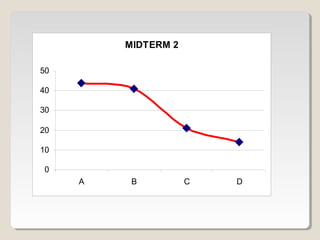
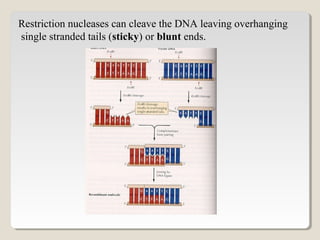
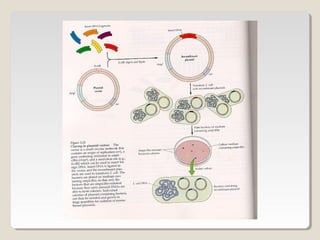
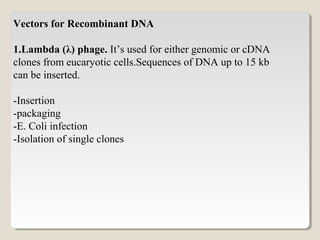
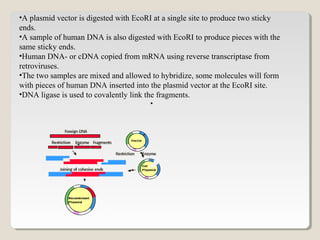
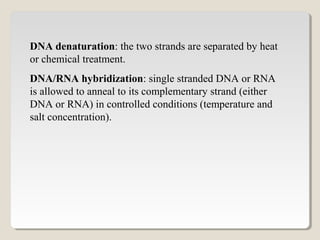
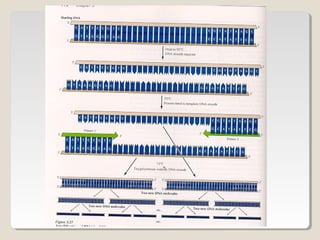
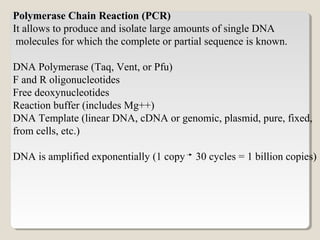
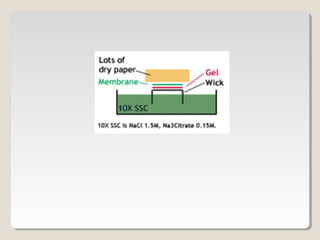
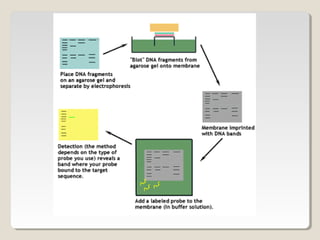
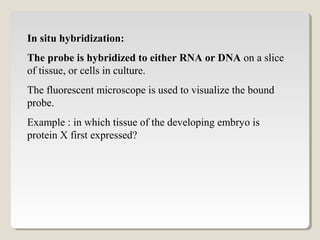
Restriction endonucleases are enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences. They have been used to map DNA by cutting it into fragments of different sizes that can be separated by gel electrophoresis. More than 3000 restriction endonucleases have been isolated from bacteria and are useful for applications such as cloning DNA fragments into vectors like plasmids. The ability to cut and paste DNA fragments using restriction enzymes and recombinant DNA technology has enabled scientists to study genes and their functions.