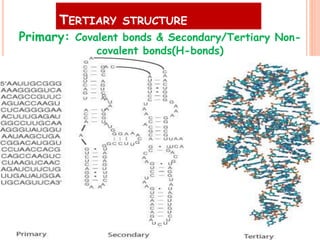
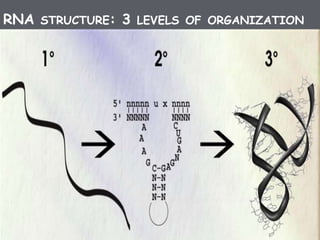
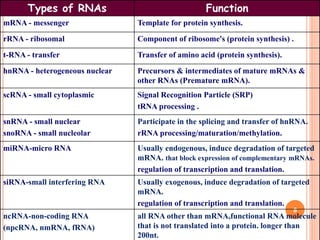
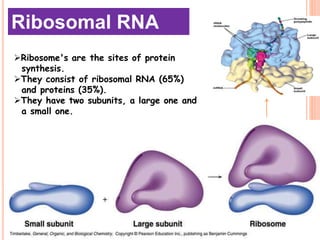
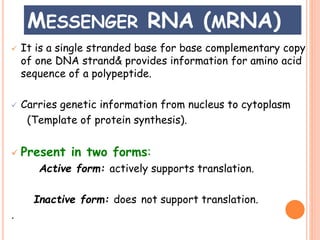
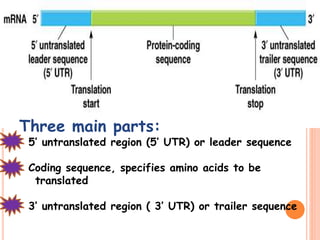
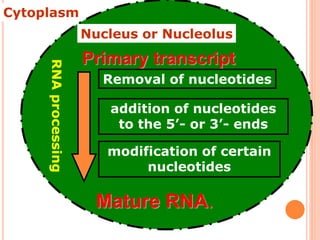
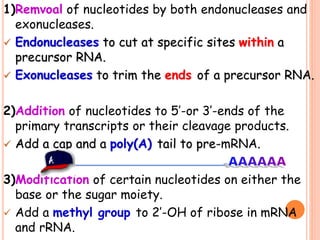
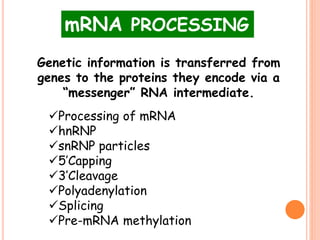
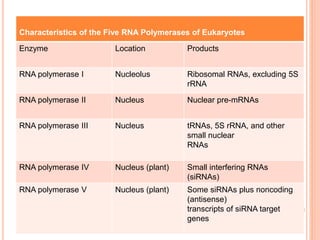
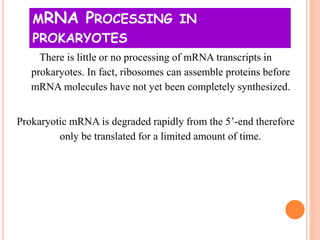
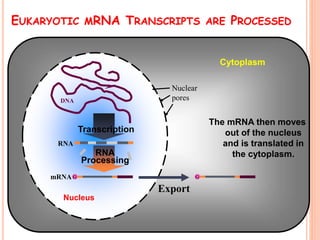
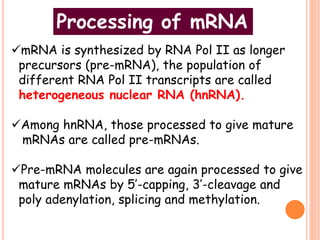
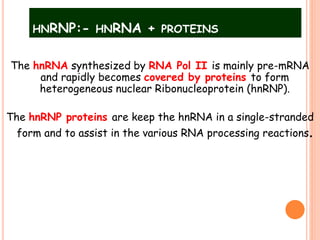
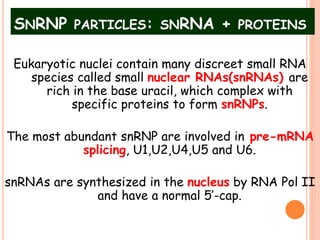
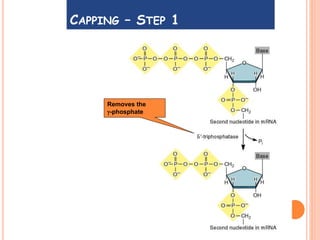
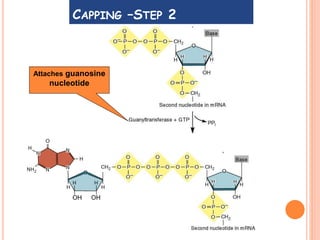
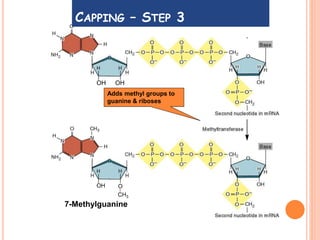
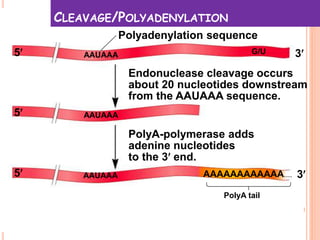
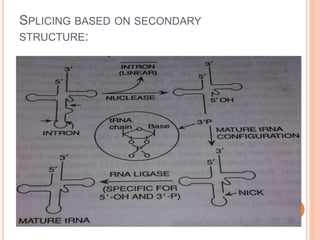
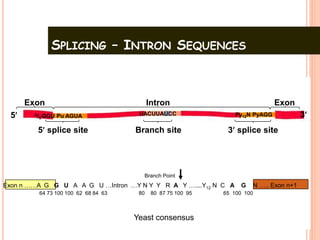
