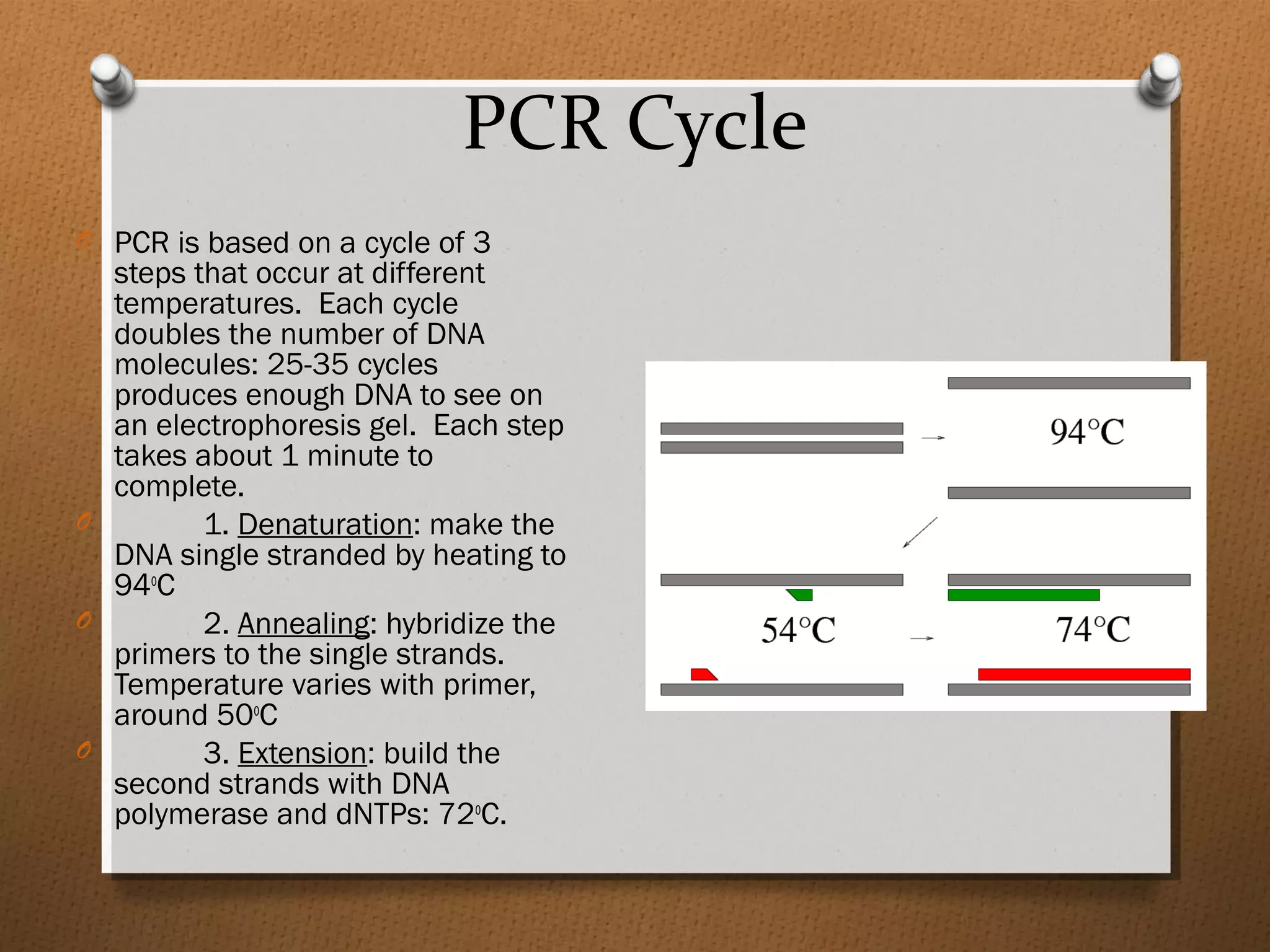
