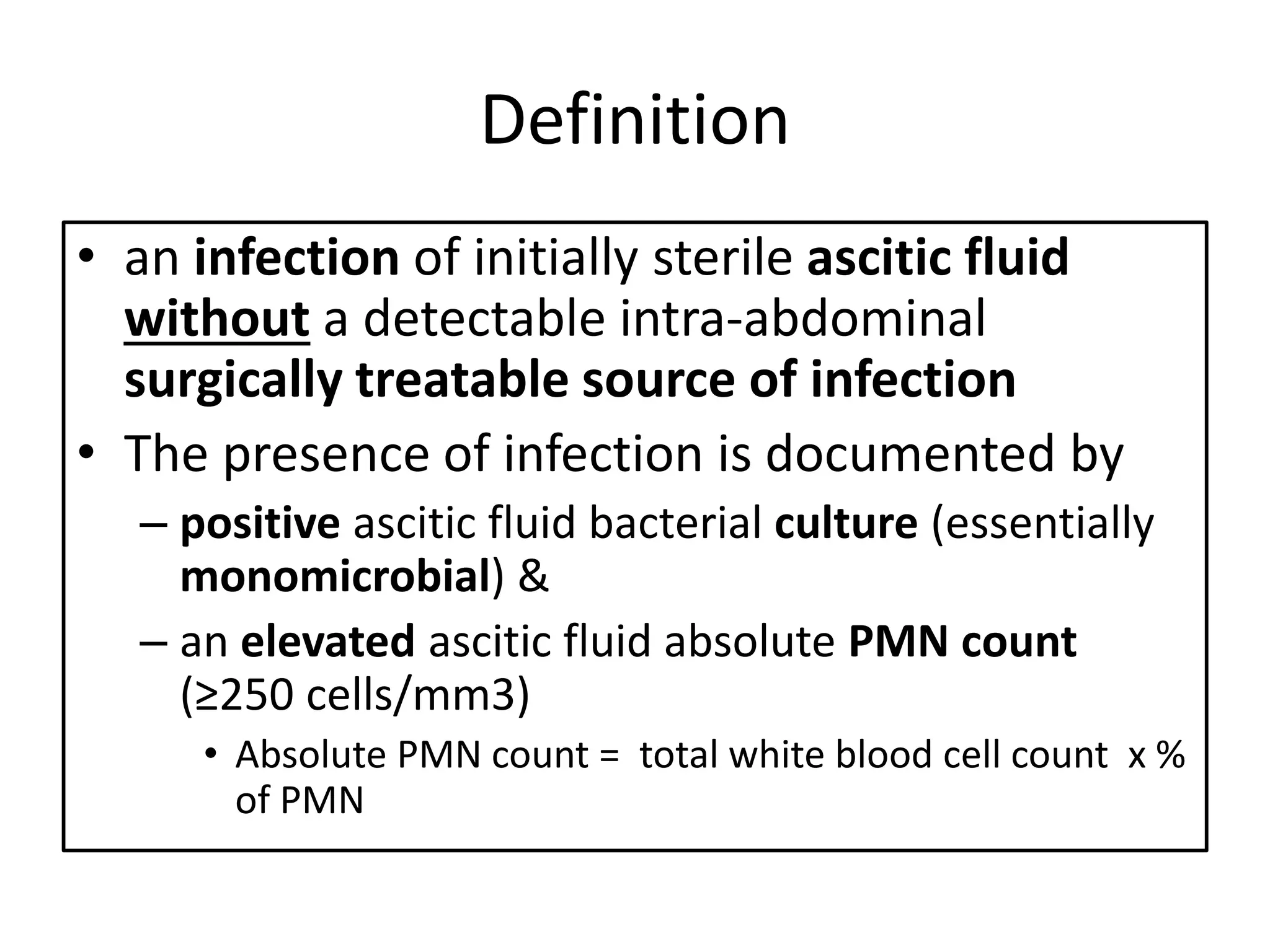
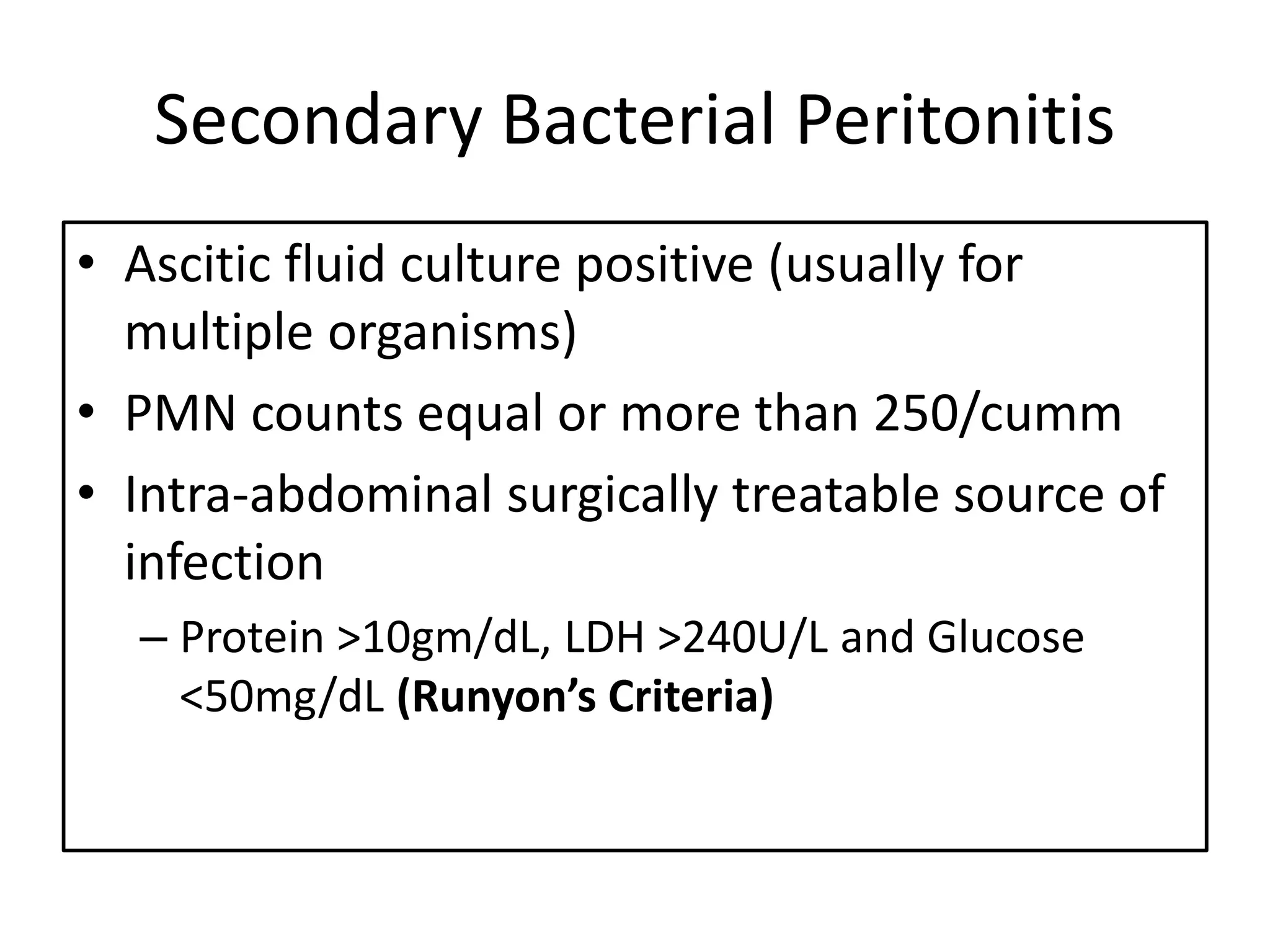
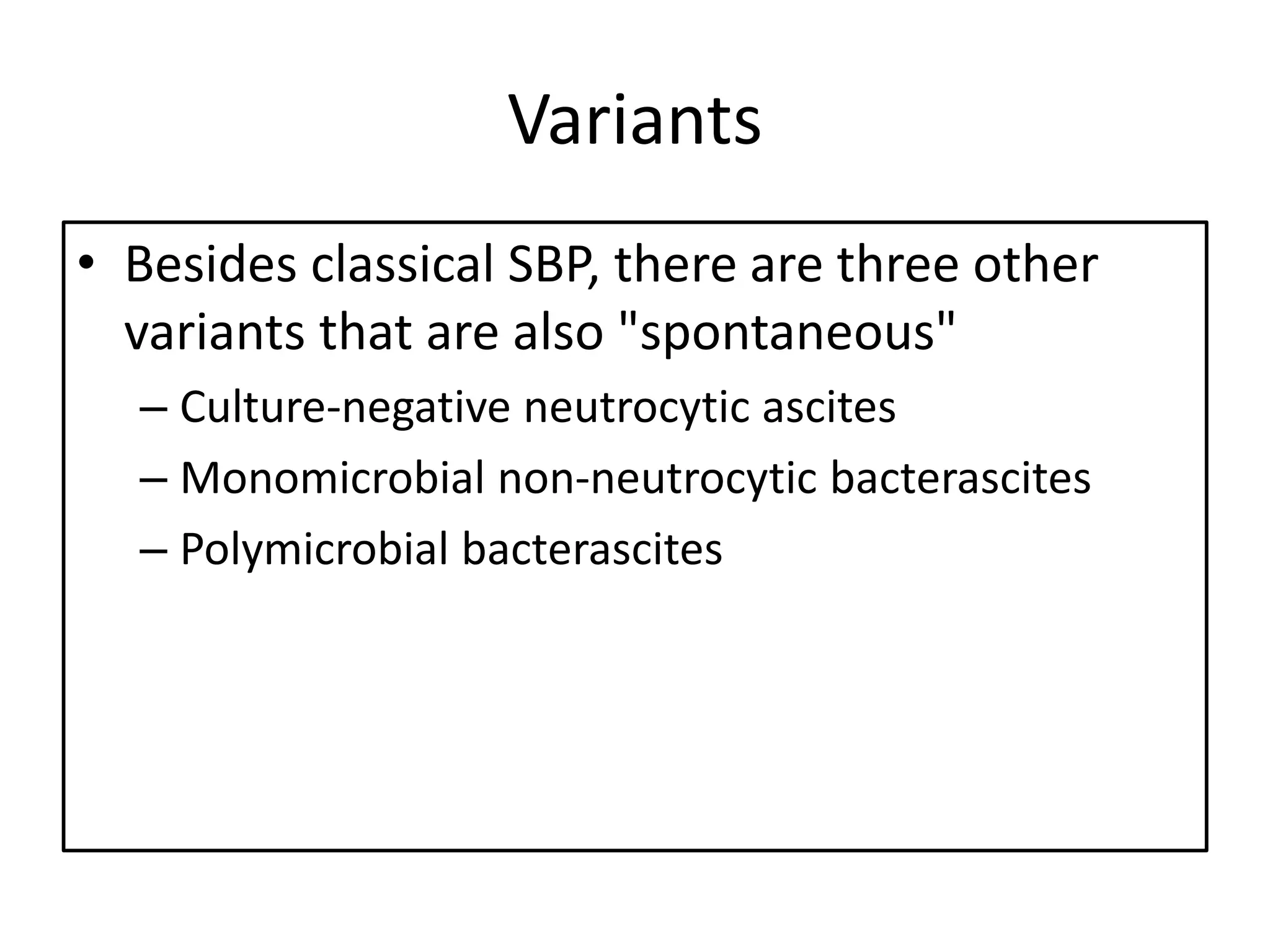
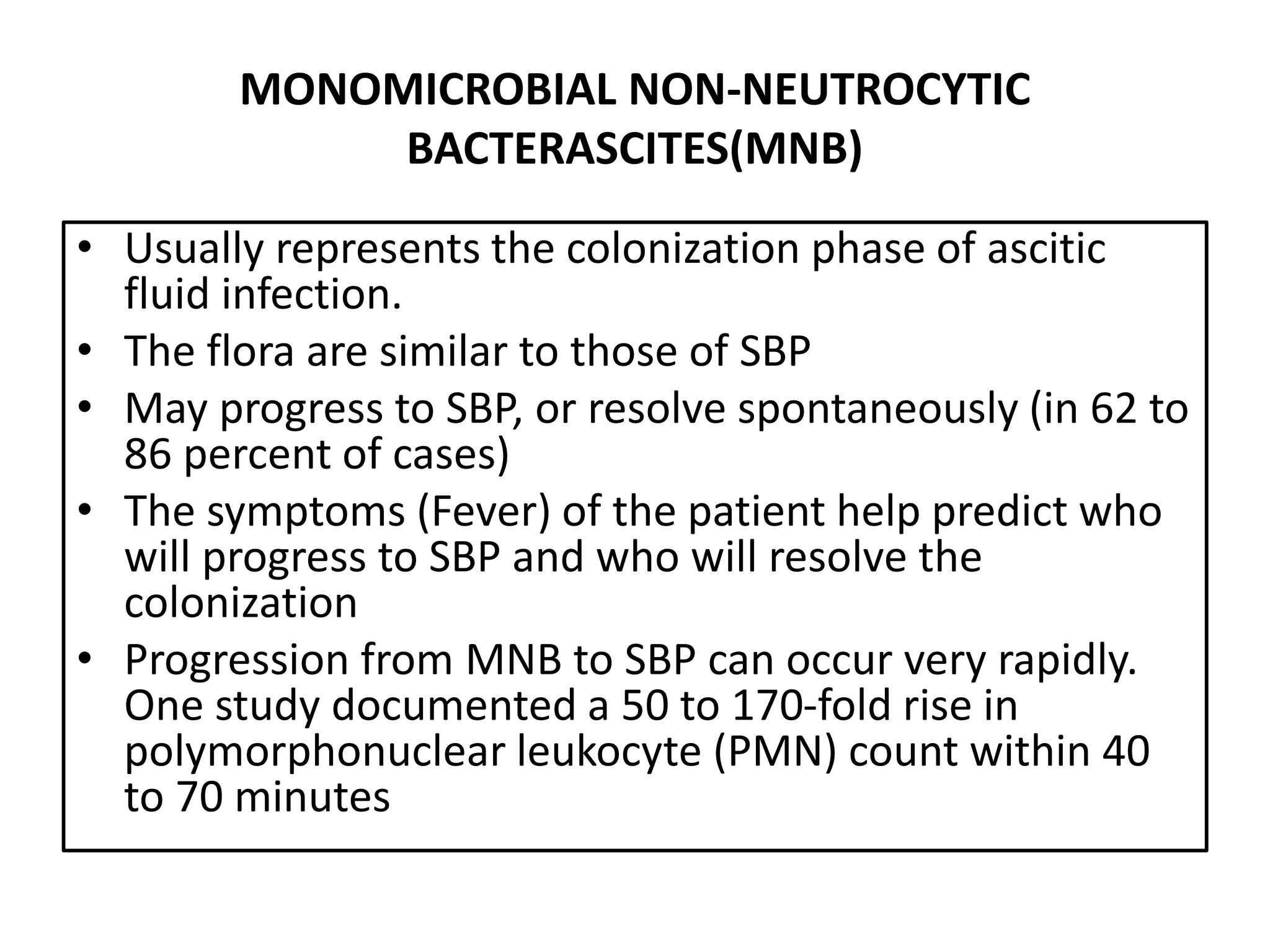
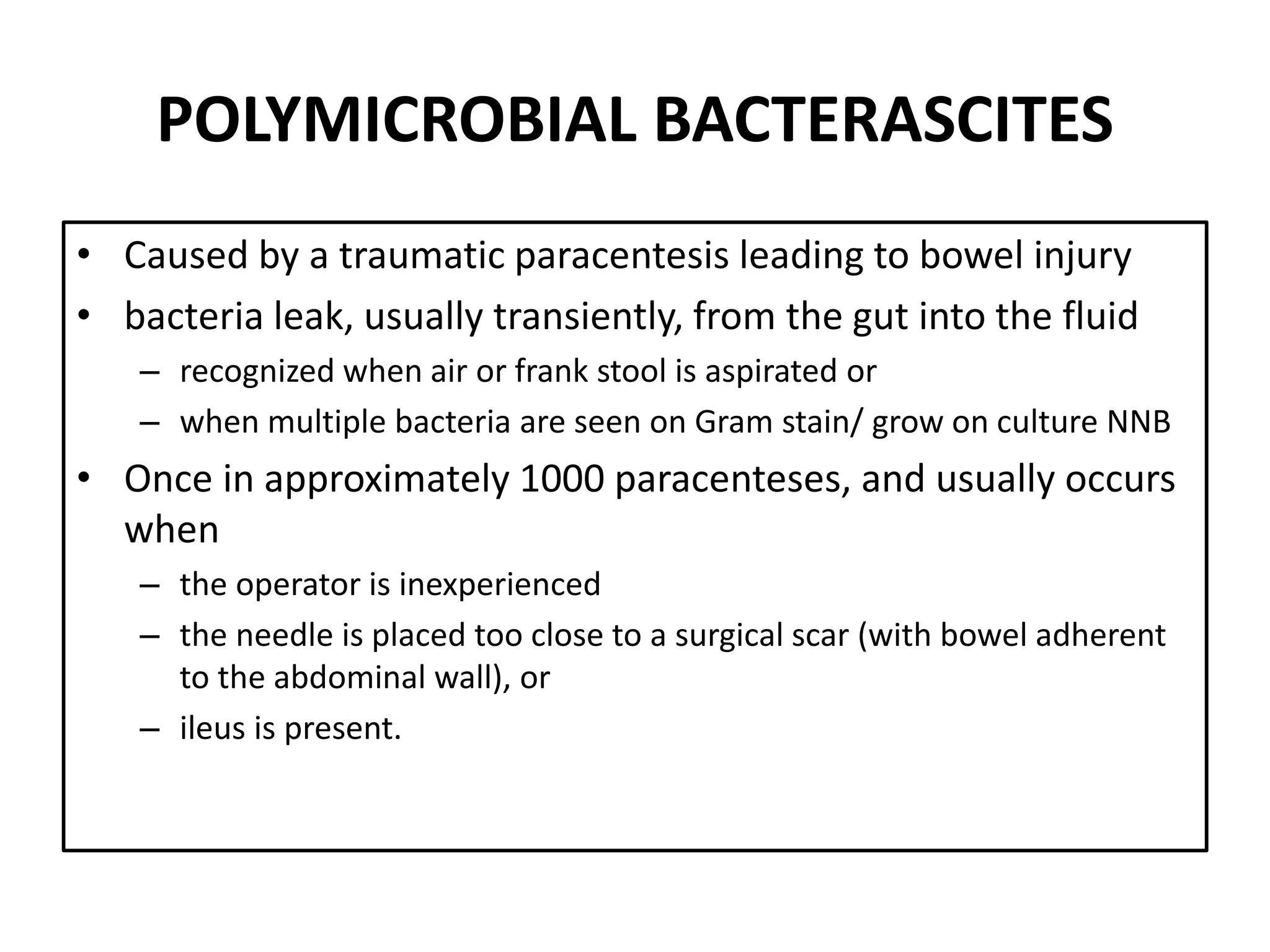
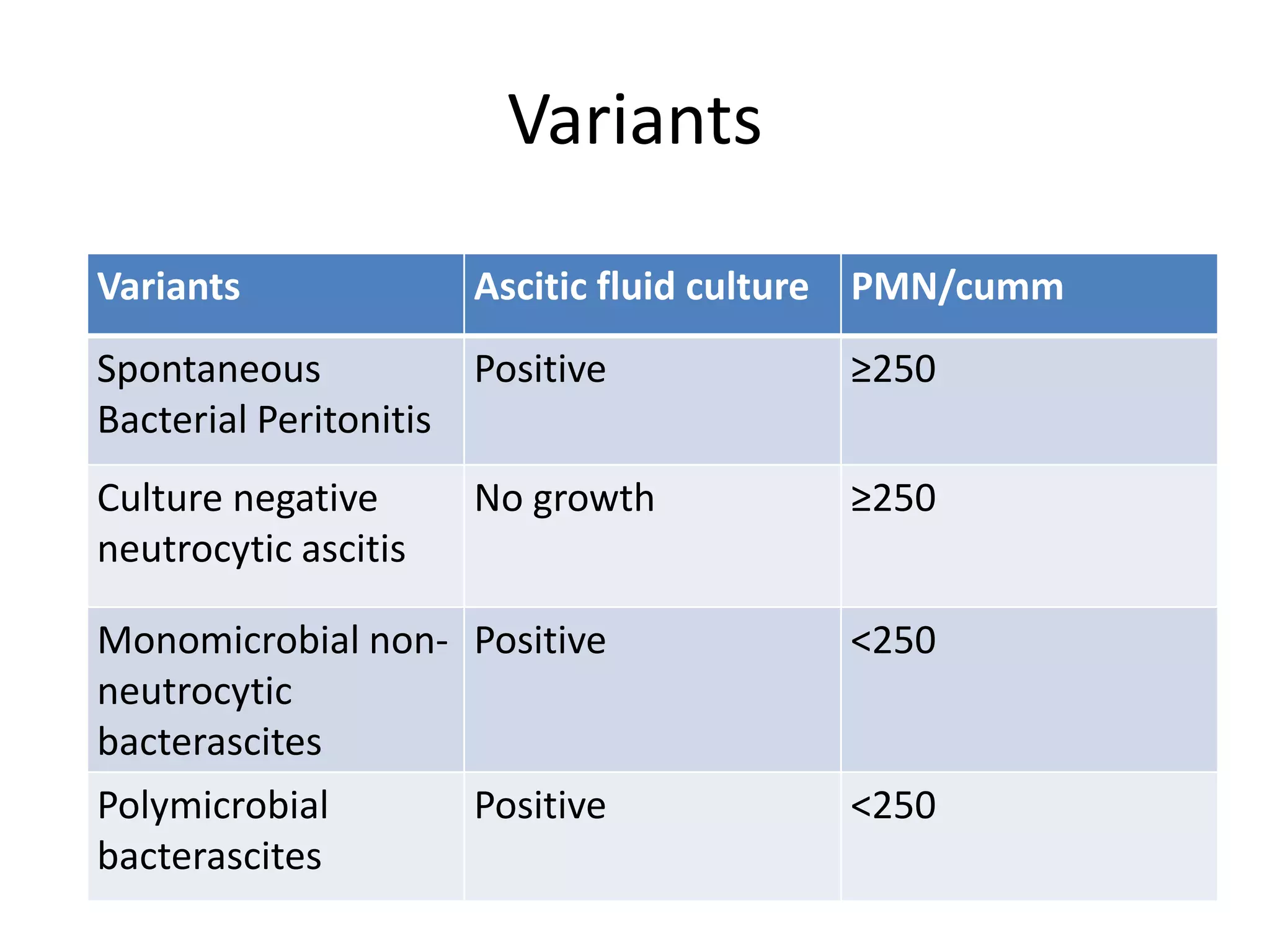
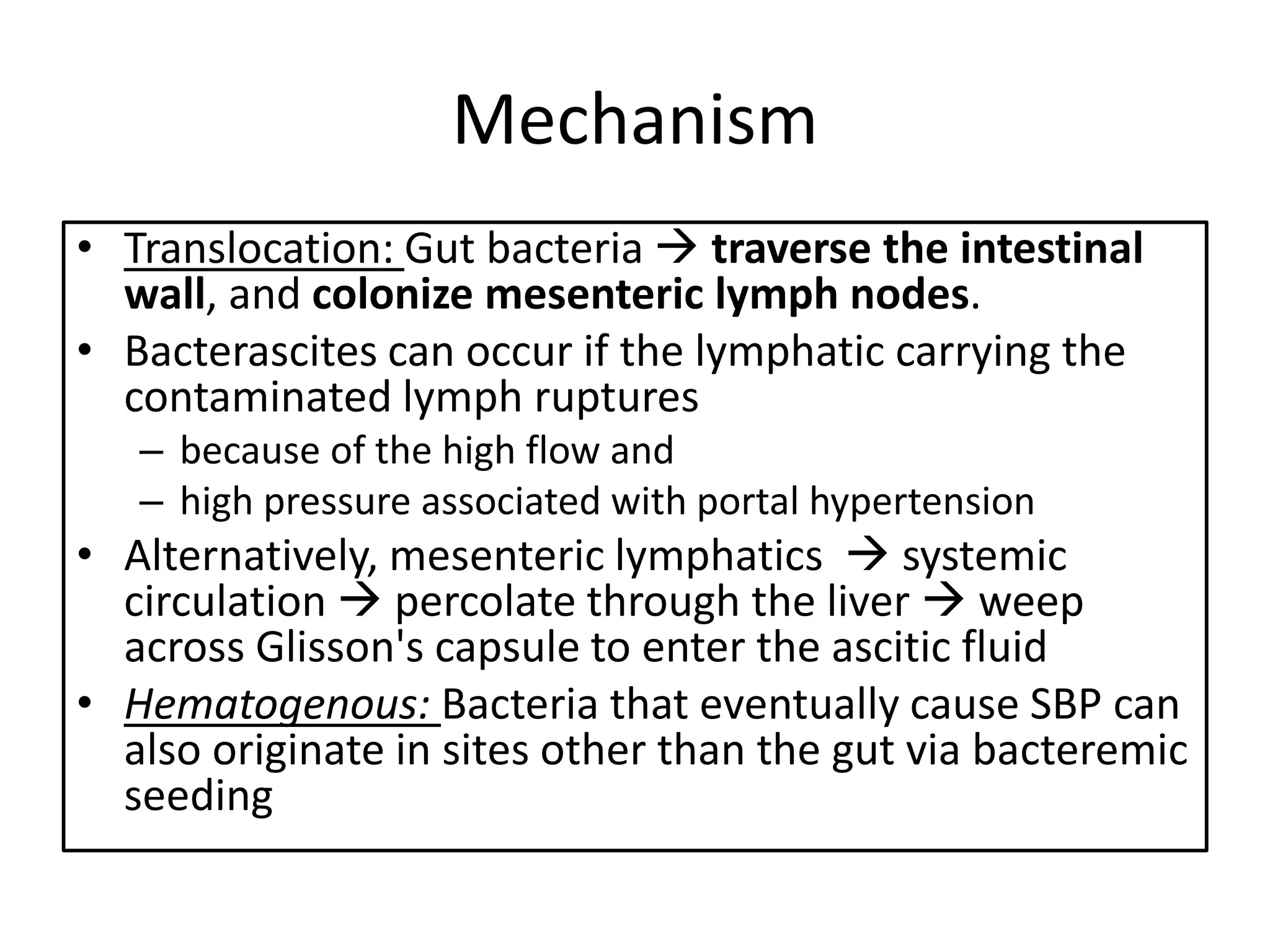
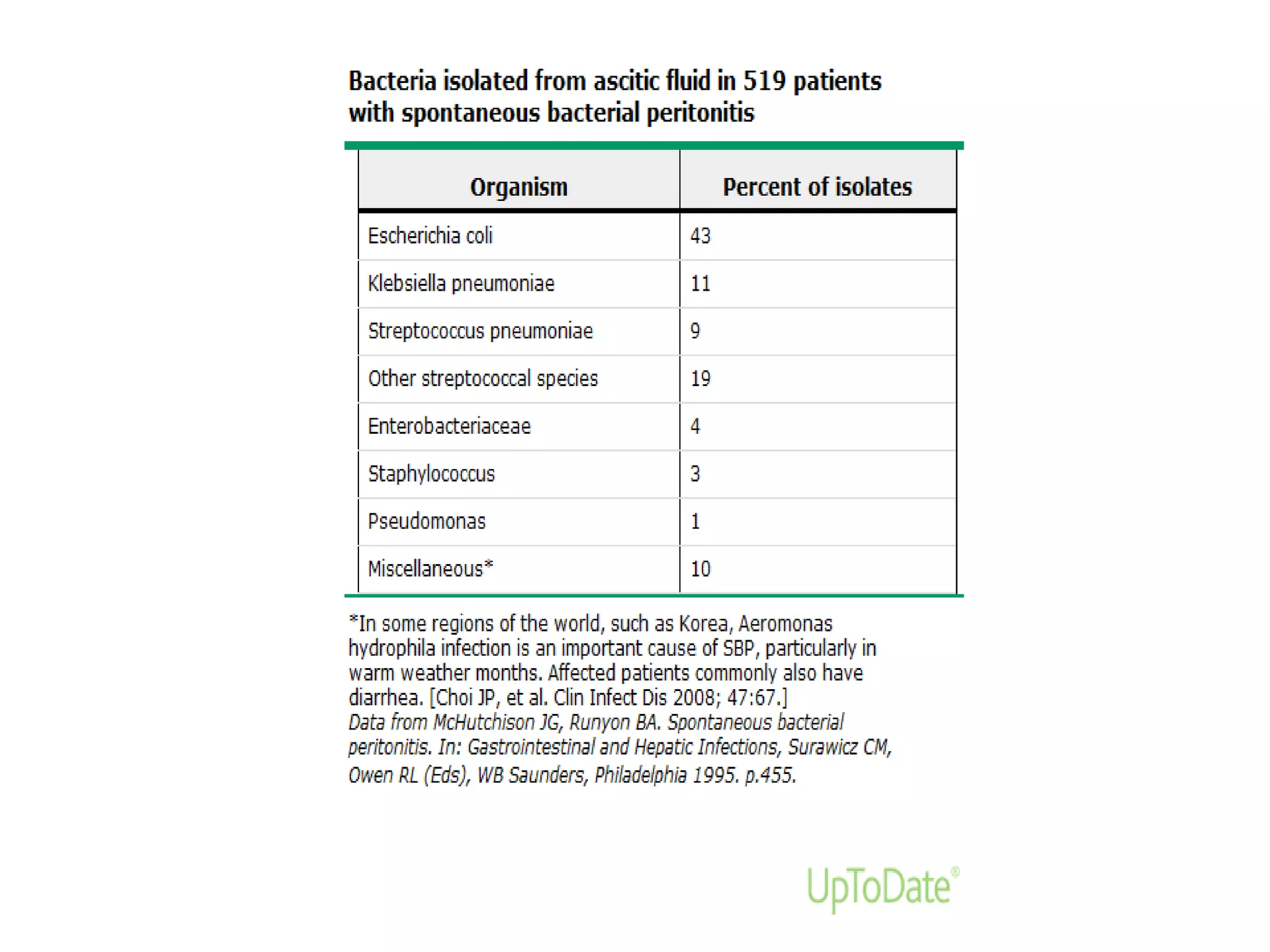
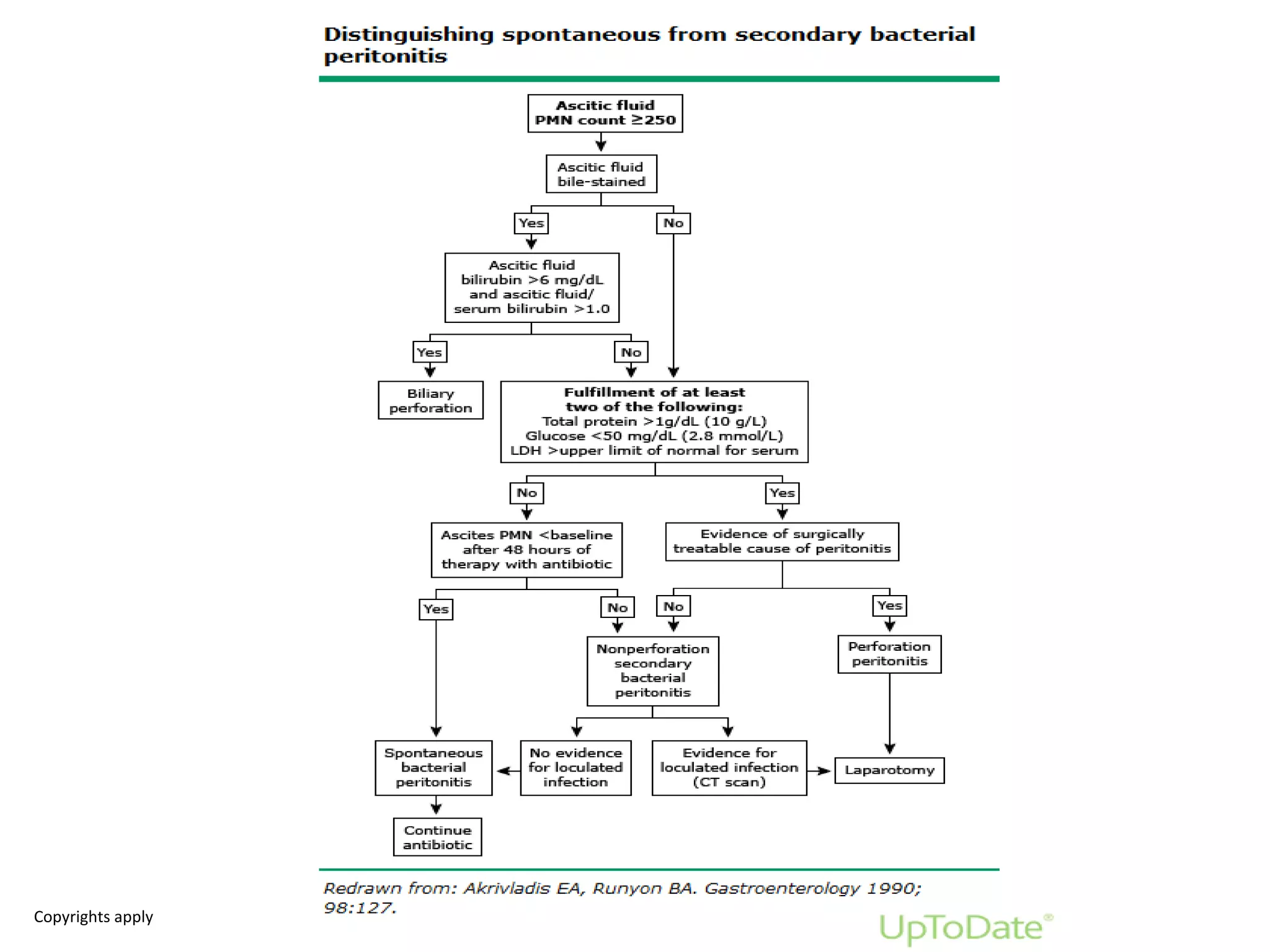
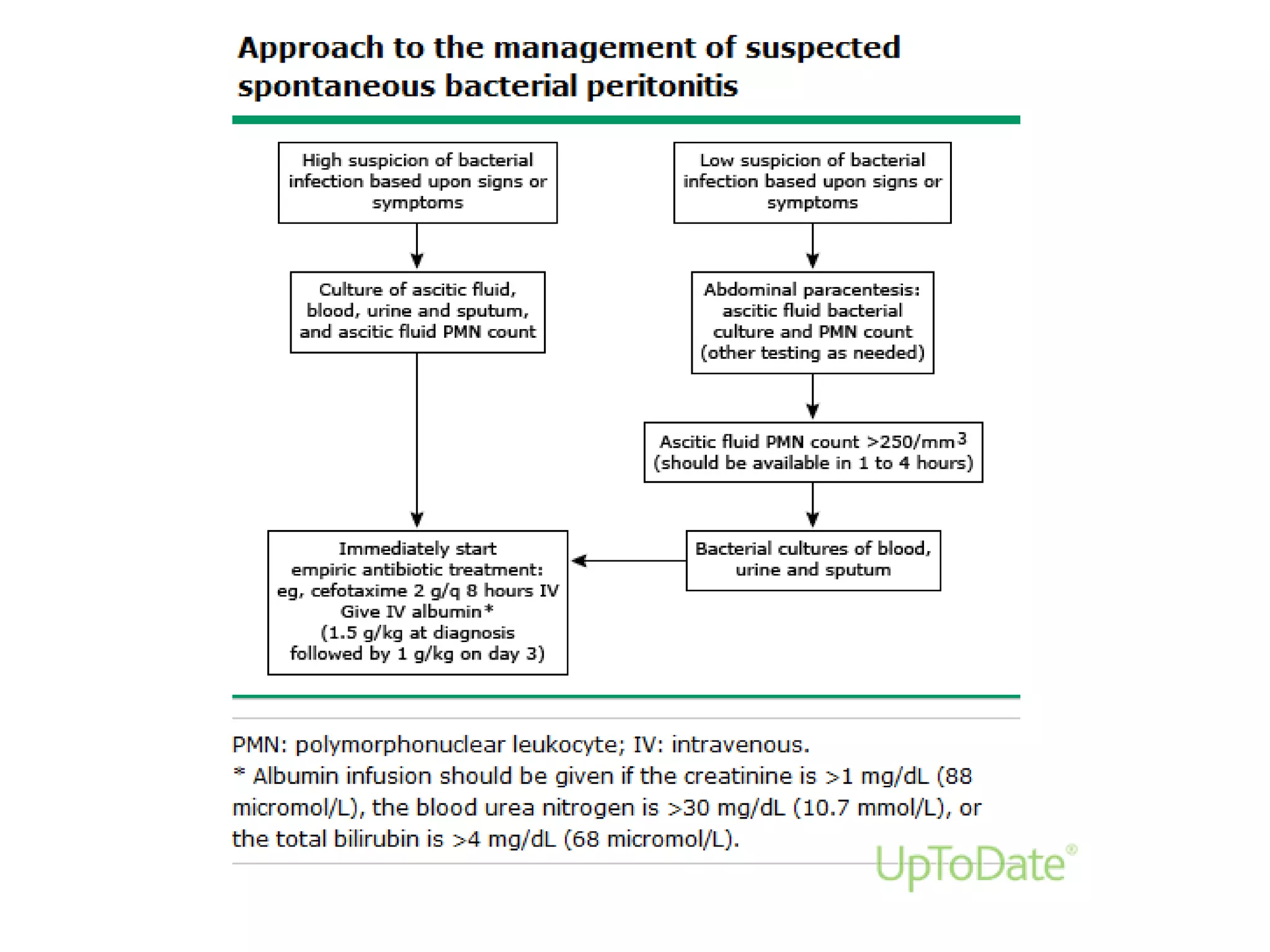
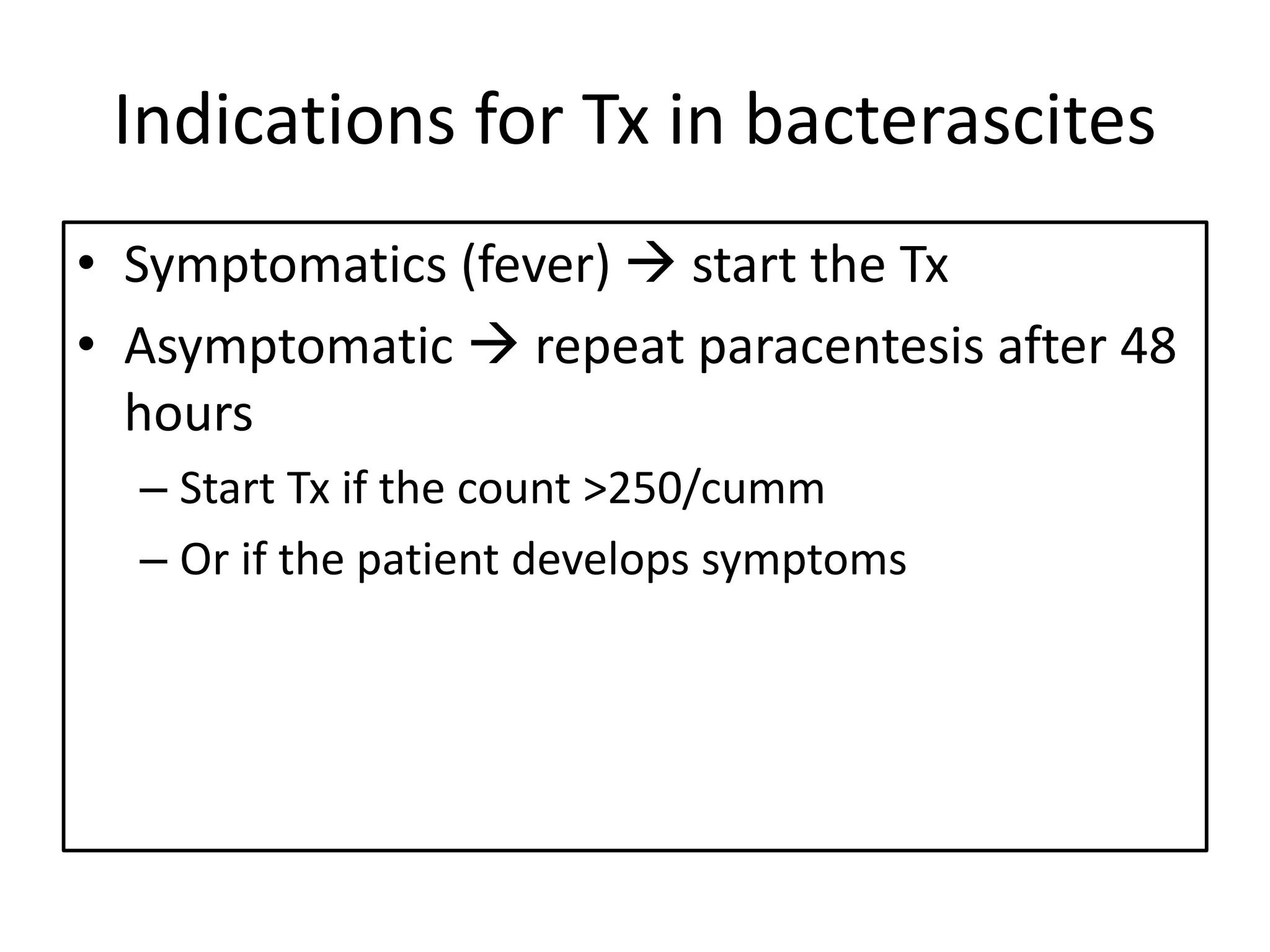
