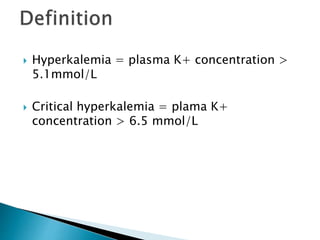
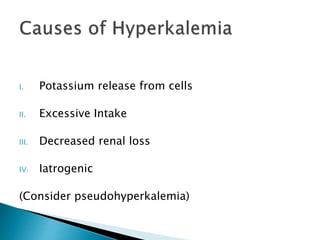
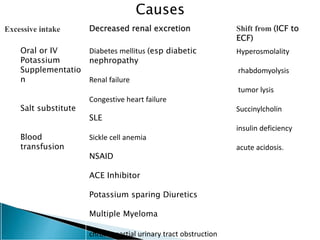
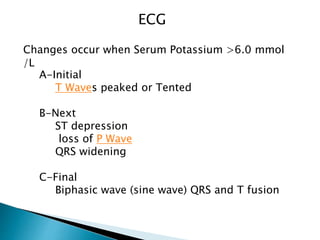
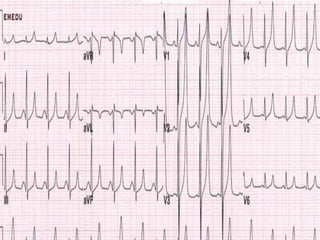
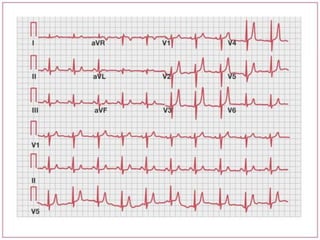
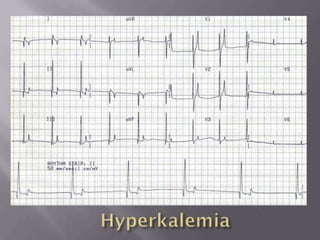
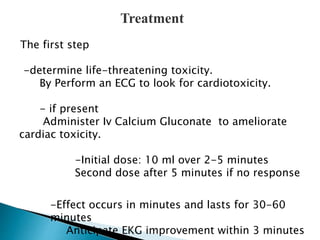
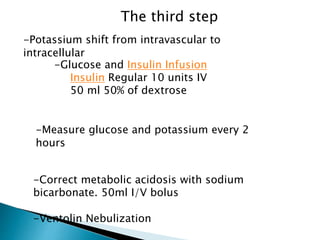
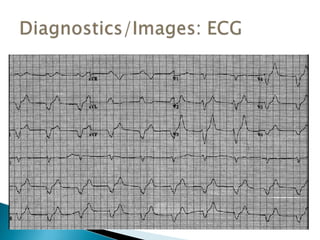
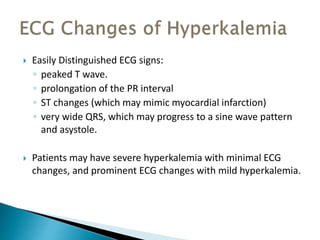
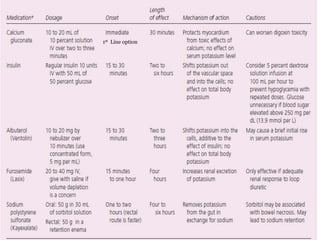
This document discusses hyperkalemia, including its definition, causes, clinical manifestations, and treatment. It provides details on potassium regulation and homeostasis in the body. The main causes of hyperkalemia are a shift of potassium from intracellular to extracellular space, excessive potassium intake, and decreased renal potassium excretion. Symptoms range from weakness to cardiac arrhythmias. Treatment involves calcium gluconate for cardiac issues, insulin with glucose to shift potassium intracellularly, sodium bicarbonate for acidosis, and diuretics or dialysis to increase renal excretion.