Portal-systemic encephalopathy is a brain disorder caused by liver dysfunction that allows toxins to reach the brain. It is characterized by alterations in mental status, neurological abnormalities, and distinctive EEG changes. The main underlying mechanism involves increased levels of ammonia in the bloodstream from the gut that are normally processed by the liver. Treatment focuses on reducing ammonia production in the colon through medications like lactulose and restricting protein intake. Prognosis depends on the underlying liver disease and can range from fully treatable acute episodes to chronic and potentially fatal cases.




.
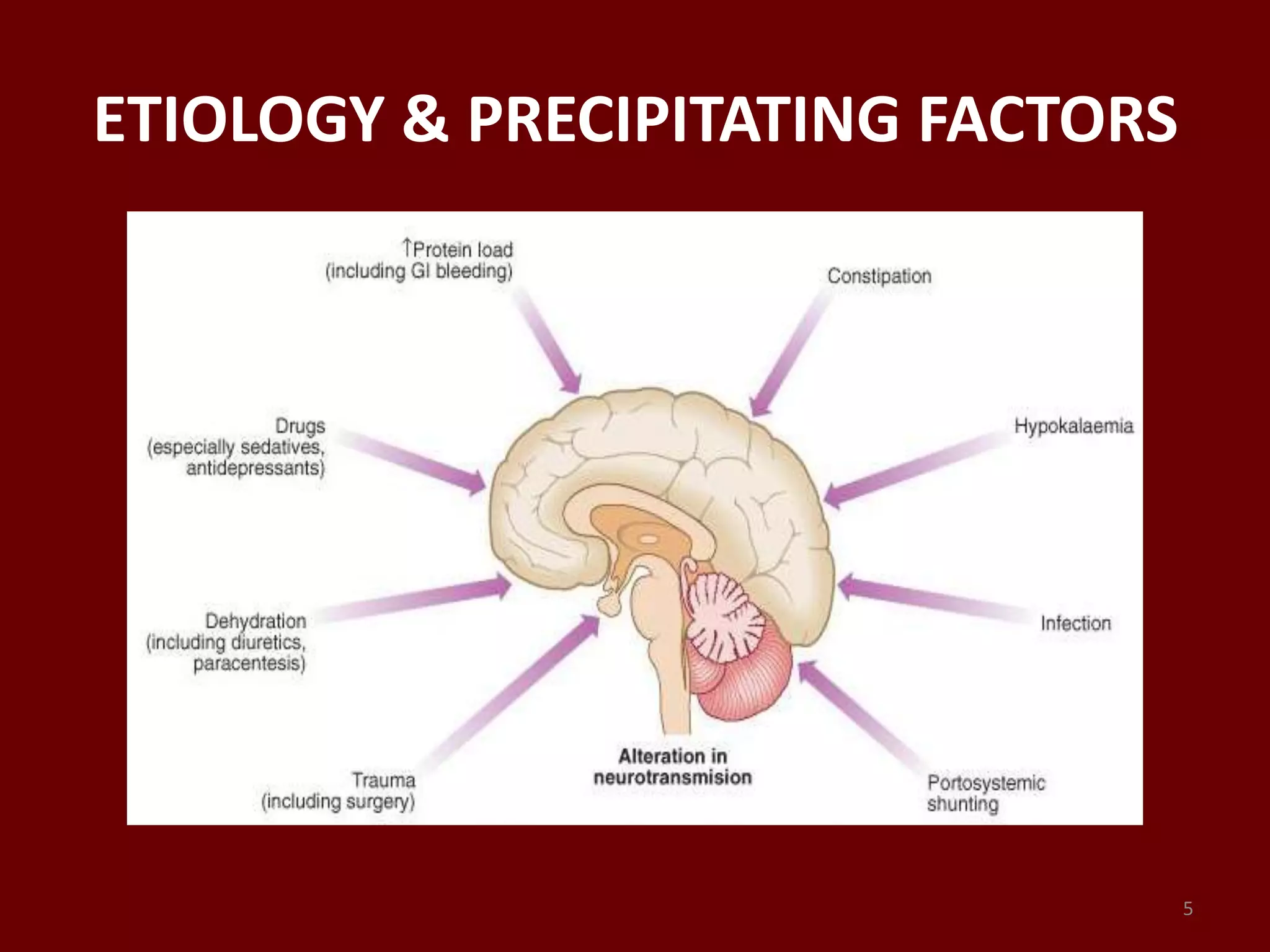
• Excessive nitrogen load- excess protein consumption, gastro-
intestinal bleeding, renal failure, constipation.
• Electrolyte or metabolic disturbance-hypokalaemia,
hyponatremia, alkalosis, dehydration, excess vomiting.
• Infections- pneumonia, UTI, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.
• Unknown- 20-30%
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hepaticencephalopathy-130711235430-phpapp02/75/Hepatic-encephalopathy-7-2048.jpg)

















![35
Positron emission tomography
(PET) of an alcoholic cirrhotic
patient with mild hepatic
encephalopathy. The blood flow
through the brain (i.e., cerebral
blood flow [CBF]) differs only
minimally between the two
subjects. However, the cerebral
metabolic rate for ammonia
(CMRA) and the permeability–
surface area product (PS)—a
measure of the extent to which
ammonia can pass the blood–
brain barrier and enter the
brain—are significantly
increased in the alcoholic
patient, as indicated by the
wider distribution and
enhanced brightness of the light](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hepaticencephalopathy-130711235430-phpapp02/75/Hepatic-encephalopathy-35-2048.jpg)