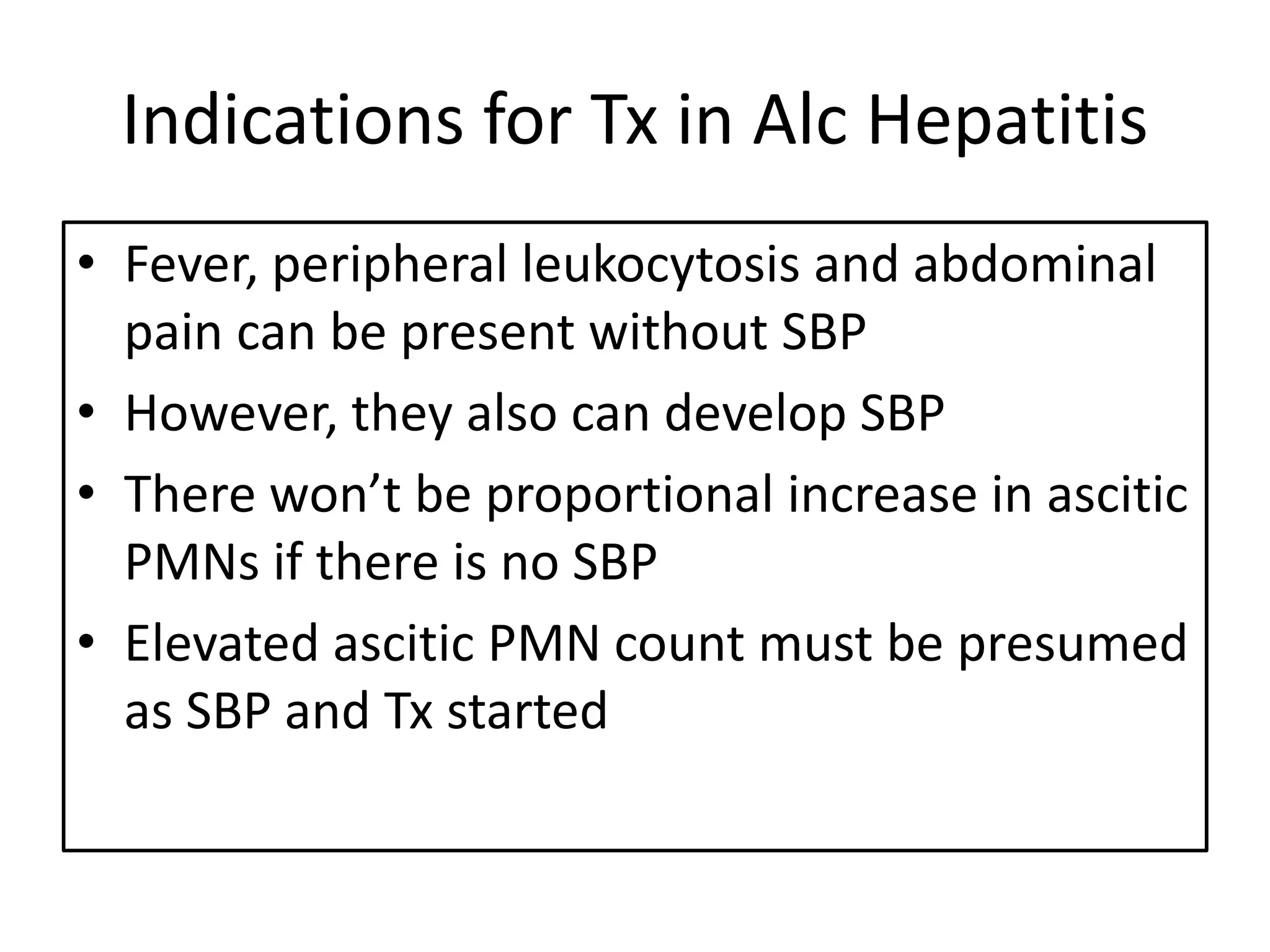
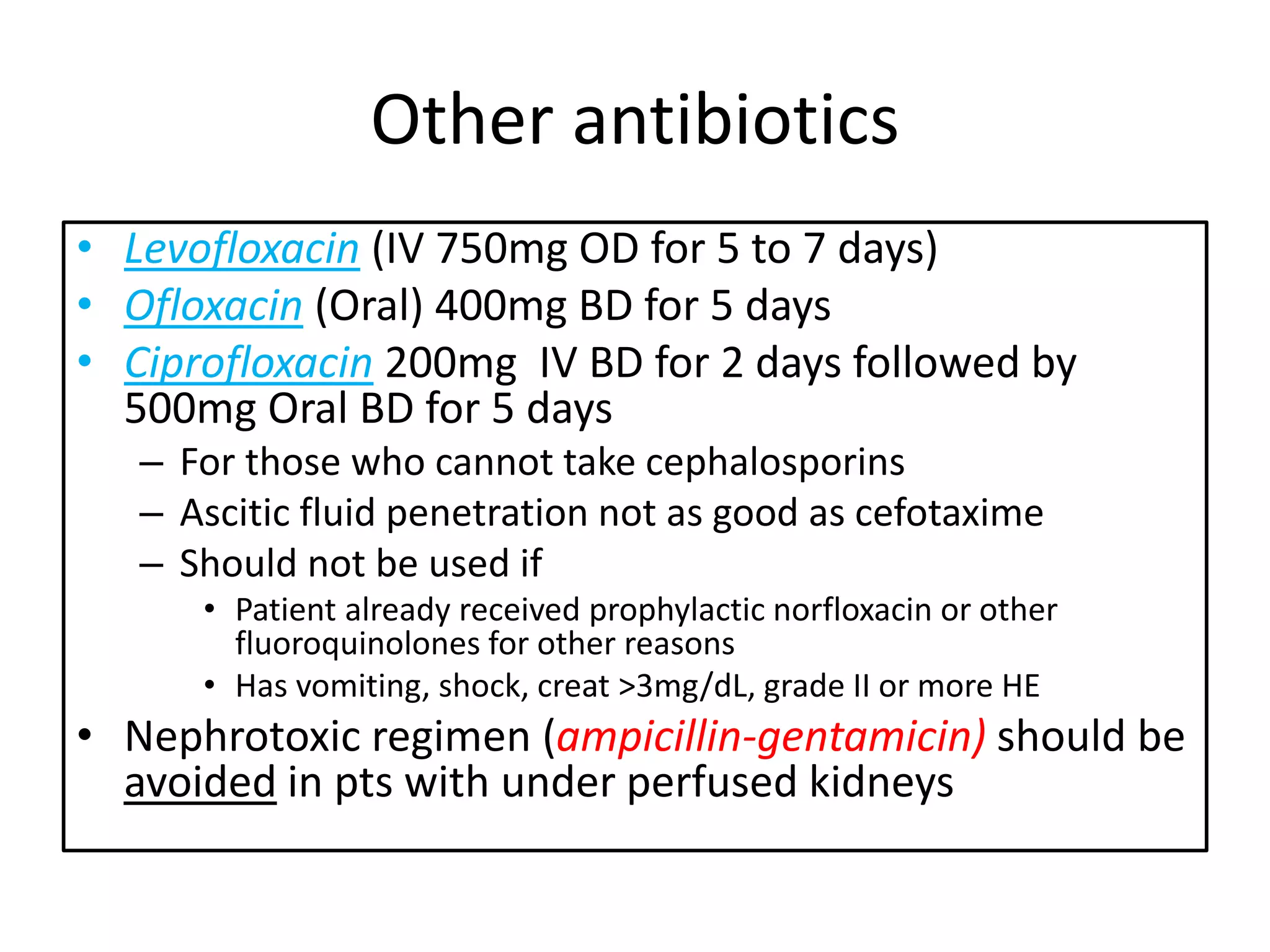
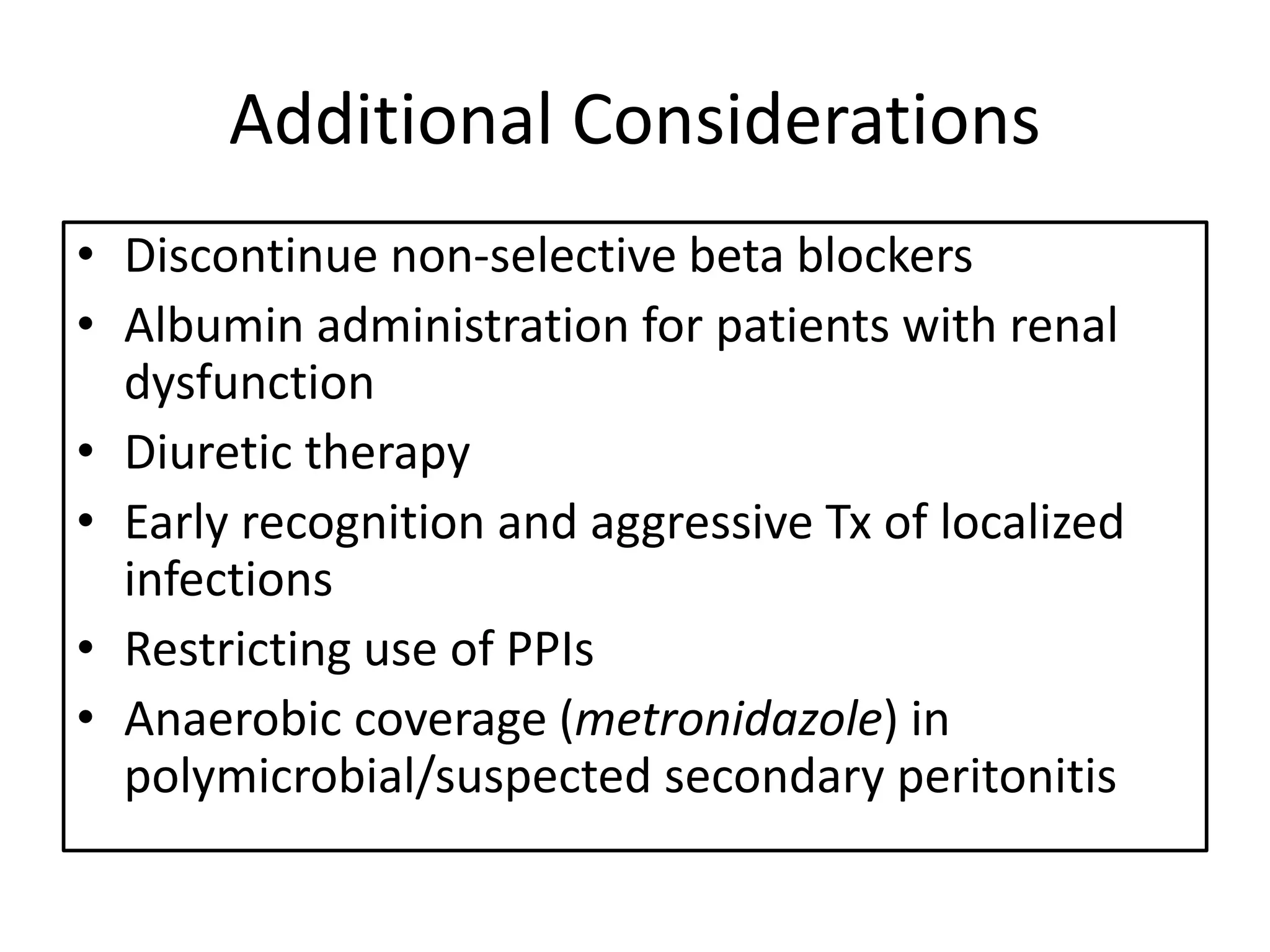
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) is an infection of ascitic fluid in people with liver cirrhosis and ascites. It is defined by a positive ascitic fluid culture with ≥250 PMN cells/mm3 in the absence of an intra-abdominal source. Risk factors include low ascitic fluid protein and prior