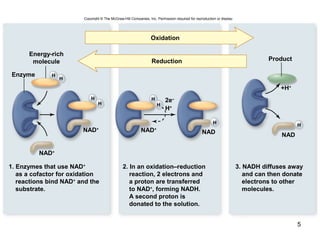
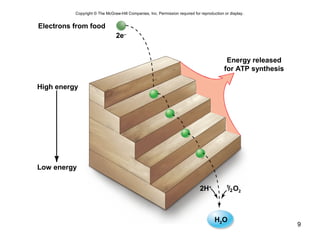
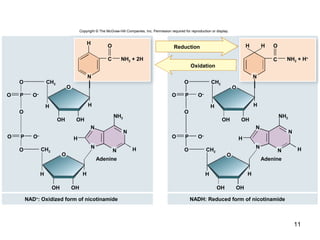
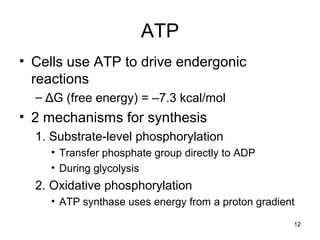
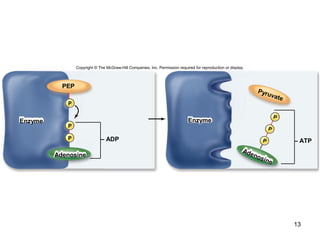
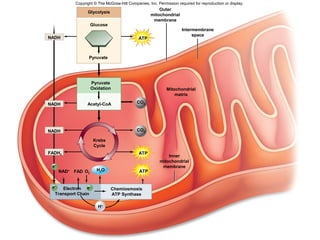
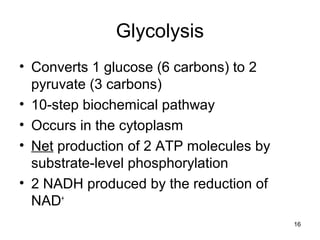
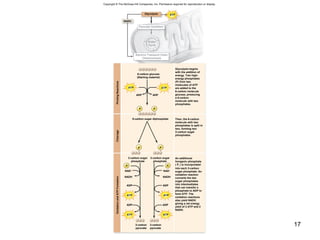
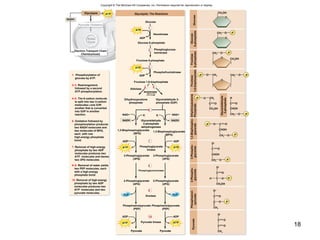
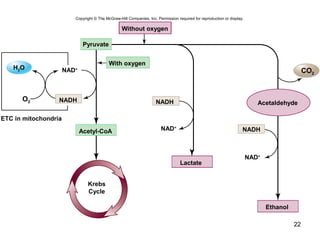
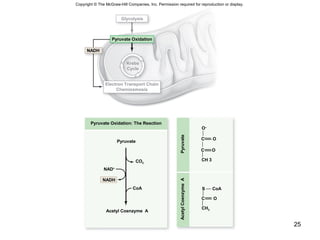
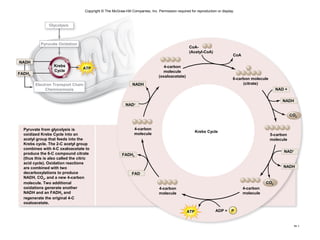
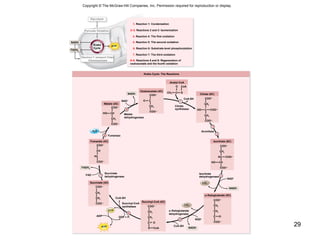
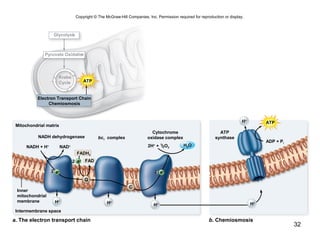
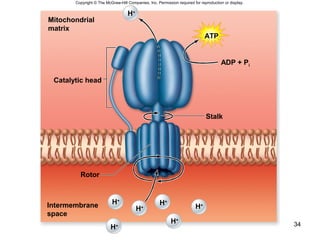
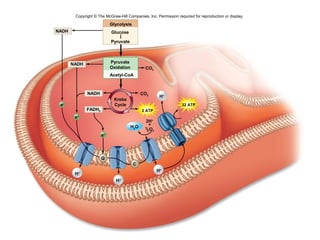
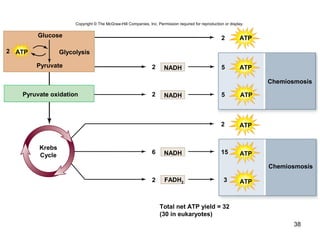
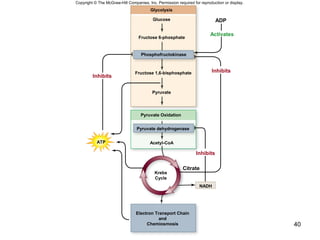
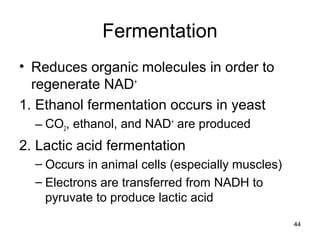
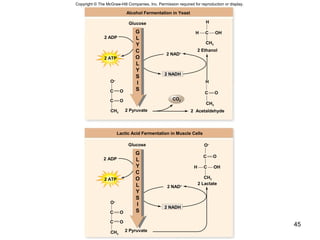
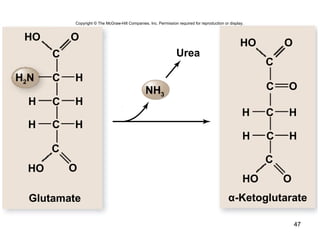
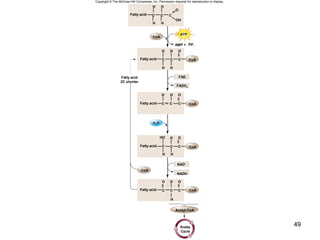
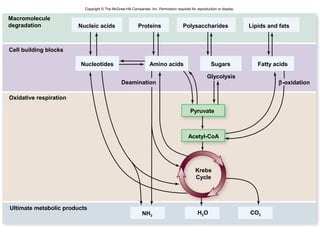
The document outlines the process of cellular respiration which involves glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis converts glucose to pyruvate, producing 2 ATP and 2 NADH. In the presence of oxygen, pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl-CoA which enters the Krebs cycle. The Krebs cycle further oxidizes acetyl-CoA, producing 3 more NADH, 1 FADH2, and 1 ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation. Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are used to build an electrochemical gradient through the electron transport chain which powers ATP synthesis through oxidative phosphorylation.