The document summarizes electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation. It discusses:
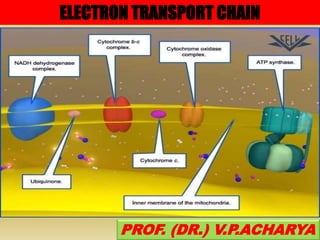
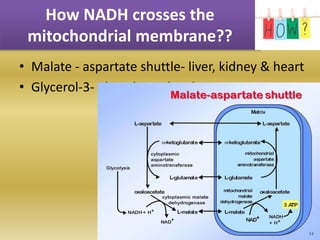
1) The four complexes of the electron transport chain located in the inner mitochondrial membrane that facilitate the transfer of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen. This creates a proton gradient used by ATP synthase to generate ATP.
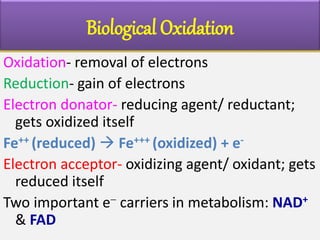
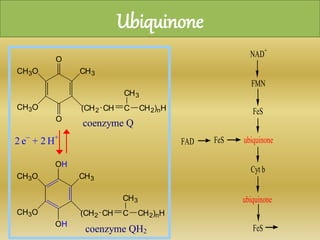
2) The enzymes, electron carriers like cytochromes and iron-sulfur proteins, and redox reactions involved in electron transport.
3) How the proton gradient is used by ATP synthase to drive ATP synthesis via chemiosmosis.
4) Inhibitors and uncouplers that disrupt the proton gradient or electron transport.