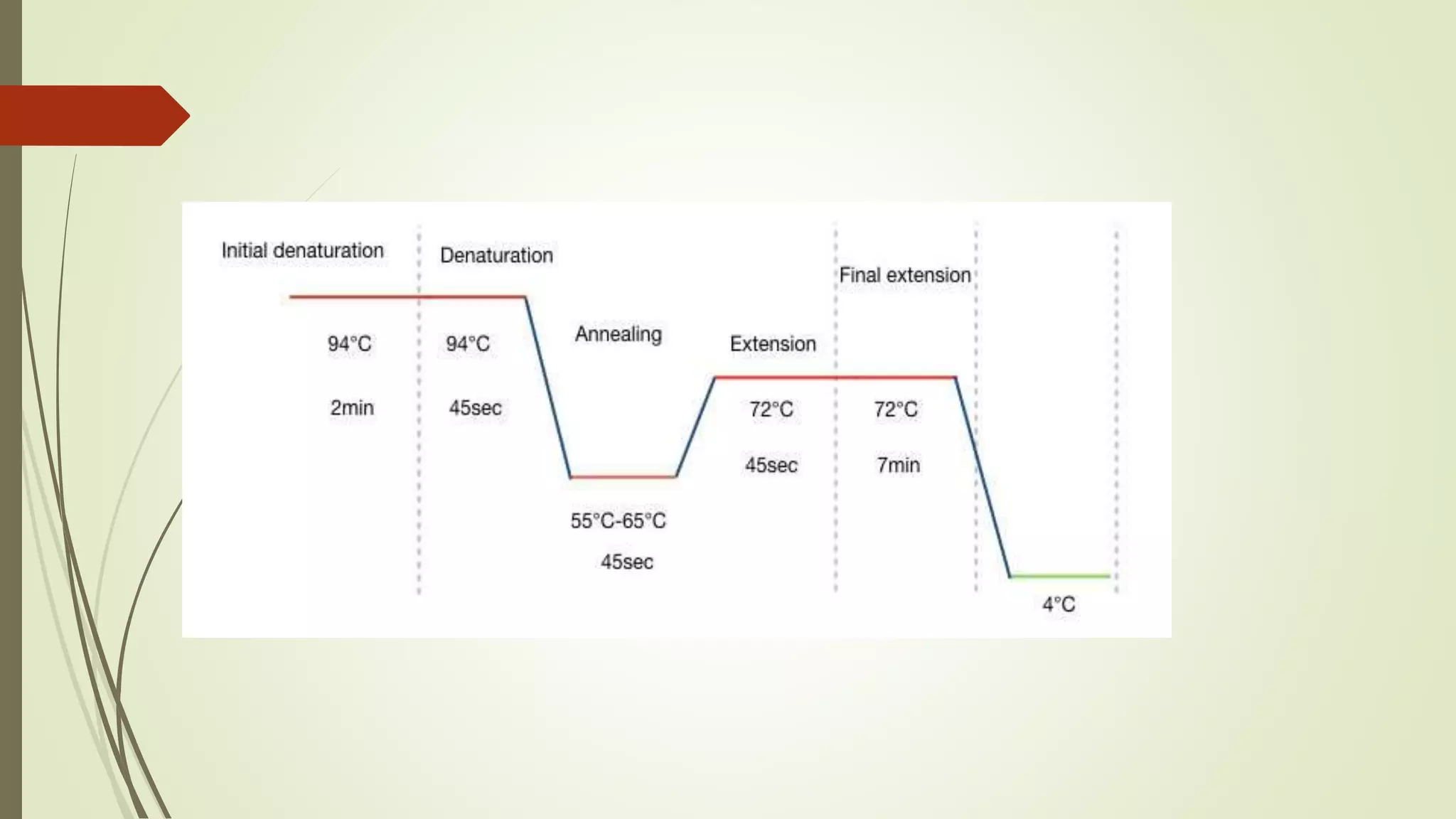
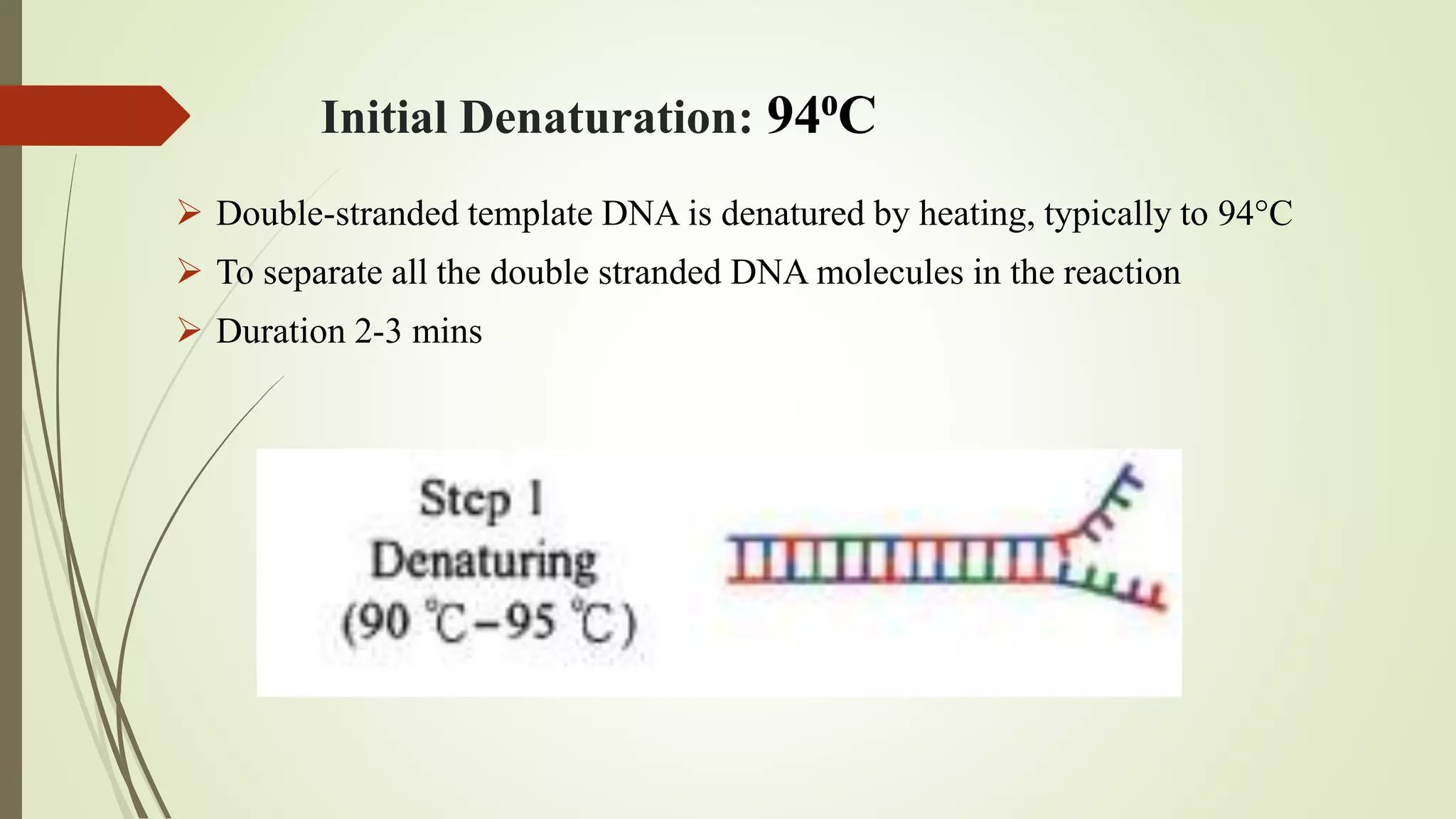
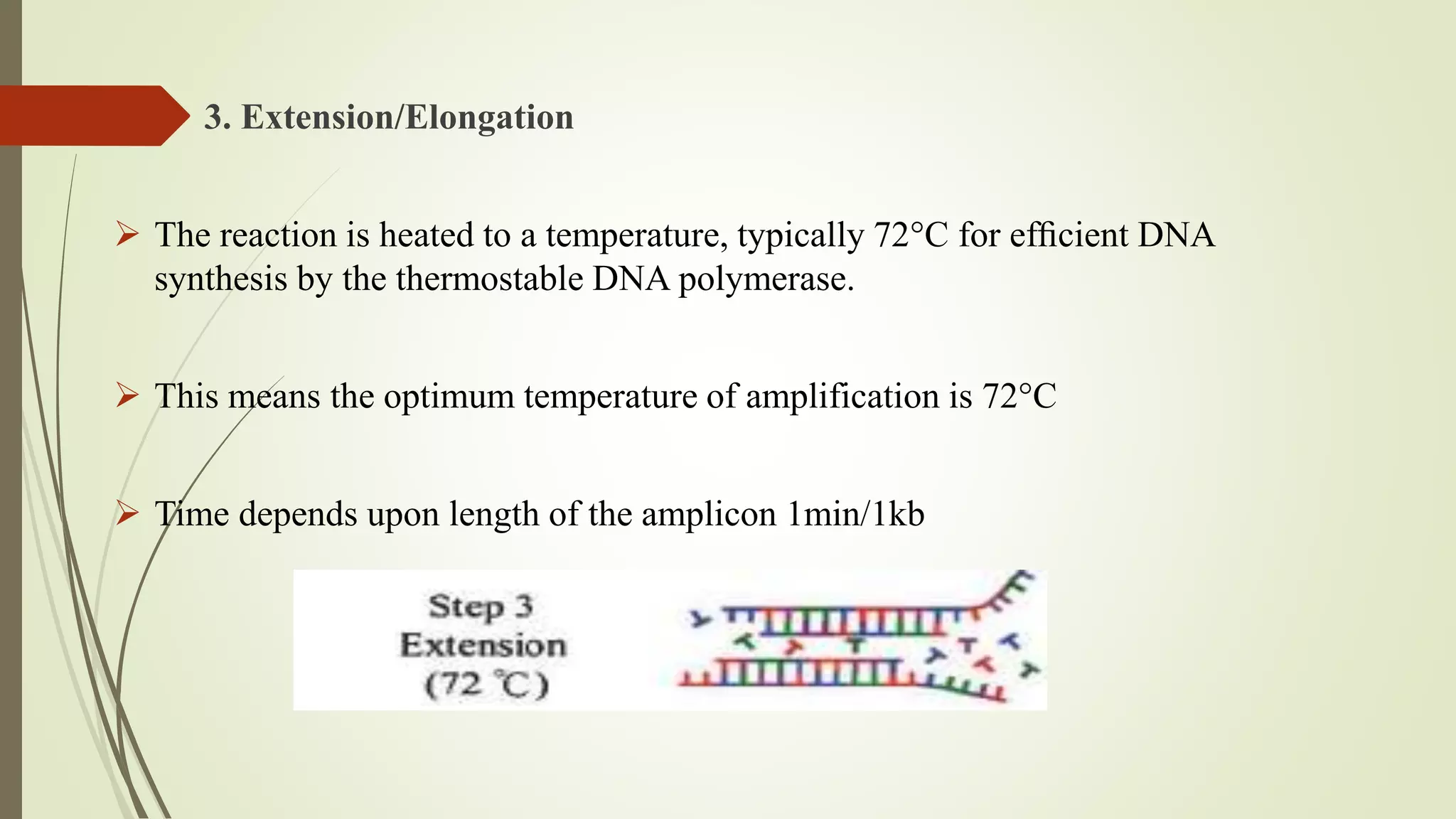