SBP. Translocation of gut bacteria through the intestinal wall and lymphatics is a main mechanism. Treatment involves antibiotics like cefotaxime for 5-7 days. Prognosis depends on clinical stability, though prophylaxis may be considered for high risk patients.




















![References
• UpToDate, Bruce A Runyon et al. 2018. Pathogenesis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.
[ONLINE] Available at: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/pathogenesis-of-spontaneous-
bacterial-
peritonitis?search=spontaneous%20bacterial%20peritonitis&source=search_result&selected
Title=4~69&usage_type=default&display_rank=4. [Accessed 30 June 2018].
• L., D., 2016. Harrisons Manual of Medicine, 19th Edition. McGraw-Hill Education / Medical.
• UpToDate, Bruce A Runyon et al. 2018. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis variants. [ONLINE]
Available at: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/spontaneous-bacterial-peritonitis-
variants?search=spontaneous%20bacterial%20peritonitis&source=search_result&selectedTitl
e=5~69&usage_type=default&display_rank=5. [Accessed 30 June 2018].
• UpToDate, Bruce A Runyon et al. 2018. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in adults: Clinical
manifestations. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/spontaneous-
bacterial-peritonitis-in-adults-clinical-
manifestations?search=spontaneous%20bacterial%20peritonitis&source=search_result&sele
ctedTitle=3~69&usage_type=default&display_rank=3. [Accessed 30 June 2018].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spontaneousbacterialperitonitissbp-190213163351/75/Spontaneous-Bacterial-Peritonitis-SBP-35-2048.jpg)
![References
• UpToDate, Bruce A Runyon et al. 2018. Spontaneous bacterial
peritonitis in adults: Diagnosis. [ONLINE] Available
at: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/spontaneous-bacterial-
peritonitis-in-adults-
diagnosis?search=spontaneous%20bacterial%20peritonitis&source
=search_result&selectedTitle=2~69&usage_type=default&display_r
ank=2. [Accessed 30 June 2018].
• UpToDate, Bruce A Runyon et al. 2018. Spontaneous bacterial
peritonitis in adults: Treatment and prophylaxis. [ONLINE] Available
at: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/spontaneous-bacterial-
peritonitis-in-adults-treatment-and-
prophylaxis?search=spontaneous%20bacterial%20peritonitis&sourc
e=search_result&selectedTitle=1~69&usage_type=default&display_
rank=1. [Accessed 30 June 2018].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spontaneousbacterialperitonitissbp-190213163351/75/Spontaneous-Bacterial-Peritonitis-SBP-36-2048.jpg)
