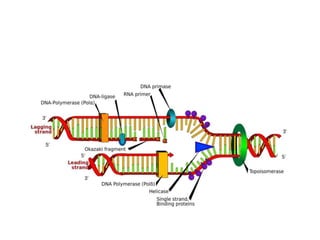
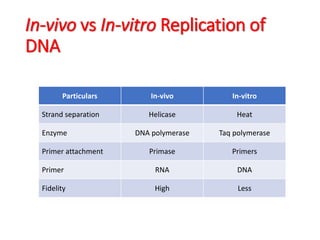
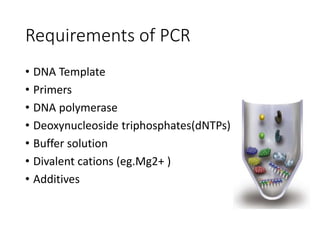
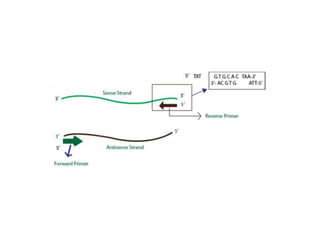
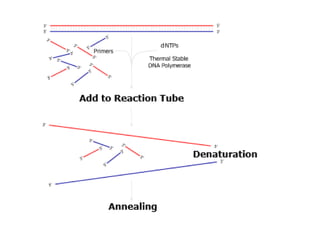
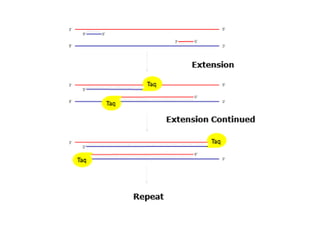
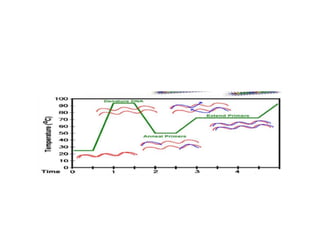
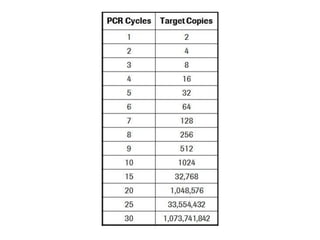
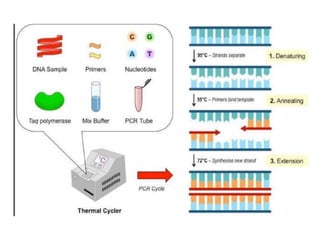
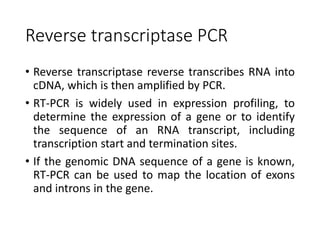
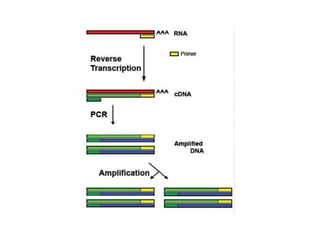
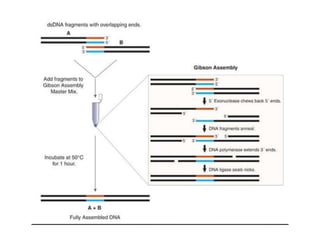
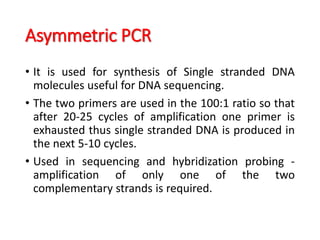
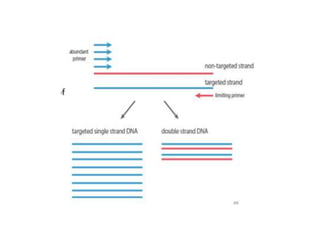
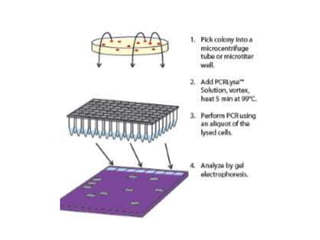
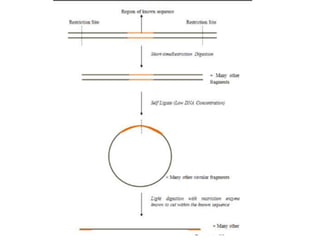
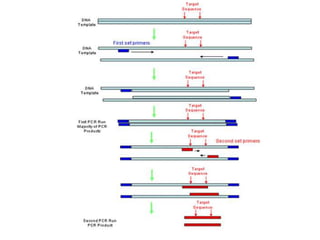
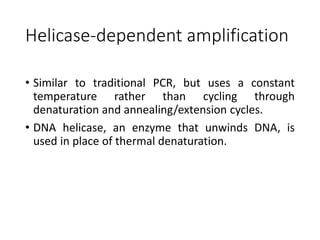
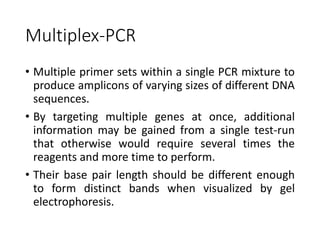