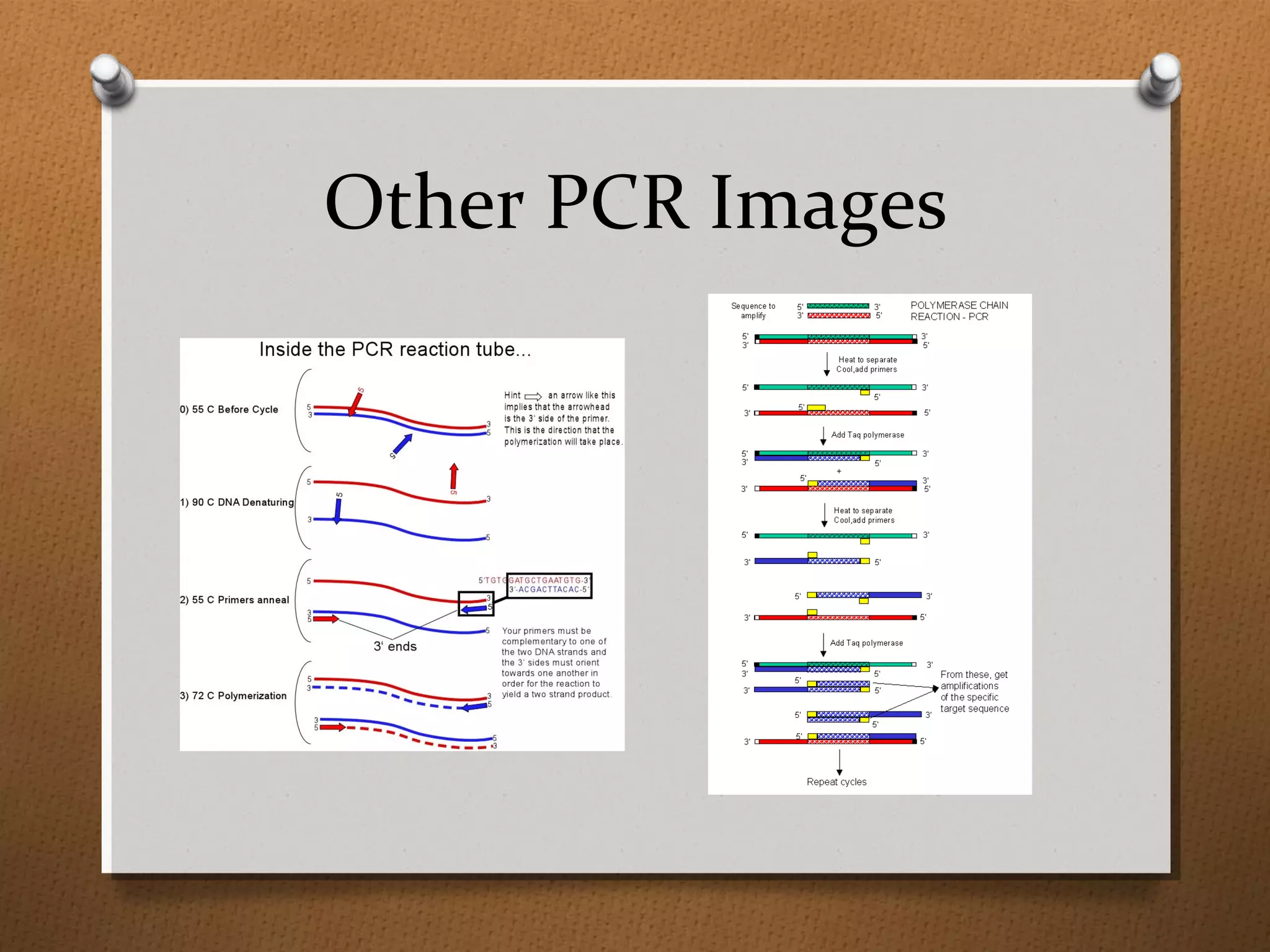
