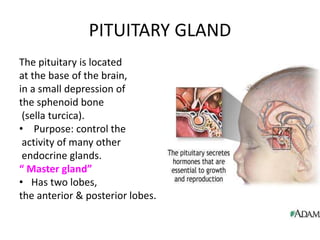
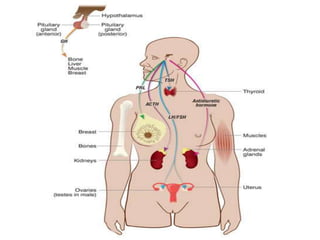
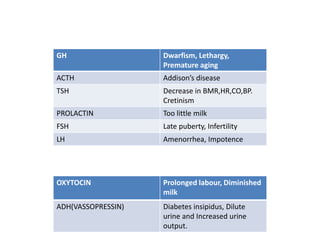
1) Hypopituitarism occurs when the pituitary gland loses its ability to produce hormones, resulting in deficiencies of growth hormone, ACTH, TSH, prolactin, FSH, LH, oxytocin, and antidiuretic hormone.
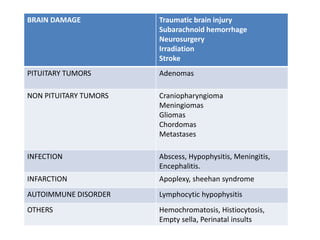
2) It can be congenital due to genetic mutations or perinatal injuries, or acquired from brain damage, tumors, infections, or other causes that damage the pituitary gland.
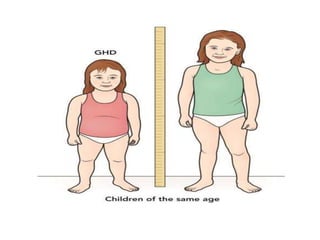
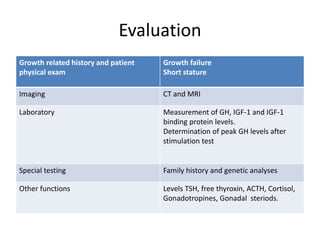
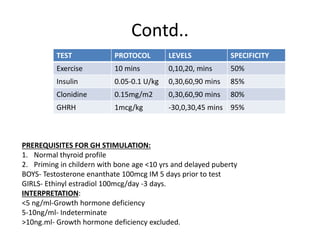
3) Symptoms depend on which hormones are deficient but may include growth failure, hypoglycemia, delayed puberty, electrolyte imbalances, and diabetes insipidus. Treatment involves hormone replacement therapy and monitoring hormone levels.