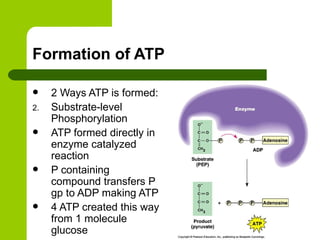
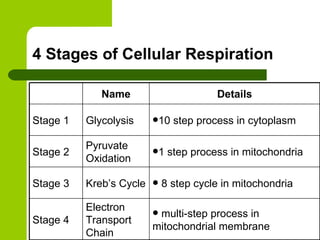
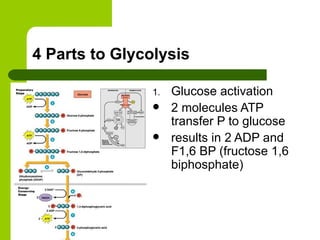
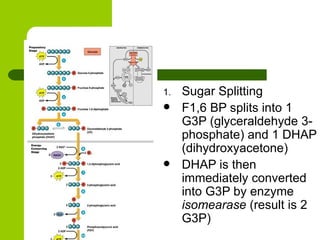
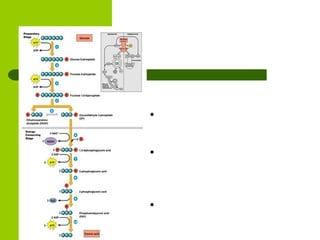
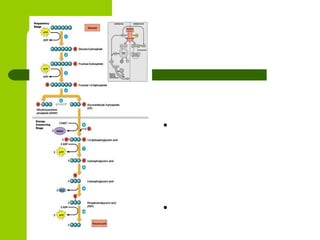
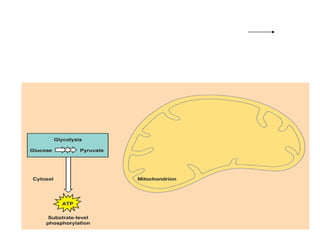
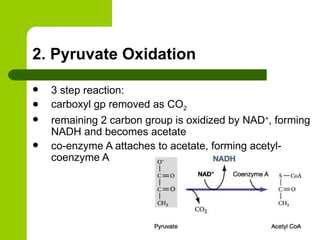
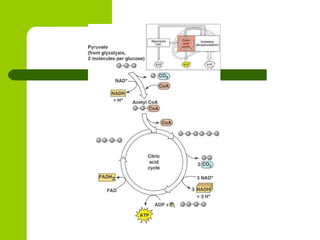
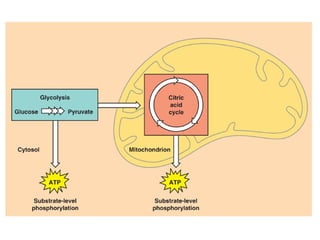
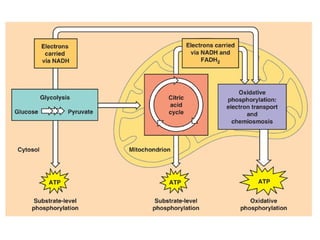
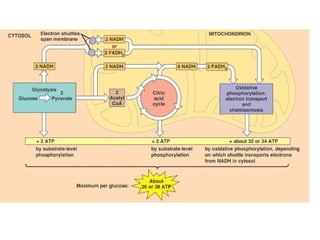
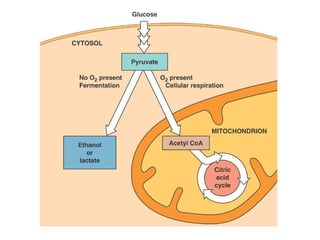
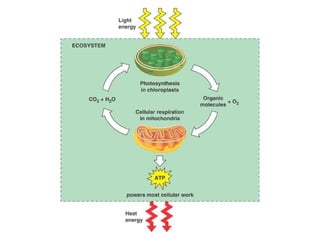
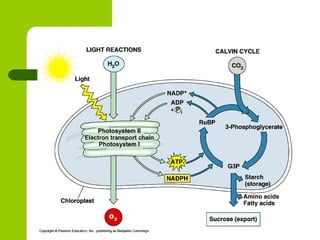
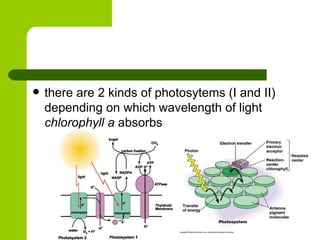
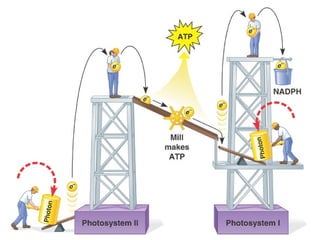
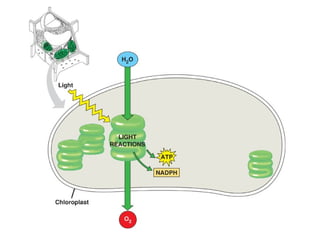
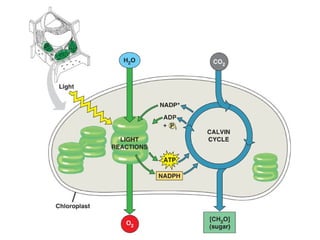
Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms convert glucose into energy in the form of ATP. It occurs in four main stages: glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP. Pyruvate then enters the mitochondria where it is further oxidized, producing NADH and FADH2. These enter the Krebs cycle to produce more NADH and FADH2. Finally, the electron transport chain uses the energy from NADH and FADH2 to pump protons across a membrane, building an electrochemical gradient used to produce a large amount of ATP through oxidative