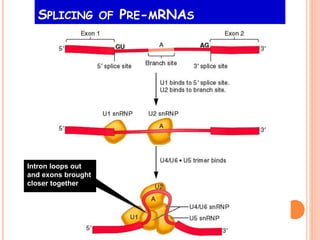
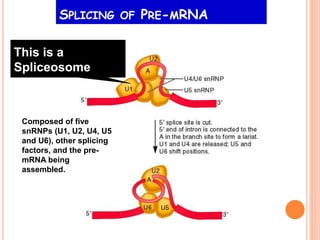
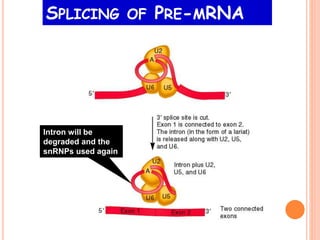
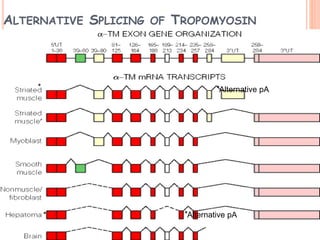
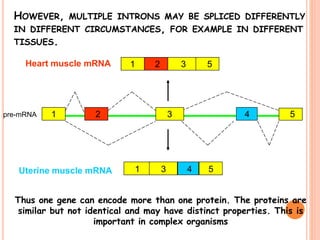
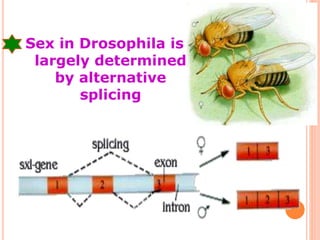
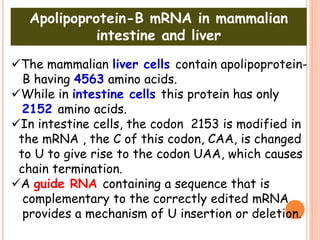
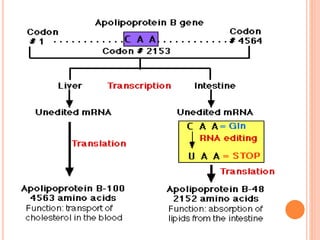
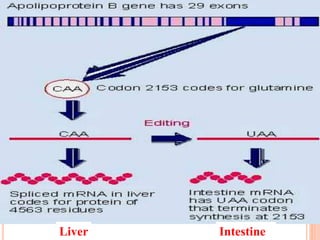
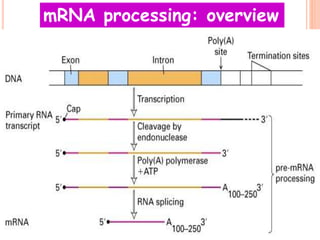
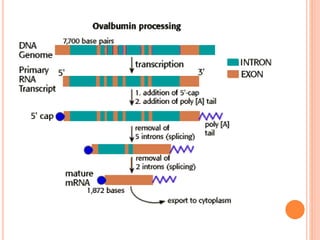
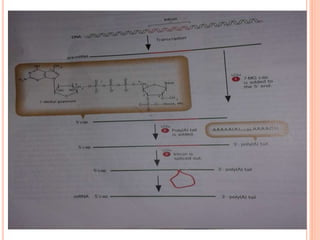
RNA processing is the modification of primary RNA transcripts into mature RNA molecules. It involves removal of introns through splicing and addition of modifications like 5' capping, 3' polyadenylation tail, and RNA editing. Alternative splicing allows a single gene to produce multiple protein isoforms by selective inclusion or exclusion of exons from the final mRNA.