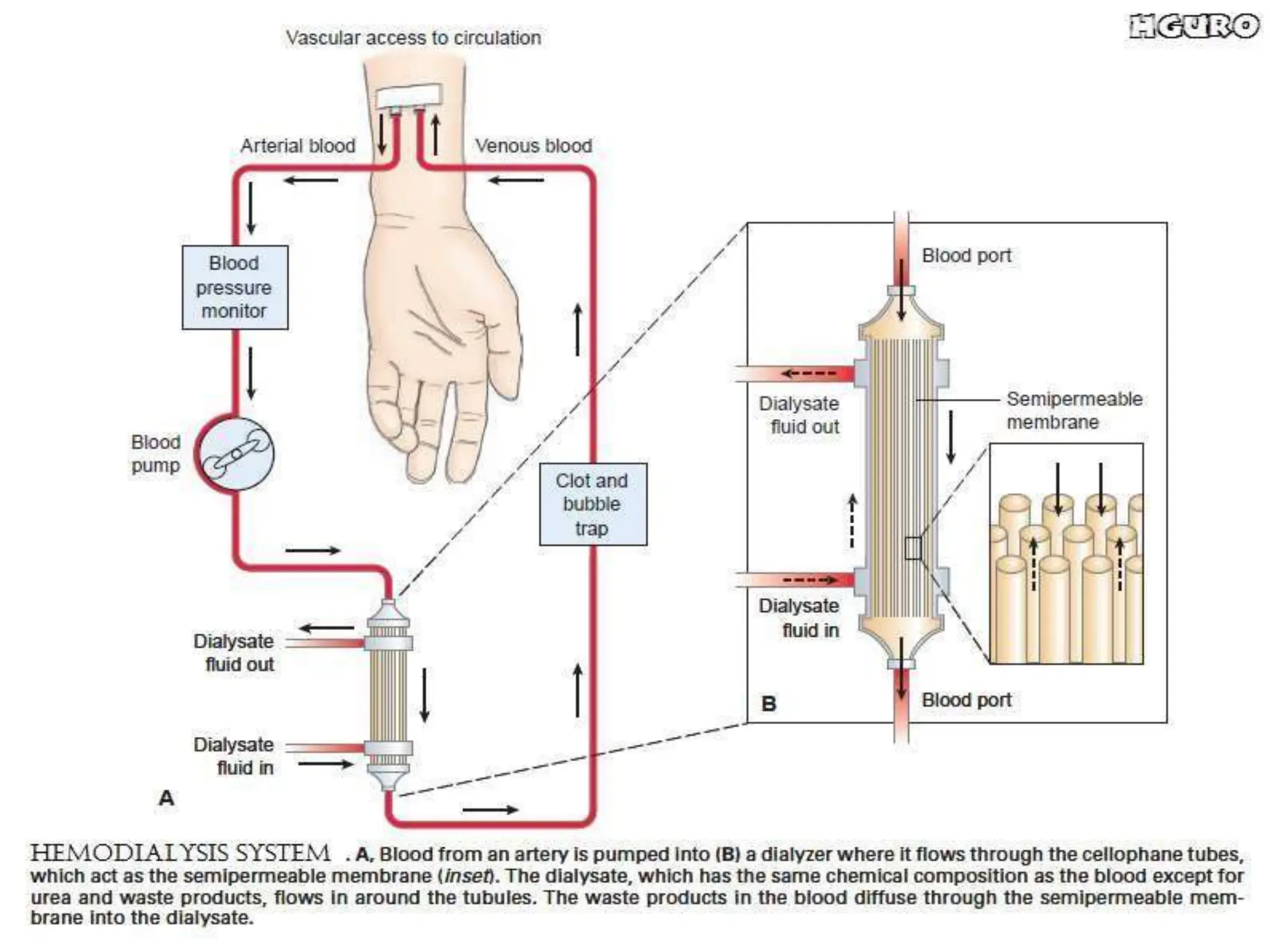
Dialysis is a procedure that replicates kidney function by allowing substances to move from the blood through a semipermeable membrane into a dialysis solution, with the primary purpose of maintaining fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance while removing toxins. There are two main types of dialysis: hemodialysis, which uses an artificial kidney to cleanse the blood, and peritoneal dialysis, which utilizes the abdominal lining for filtration. Both methods involve specific procedures, potential complications, and require careful monitoring and patient education to manage treatment effectively.