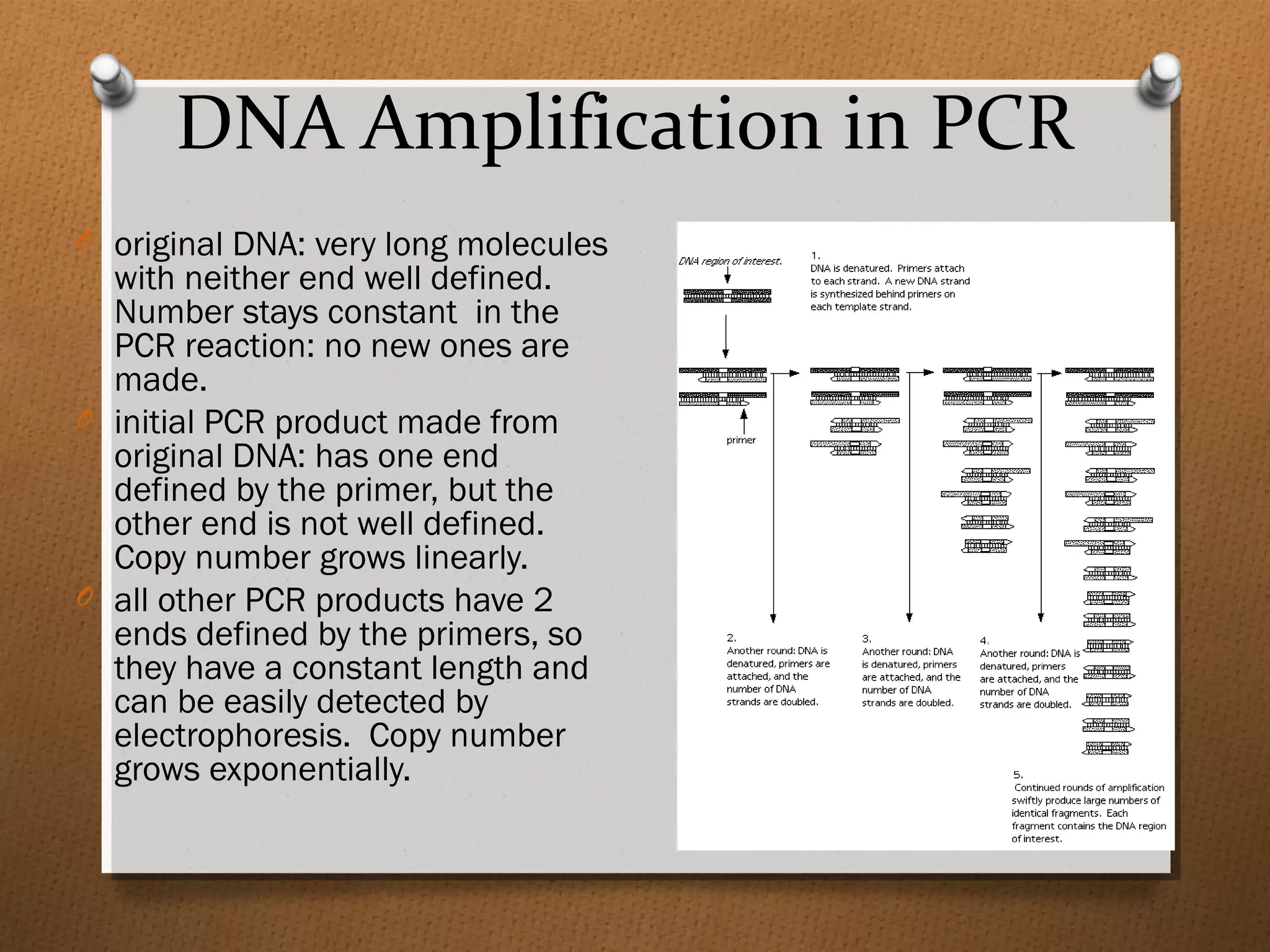
