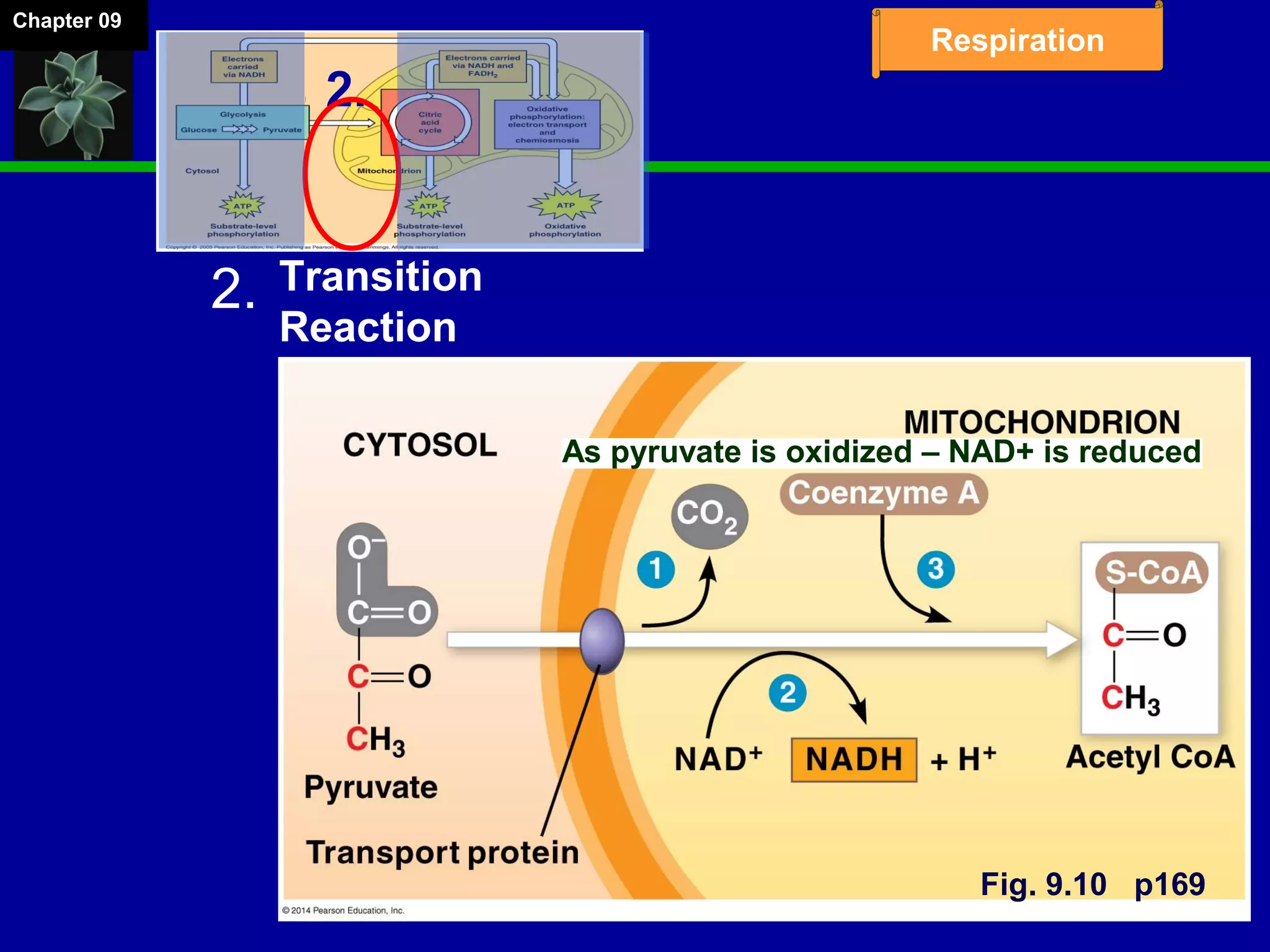
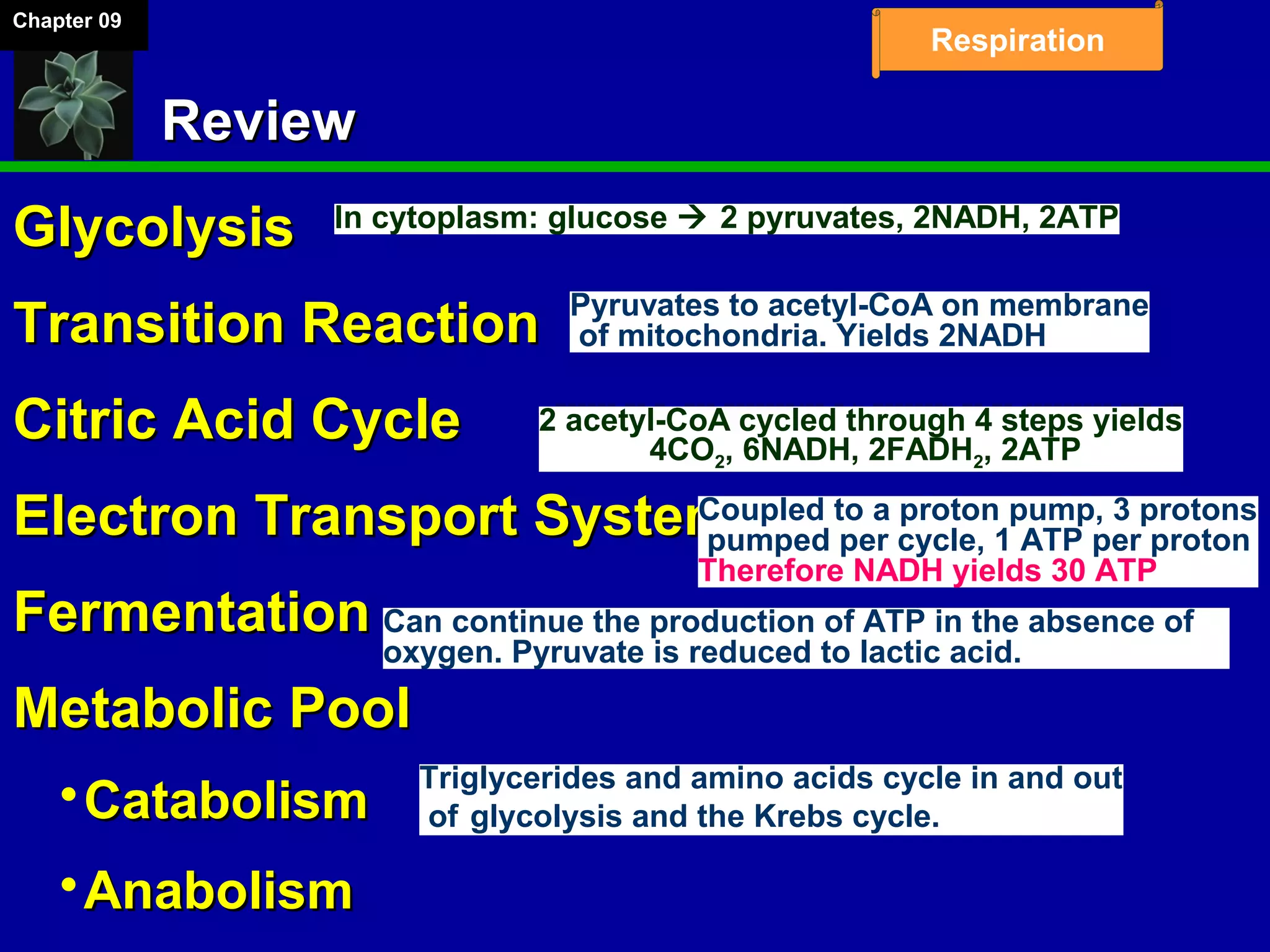
2. Glucose is broken down through glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. This releases energy that is used to synthesize ATP.