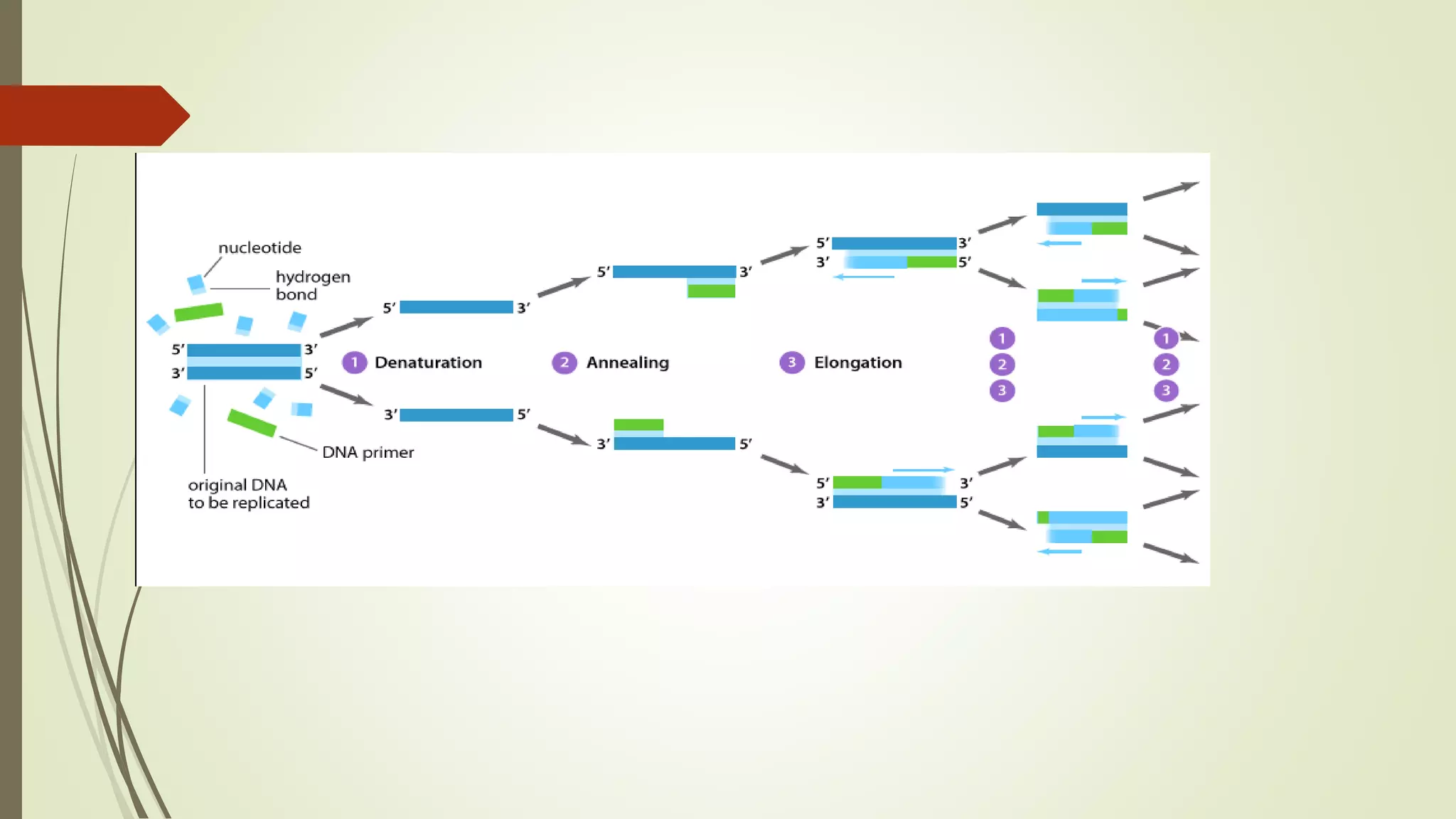
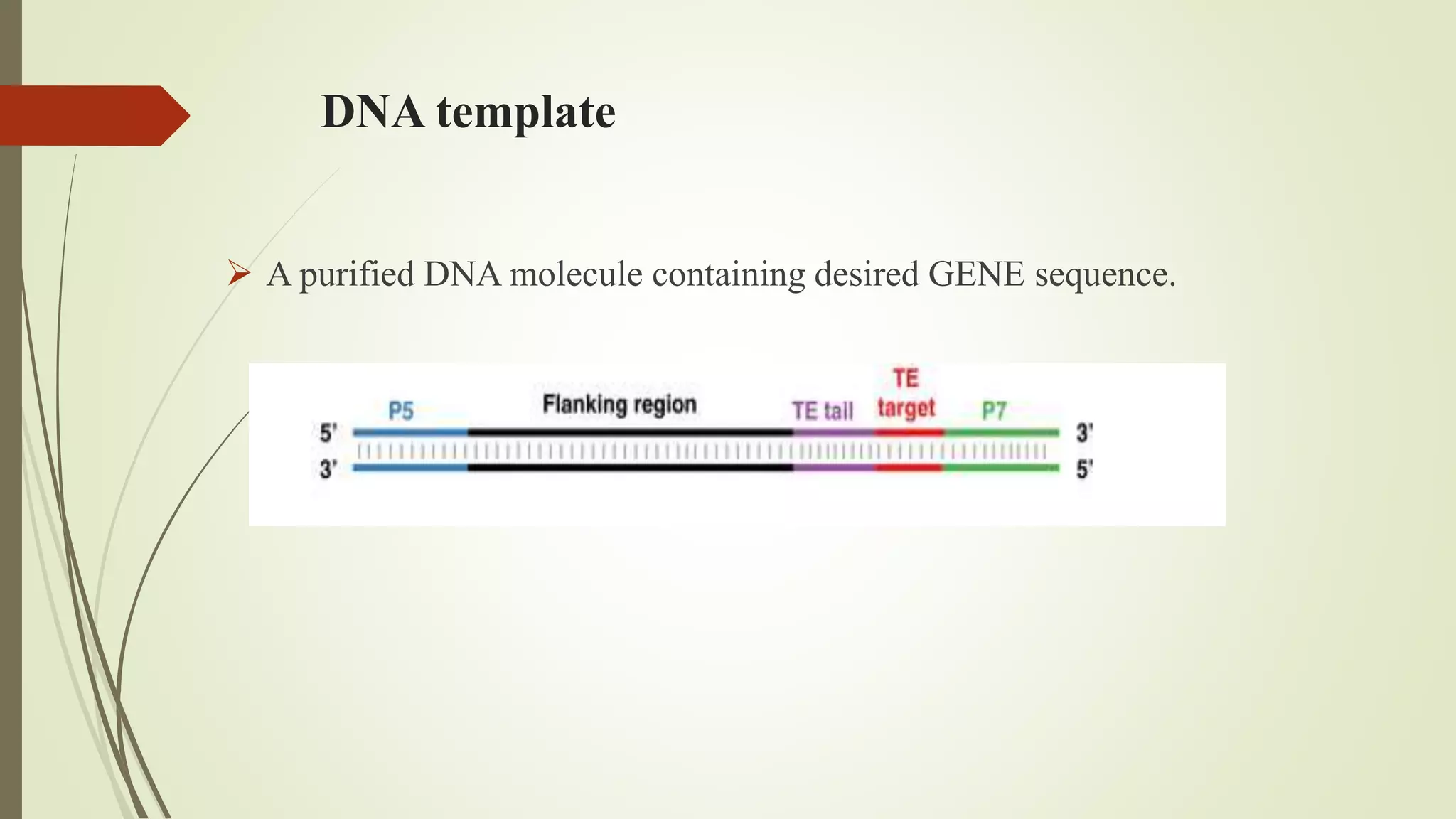
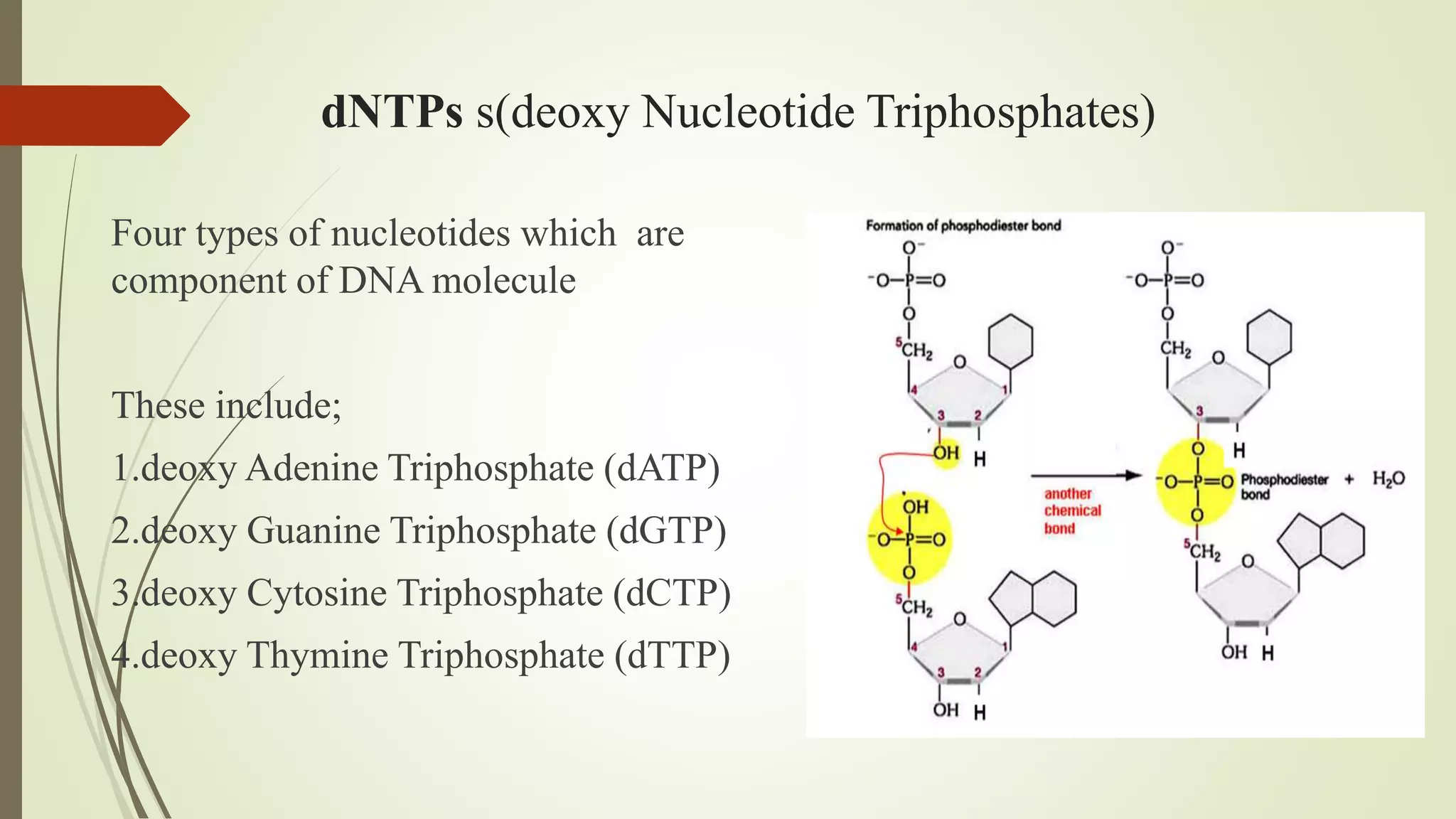
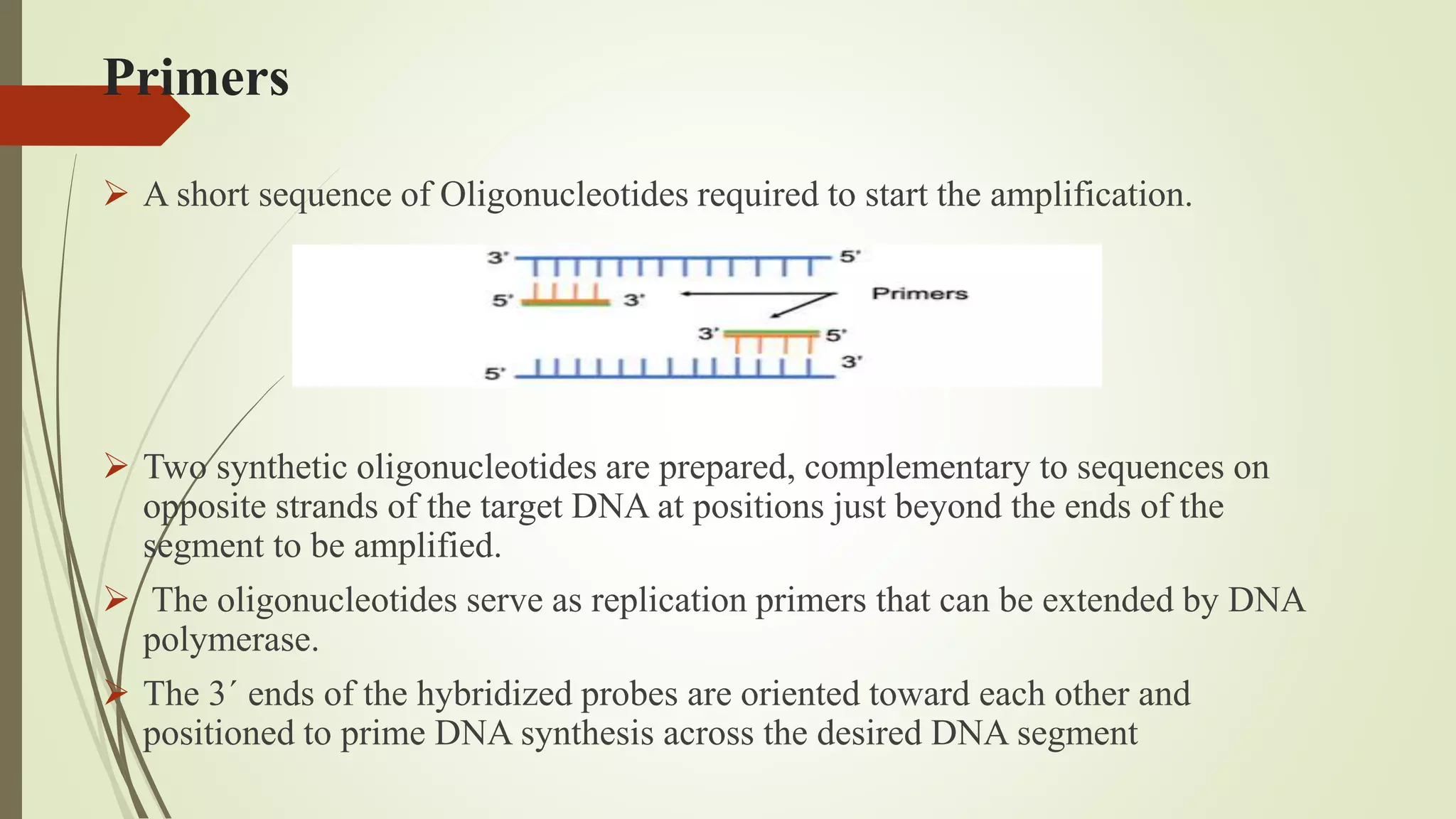