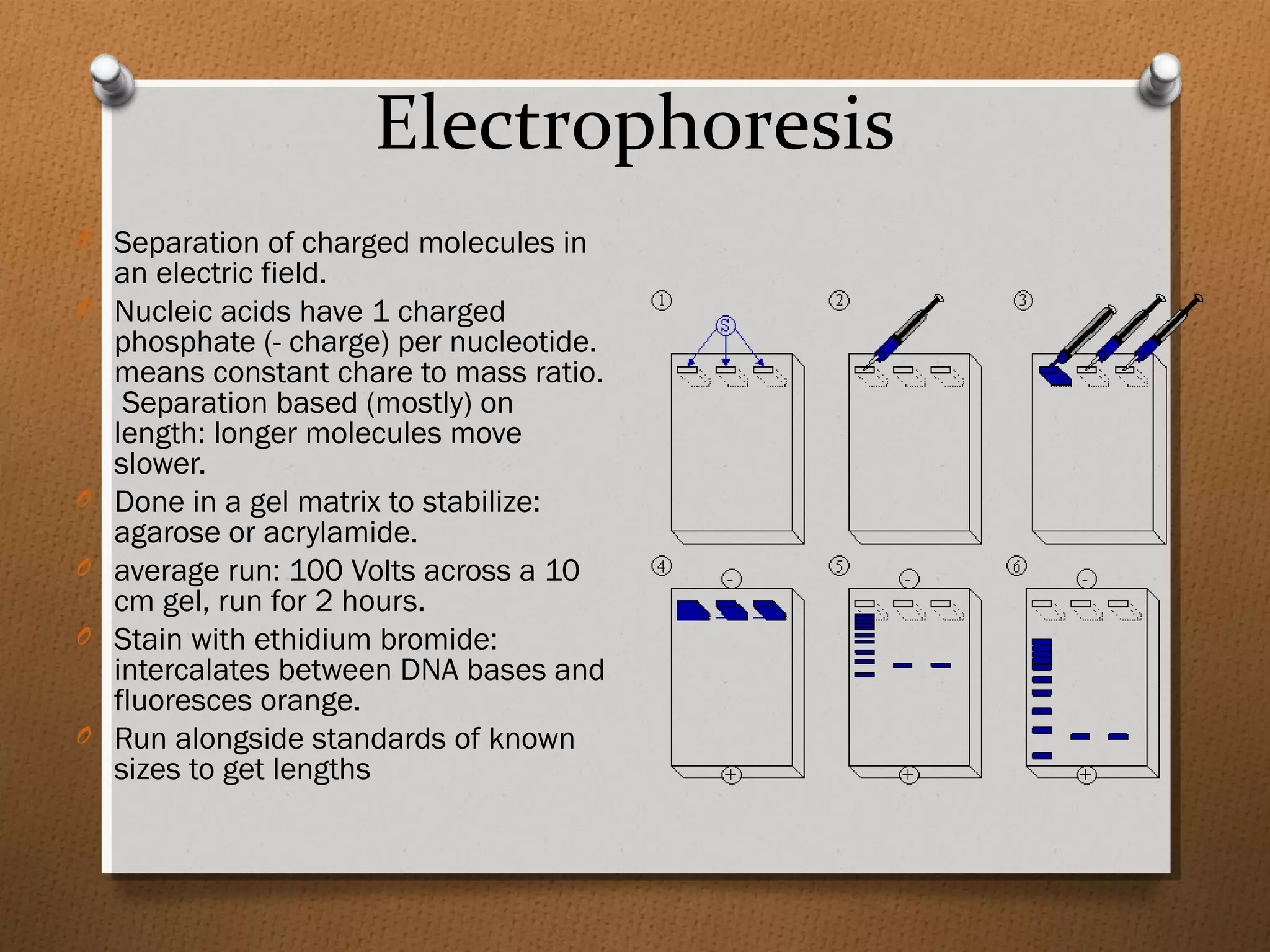