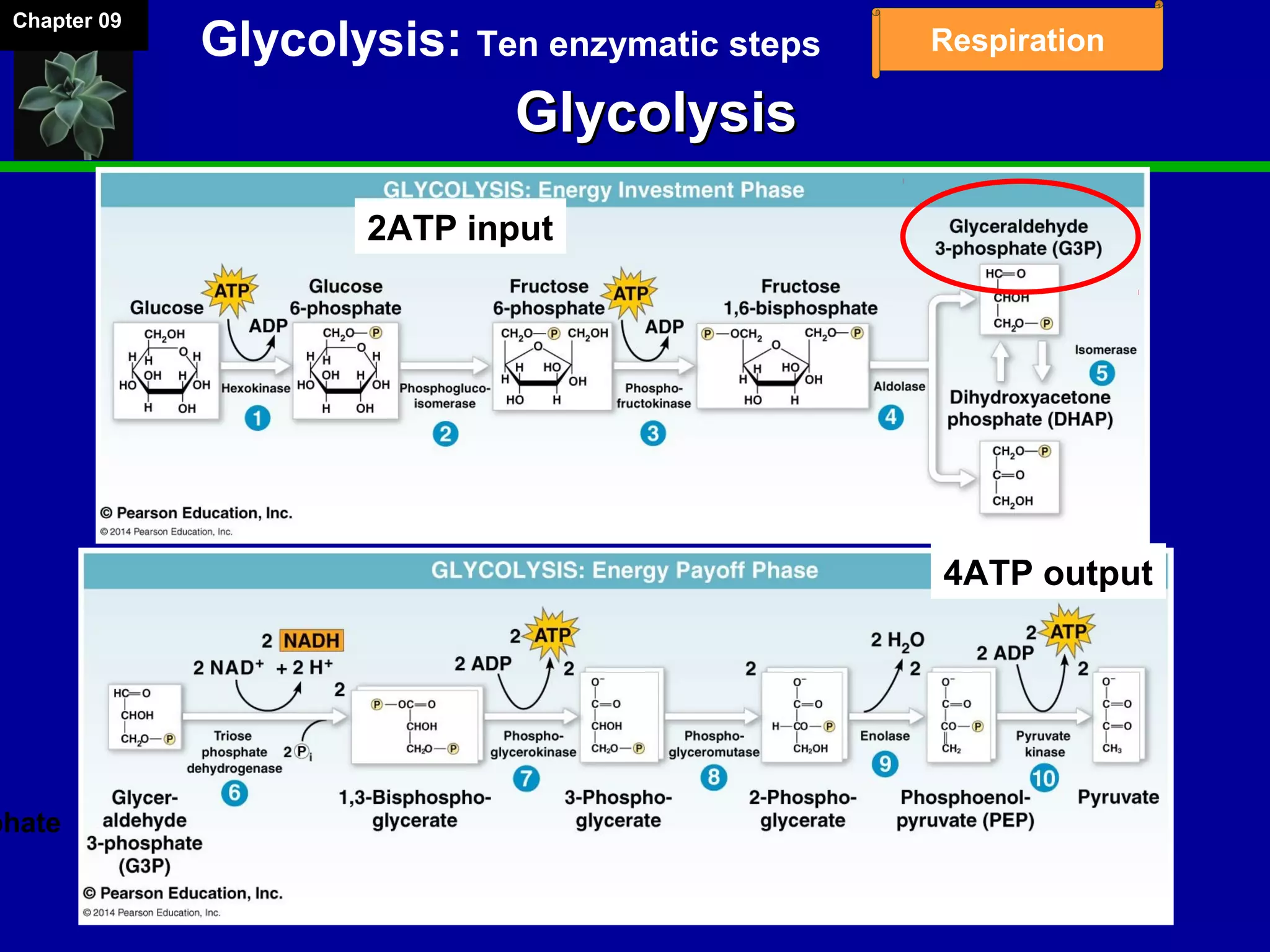
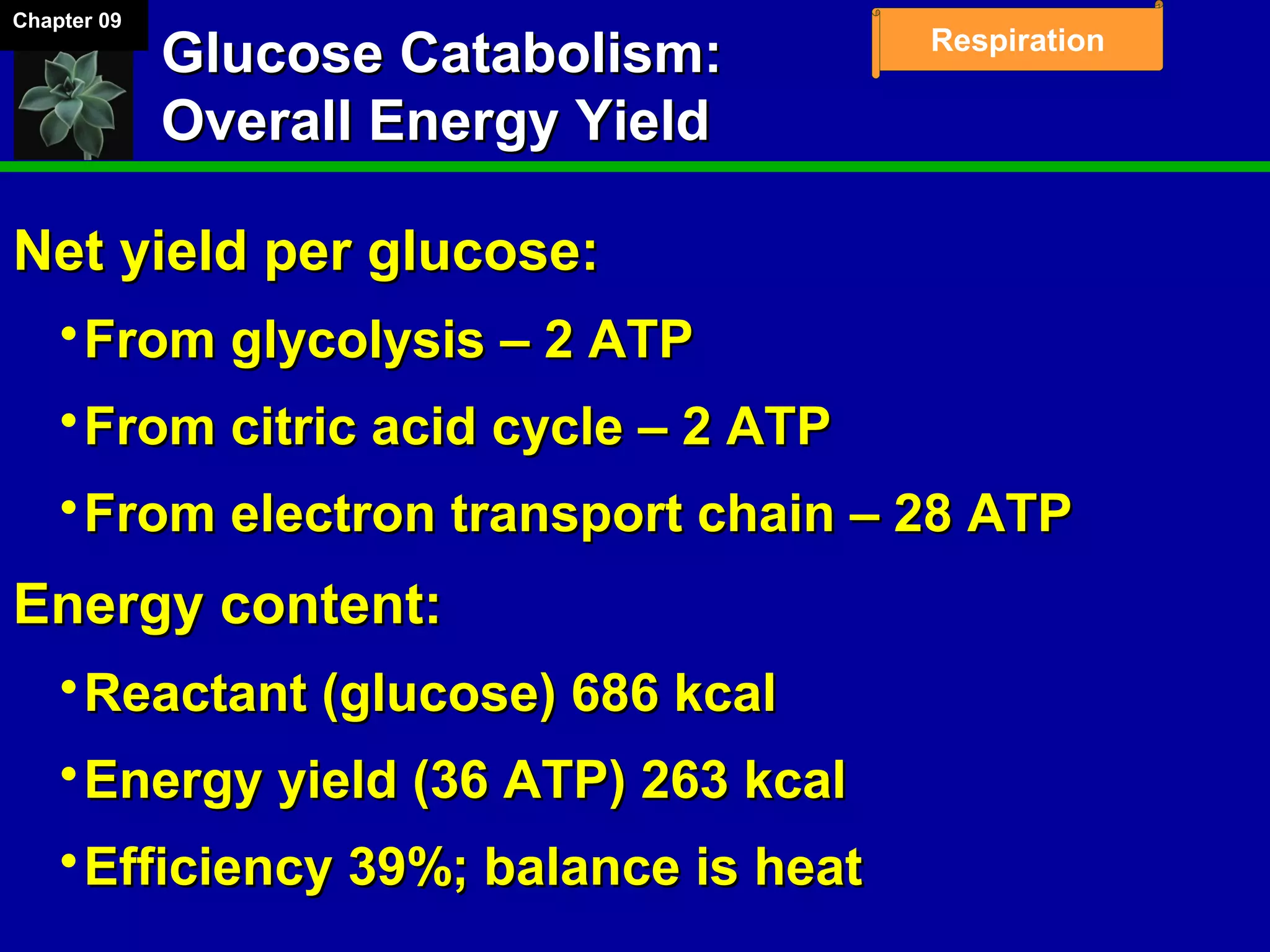
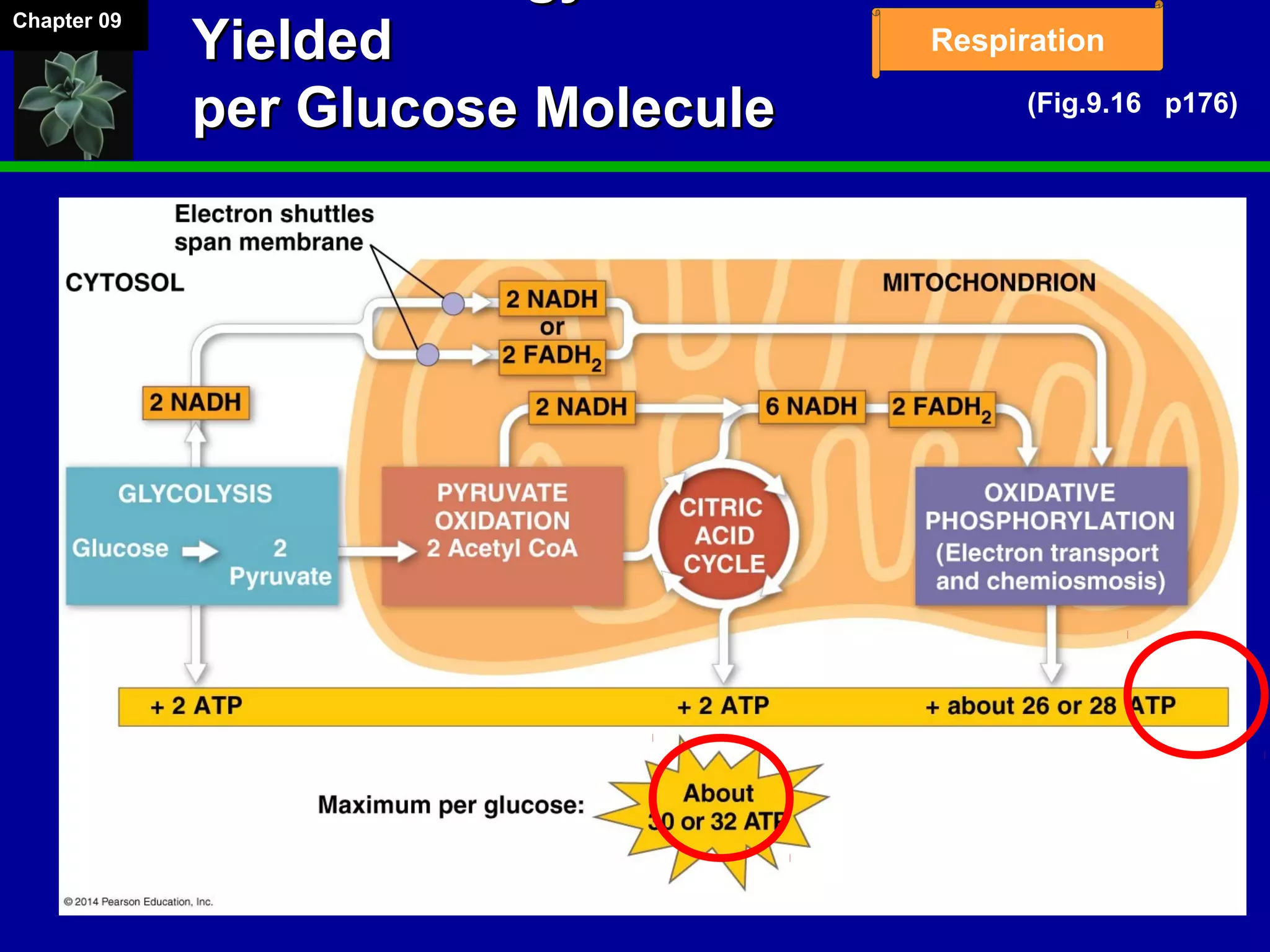
3. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and yields 2 ATP per glucose. The citric acid cycle and electron transport chain occur in the mitochondria and yield 34 more ATP. Overall, cellular respiration generates around 36 ATP from one glucose molecule.