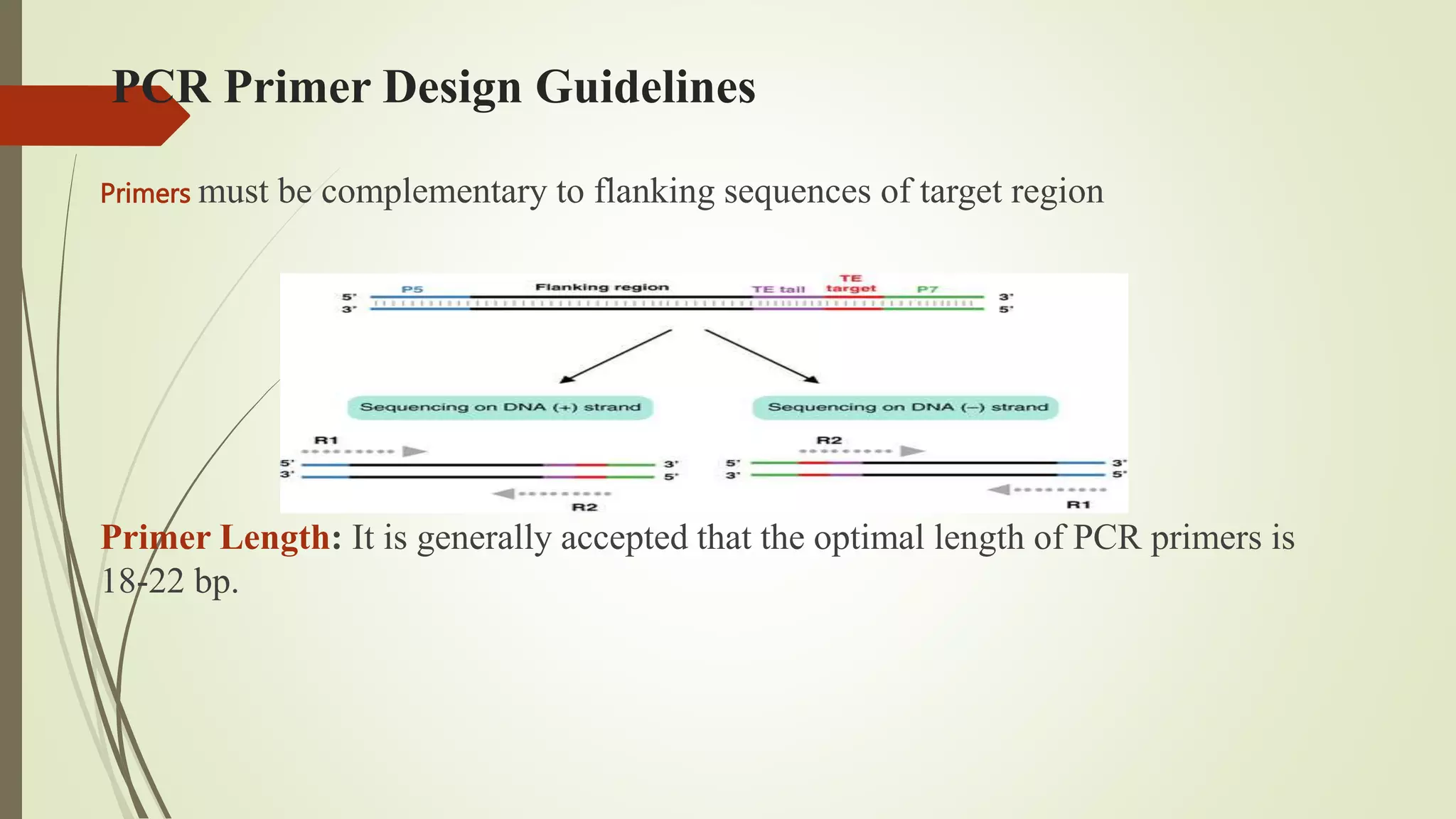
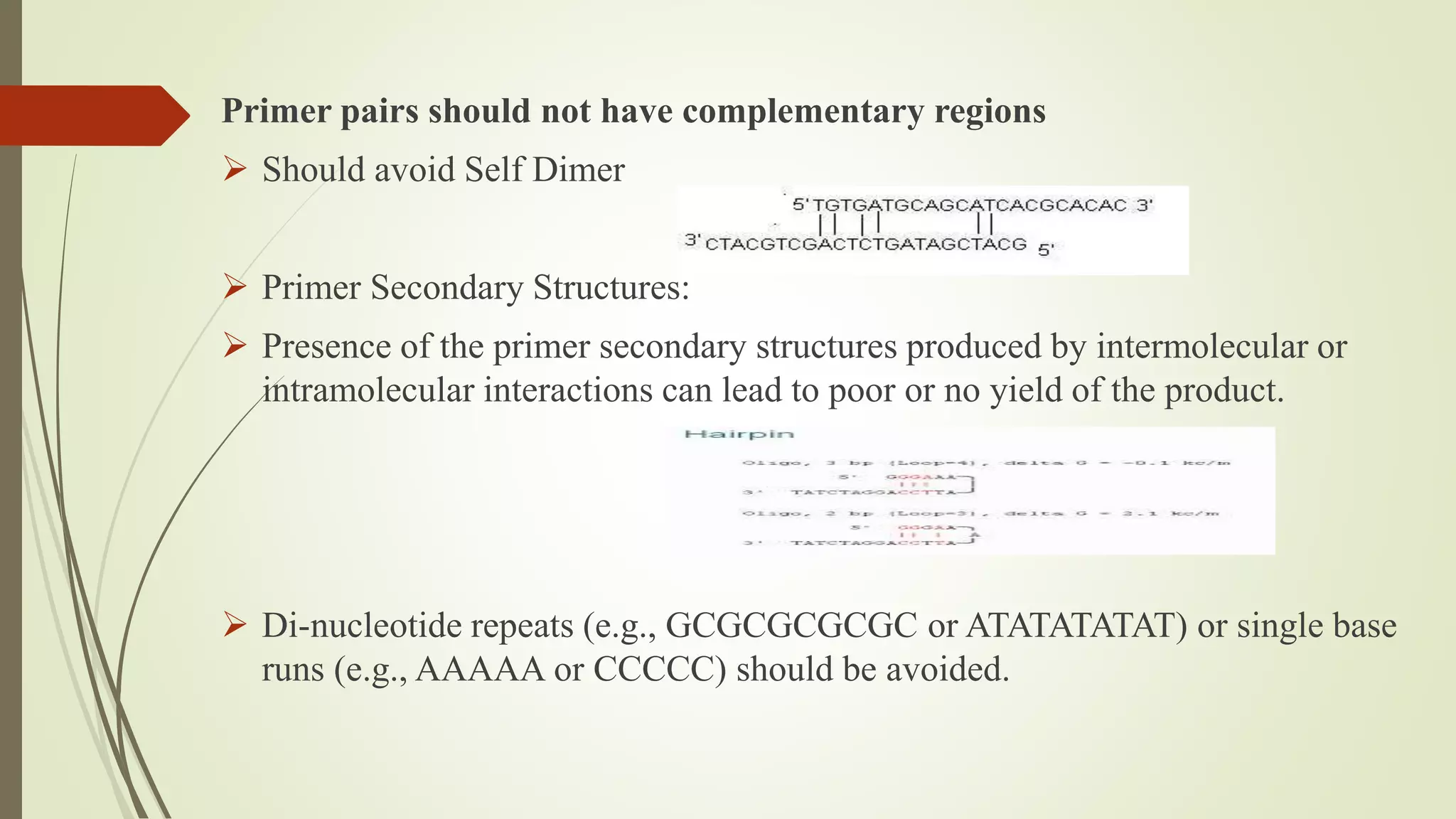
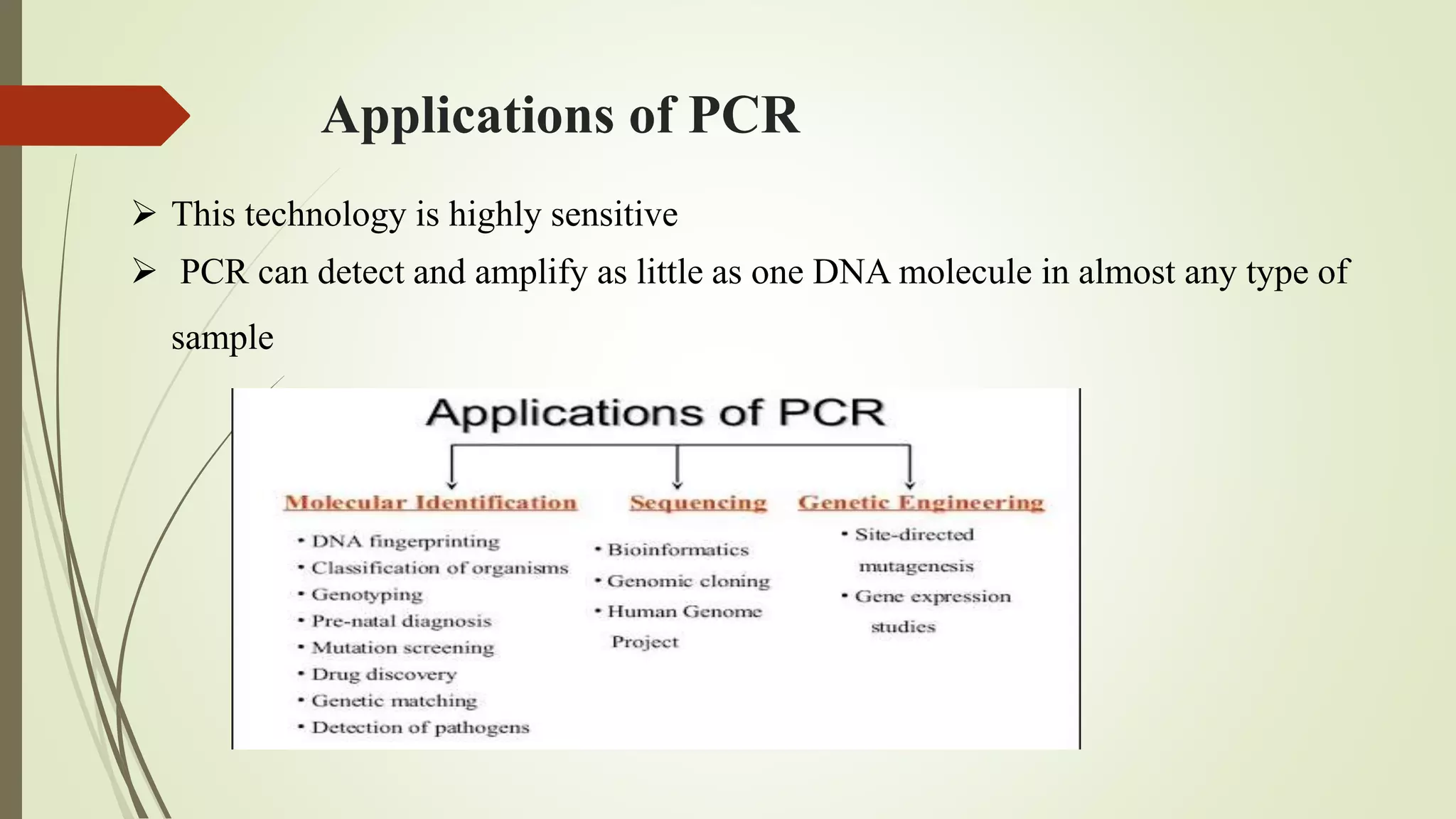