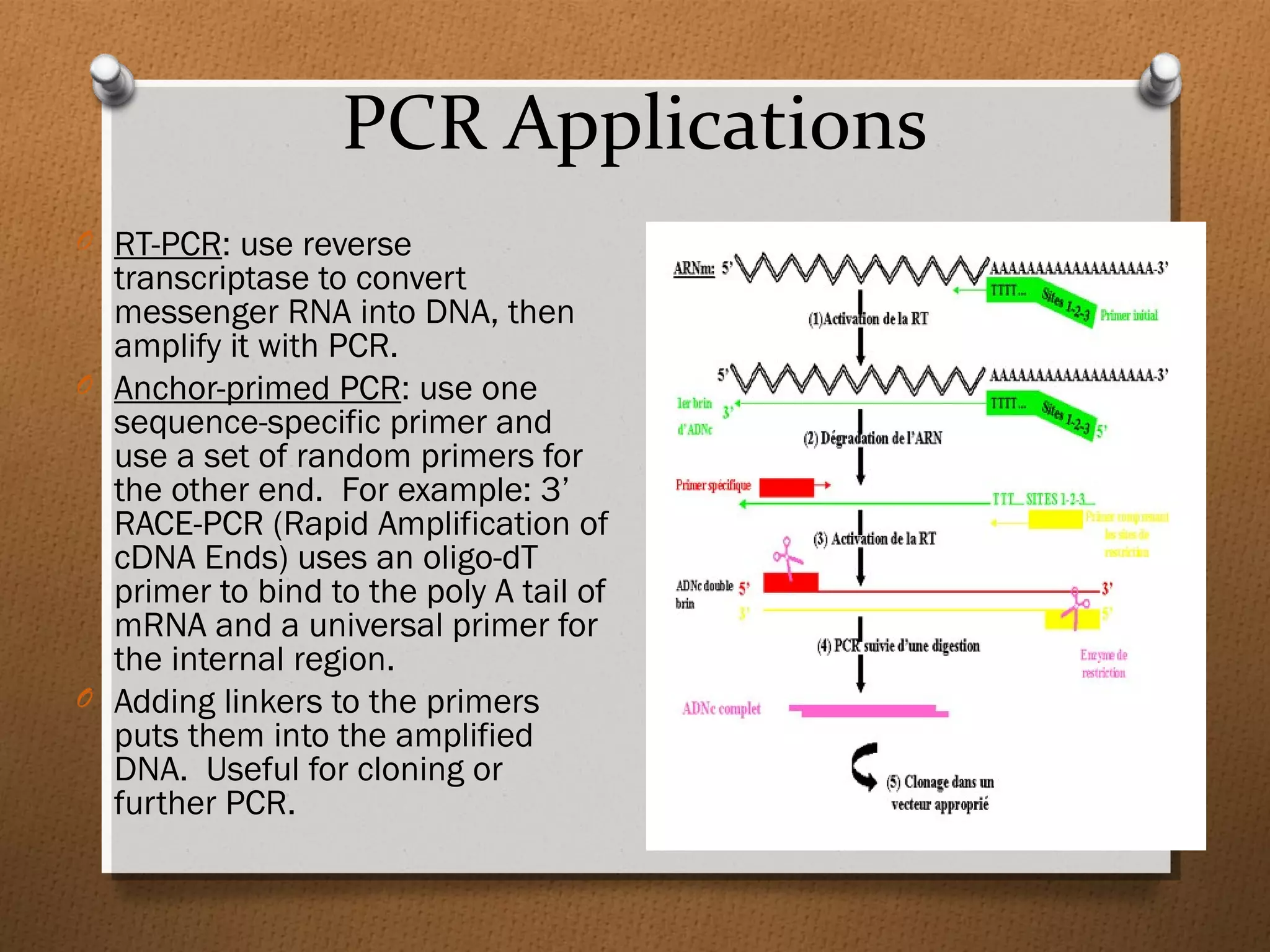
