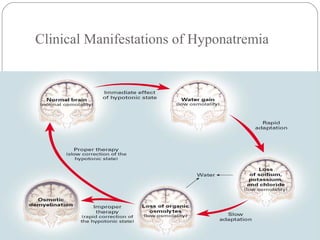
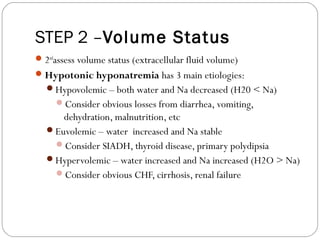
Dr. Arun Karmakar presented on hyponatremia. Hyponatremia is defined as a serum sodium below 135 mmol/L and is the most common electrolyte disorder. It is clinically important because acute severe hyponatremia can cause morbidity and mortality, and outcomes are worse in hyponatremic patients with underlying diseases. Hyponatremia can be hypovolemic, euvolemic, or hypervolemic depending on water and sodium levels. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of hyponatremia, with aggressive correction for symptomatic cases and slower correction for chronic cases to avoid osmotic demyelination syndrome.

![Introduction
Defined as a serum [Na] below 135 mmol/L.
Most common disorder of electrolytes encountered in
clinical practice, occurring in 22% of hospitalized
patients.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyponatremiappt-170315180214/85/Hyponatremia-ppt-final-2-320.jpg)




![Characterized by hyponatremia with ECF volume
contraction (provides the nonosmotic stimulus for
vasopressin release).
Urine [Na+
] above 20 mmol/l, and high serum K+
.
Mineralocorticoid (Aldosterone) Deficiency](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyponatremiappt-170315180214/85/Hyponatremia-ppt-final-9-320.jpg)





















![Goal:
Minimum correction of serum [Na] by 4-8 mmol/L per
day, with a lower goal of 4-6 mmol/L per day if the risk of
ODS is high.
Limits not to exceed:
• 8-10 mmol/L in any 24-hour period.
Treatment of chronic hyponatremia(Avoiding
ODS)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyponatremiappt-170315180214/85/Hyponatremia-ppt-final-34-320.jpg)


![ Glucocorticoid Deficiency-glucocorticoid replacement
at either maintenance or stress doses, depending on
the degree of intercurrent illness.
Severe Hypothyroidism-thyroid hormone replacement at
standard weight-based doses; several days may be needed
to normalize the serum [Na].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyponatremiappt-170315180214/85/Hyponatremia-ppt-final-37-320.jpg)
![Heart Failure-for patients with mild to moderate
symptoms, begin with fluid restriction (1 L/d total) and, if
signs of volume overload are present, administer loop
diuretics.
If the serum [Na] does not correct to the desired level, lift the
fluid restriction and start either conivaptan or tolvaptan.
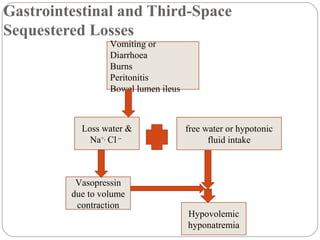
Treatment of hypovolemic hyponatremia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyponatremiappt-170315180214/85/Hyponatremia-ppt-final-38-320.jpg)
![
Cirrhosis-Severe daily fluid restriction,
Vaptans an alternative choice if fluid restriction has failed to maintain
a serum [Na] 130 mmol/L; however, tolvaptan use should be
restricted to cases where the potential clinical benefit outweighs the
risk of worsened liver function, such as in patients with end-stage
liver disease and severe hyponatremia who are awaiting imminent
liver transplantation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyponatremiappt-170315180214/85/Hyponatremia-ppt-final-39-320.jpg)







![Starting serum [Na] ≥120 mmol/L: Intervention unnecessary.
Starting serum [Na] <120 mmol/L:
Withhold the next dose of vaptan if the correction is >8
mmol/L;
Consider therapeutic re-lowering of serum [Na] if
correction exceeds therapeutic limits;
Consider administration of high-dose glucocorticoids (eg,
dexamethasone, 4 mg every 6 hrs) for 24-48hrs following
the excessive correction.
Managing excessive correction of chronic hyponatremia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyponatremiappt-170315180214/85/Hyponatremia-ppt-final-47-320.jpg)
![Re-lowering serum [Na]:
Administer desmopressin to prevent further water losses:
2-4 mg every 8 hours parenterally;
Replace water orally or as 5% dextrose in water
intravenously: 3 mL/kg/h;
Recheck serum [Na] hourly and continue therapy infusion
until serum [Na] is reduced to goal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyponatremiappt-170315180214/85/Hyponatremia-ppt-final-48-320.jpg)

