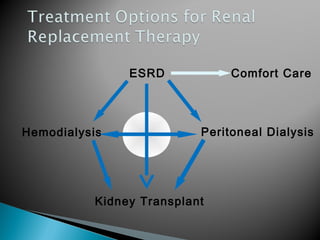
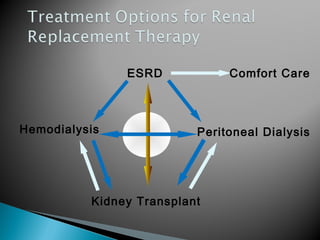
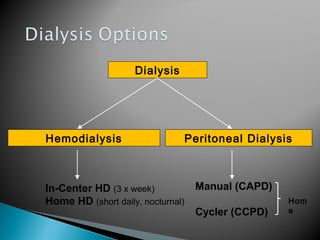
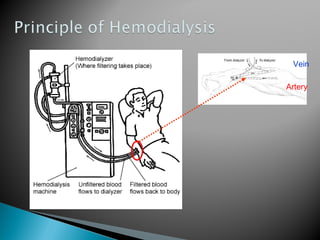
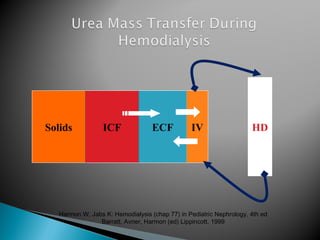
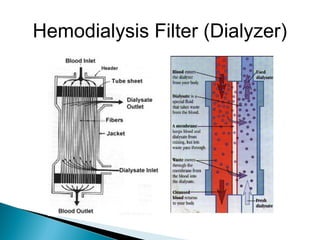
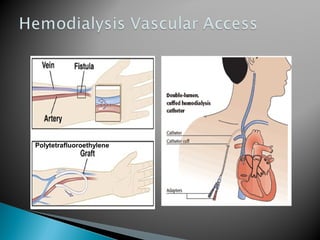
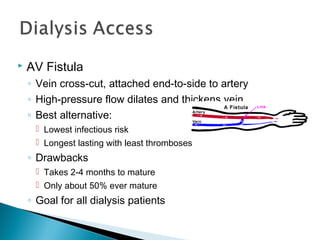
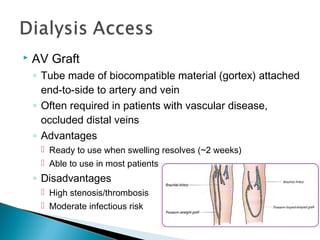
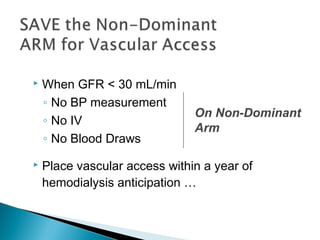
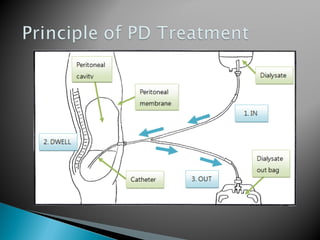
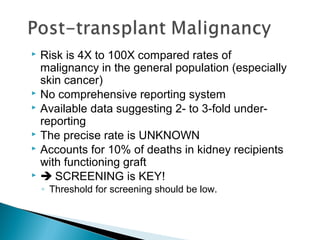
The document discusses renal replacement therapy options for patients with end-stage renal disease, including hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and kidney transplantation. It provides details on each treatment modality and emphasizes the importance of early referral to a nephrologist to allow time for vascular access placement, transplant evaluation, and patient education. The best vascular access for hemodialysis is an arteriovenous fistula due to its lower risk of infection and greater longevity. All statements regarding kidney transplantation timing and criteria are correct. Screening for malignancies is important in transplant recipients due to higher cancer risks with immunosuppression.
















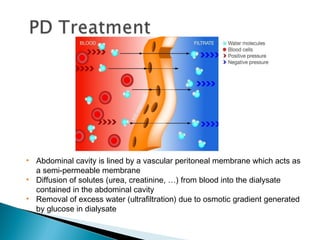
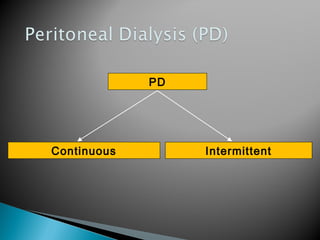
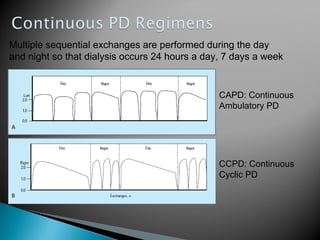
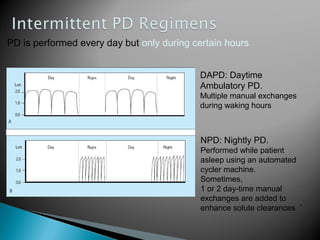








![ Kidney transplantation is the most cost-effective
modality of renal replacement
Transplanted patients have a longer life and better
quality of life
Early transplantation (before [pre-emptive] or within 1
year of dialysis initiation) yields the best results
Living donor kidney outcomes are superior to
deceased donor kidney outcomes
Early transplantation is more likely to occur in
patients that are referred early to nephrologists
Refer for transplant evaluation when eGFR < 20
mL/min/1.73m2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hemodialysismaagementandcare-170118021103/85/Renal-Replacement-therapy-52-320.jpg)