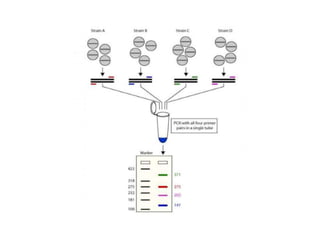
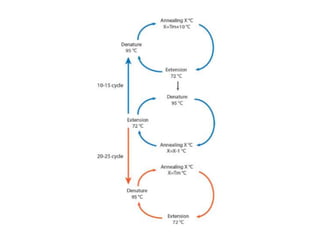
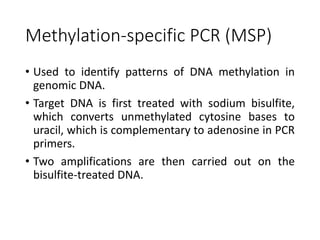
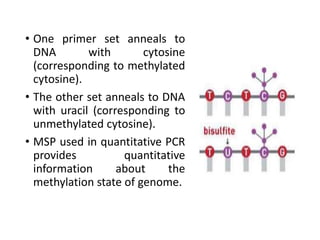
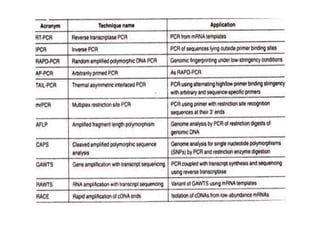
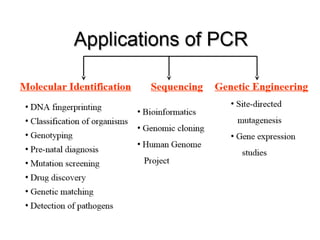
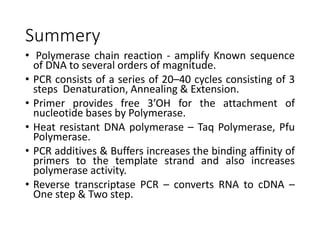
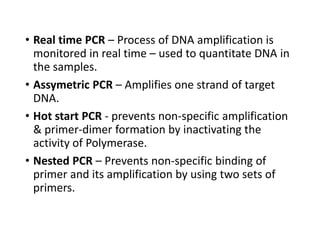
PCR is a technique used to amplify a specific DNA sequence. It involves repeated cycles of heating and cooling of the DNA sample to separate and copy the DNA strands. Key components of PCR include primers, DNA polymerase, and dNTPs. Variations of PCR allow for applications such as detecting gene expression, sequencing DNA, and quantifying DNA. Limitations include errors during amplification and potential contamination issues.