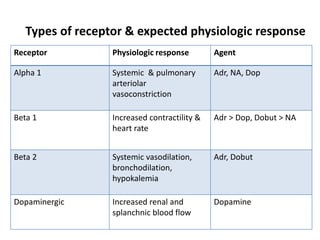
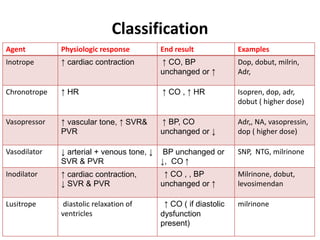
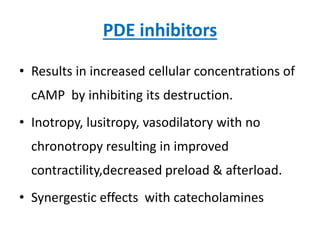
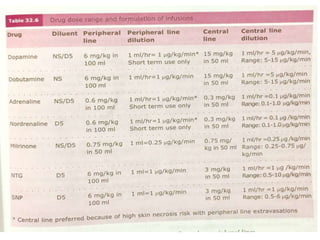
This document discusses various inotropes and vasoactive agents used to support hemodynamics. It describes the classification of agents as inotropes, chronotropes, vasopressors, or vasodilators. Key agents covered include dopamine, dobutamine, adrenaline, noradrenaline, milrinone, vasopressin, nitroglycerine, and sodium nitroprusside. For each agent, the document discusses receptor physiology, hemodynamic effects, indications, dosing, side effects, and monitoring considerations. It concludes with describing a vasoactive inotrope score used to quantify cardiovascular support.