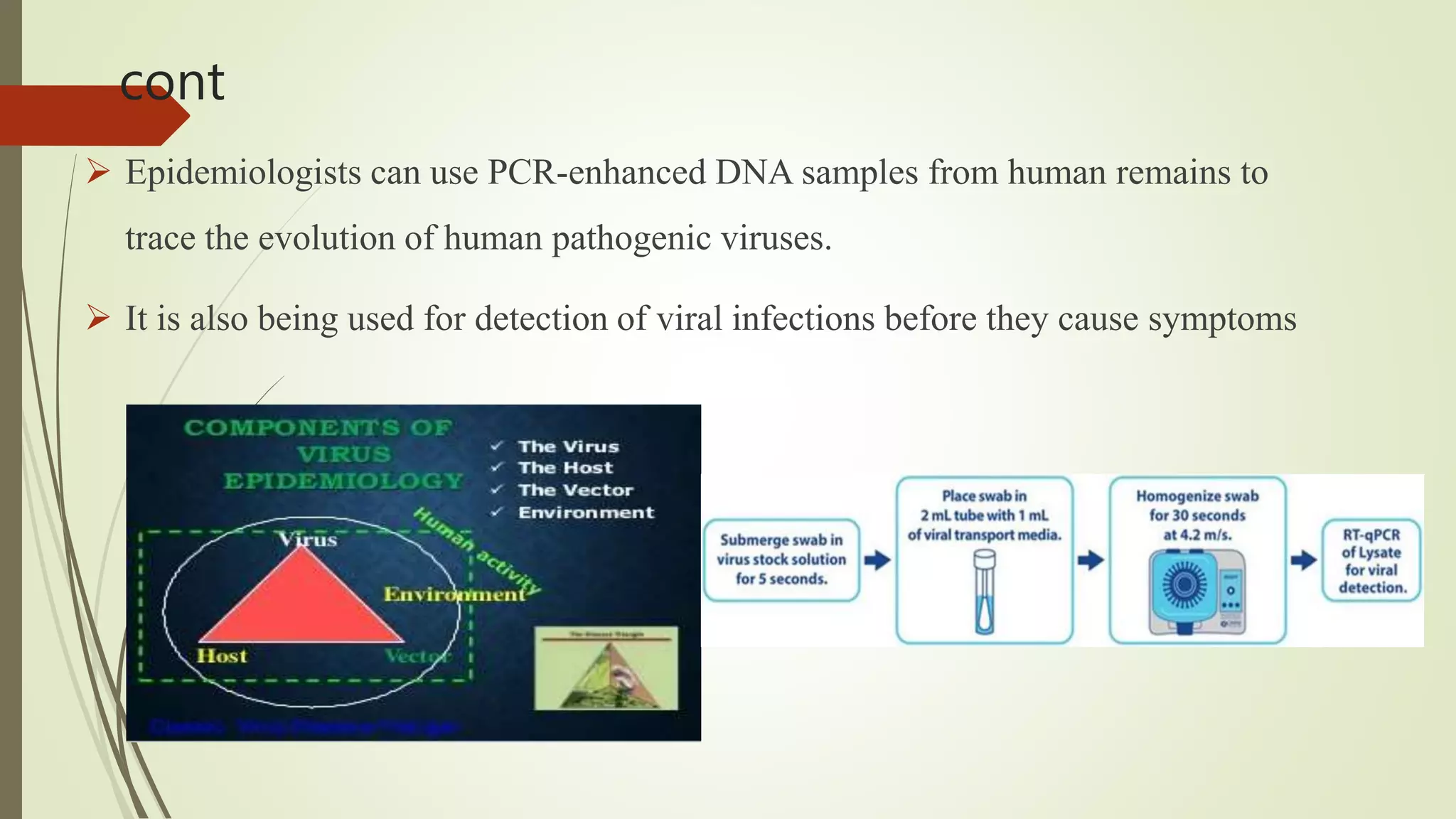
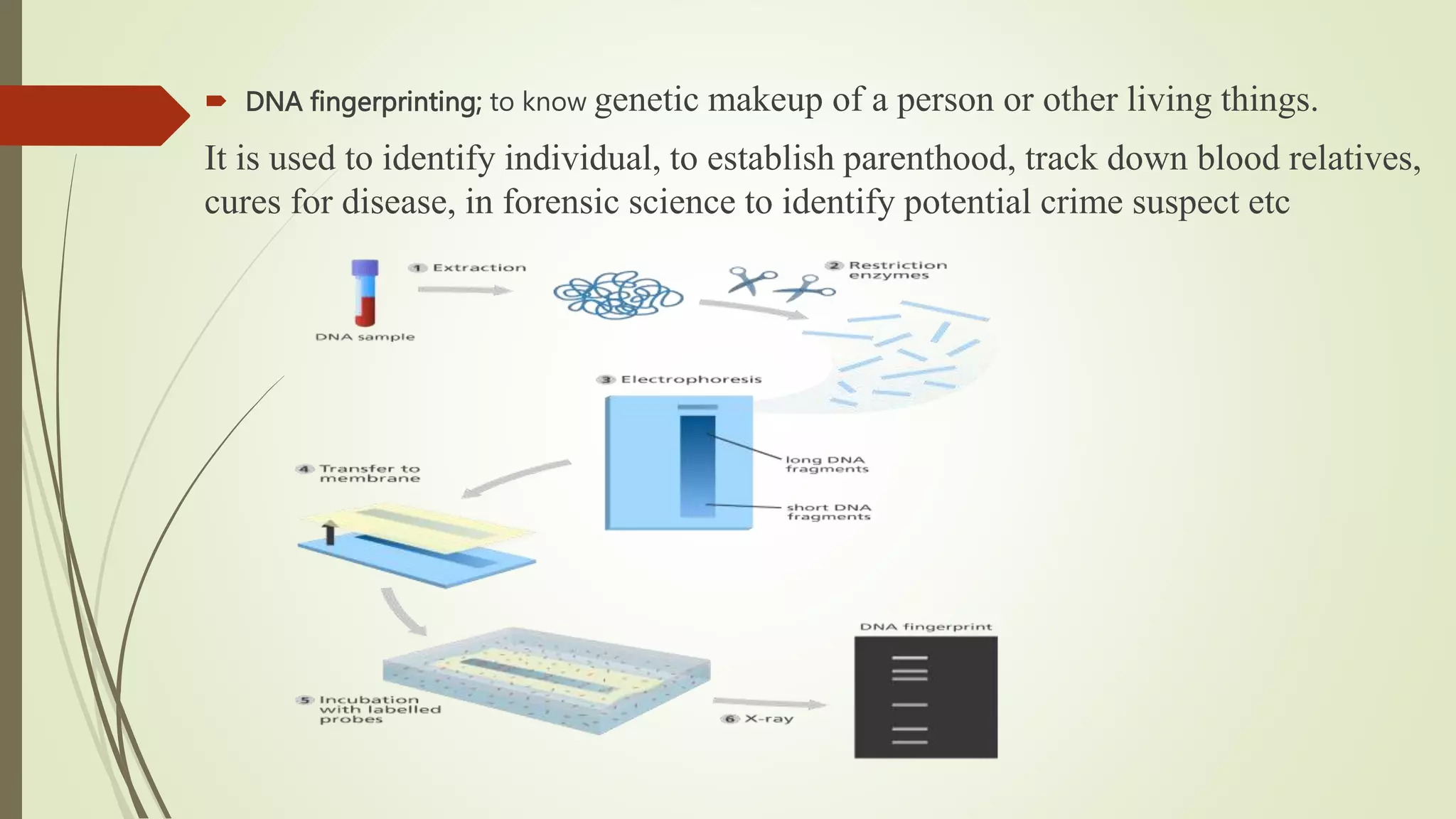
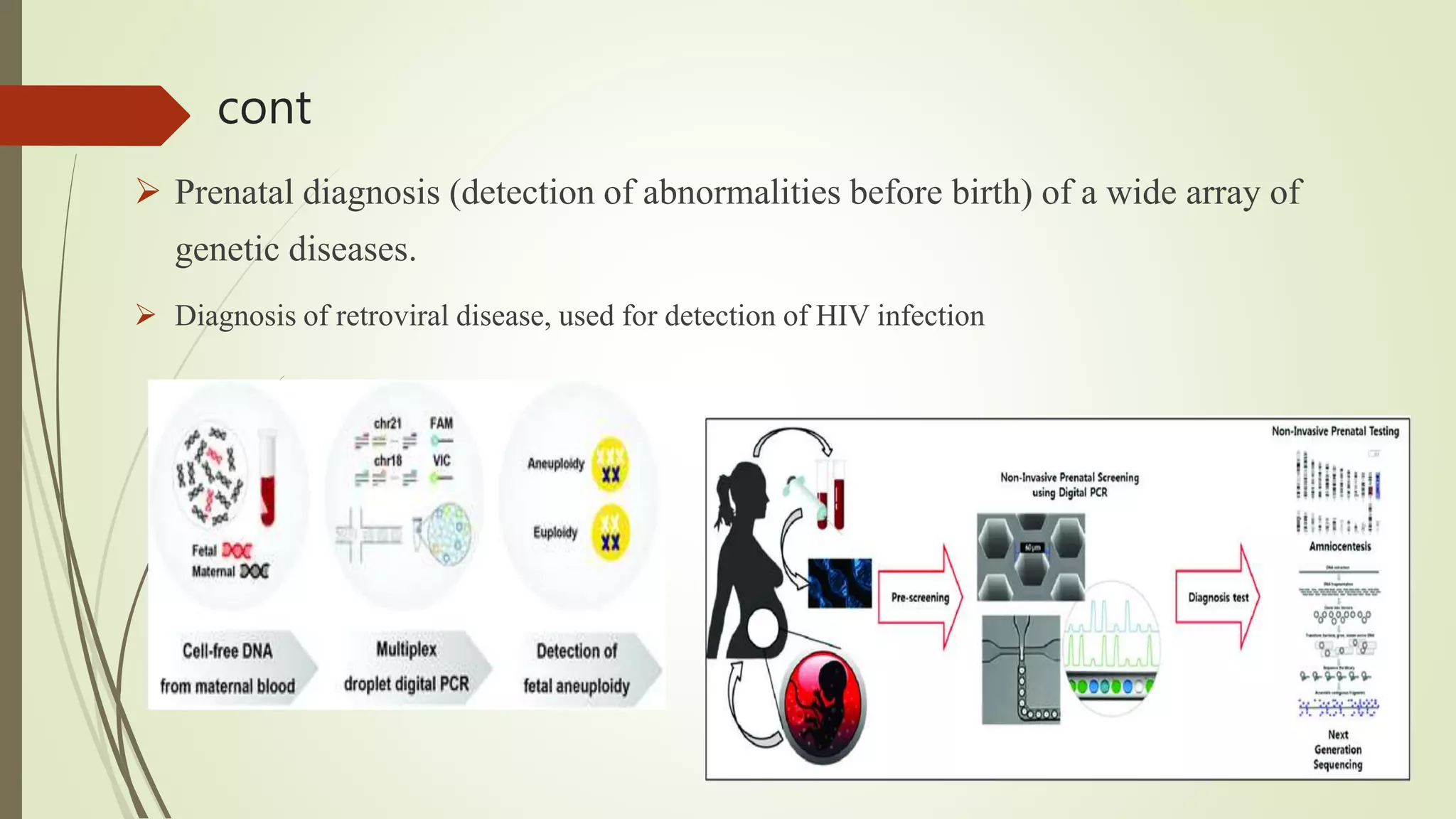
The document describes a lecture on polymerase chain reaction (PCR). PCR is a technique used to amplify a specific segment of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence. The key components required for PCR are a DNA template, primers, DNA polymerase, dNTPs, buffer and magnesium chloride. The process involves repeated cycles of heating and cooling of the reaction to denature and extend DNA. Applications of PCR include DNA fingerprinting, prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases, diagnosis of viral infections, and studying ancient DNA samples.