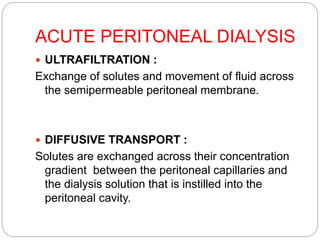
Renal replacement therapy replaces the normal filtering function of the kidneys using modalities like hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, or renal transplantation. Peritoneal dialysis uses the peritoneal membrane for diffusion and ultrafiltration of solutes and fluid, while hemodialysis uses an external dialyzer to filter the blood via diffusion and convection. Both therapies aim to control uremia, electrolyte abnormalities, and fluid balance. Choice of modality depends on factors like age, cardiovascular status, and expertise available. Continuous renal replacement therapy is preferred for critically ill patients who are hemodynamically unstable.