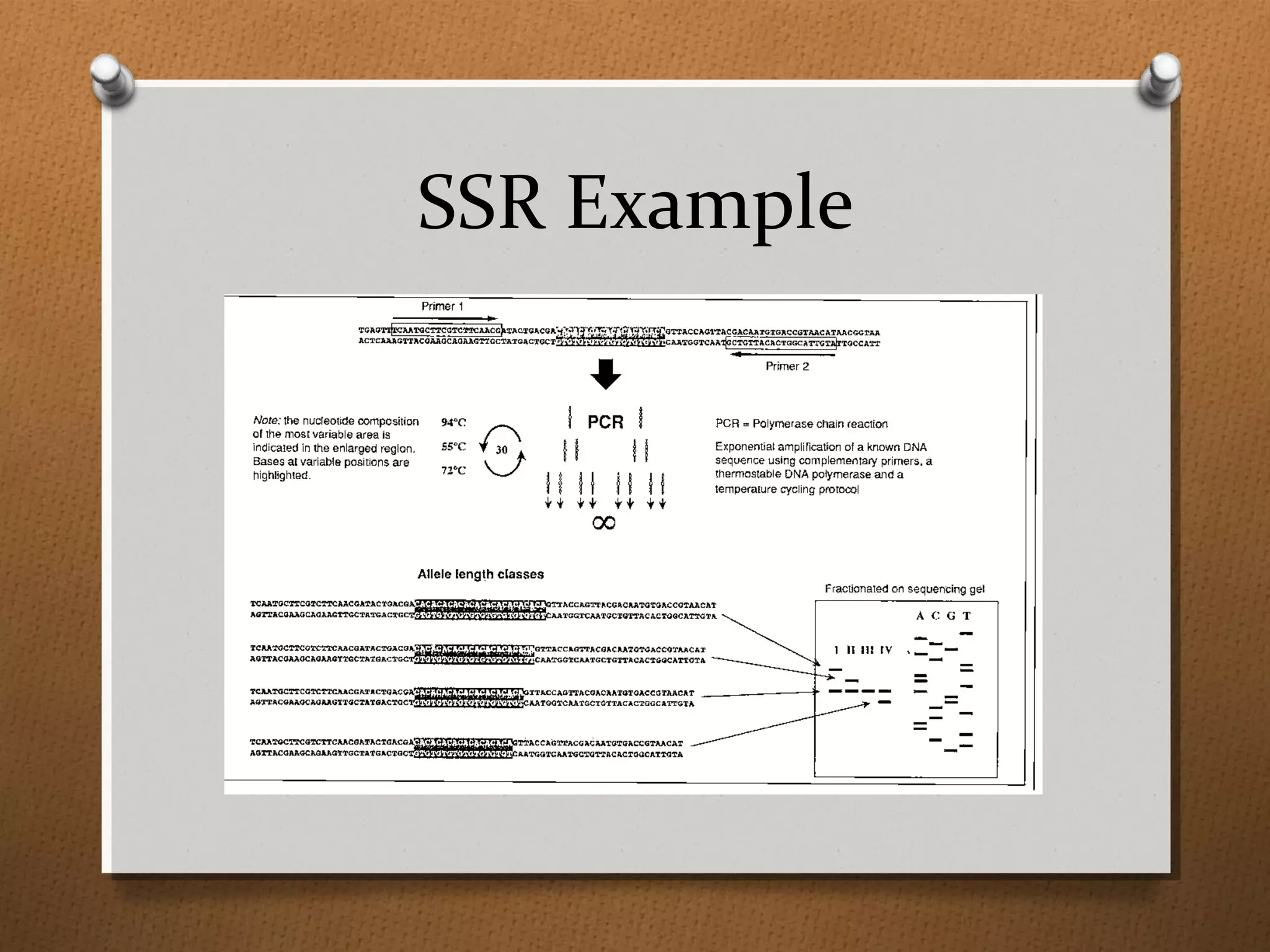
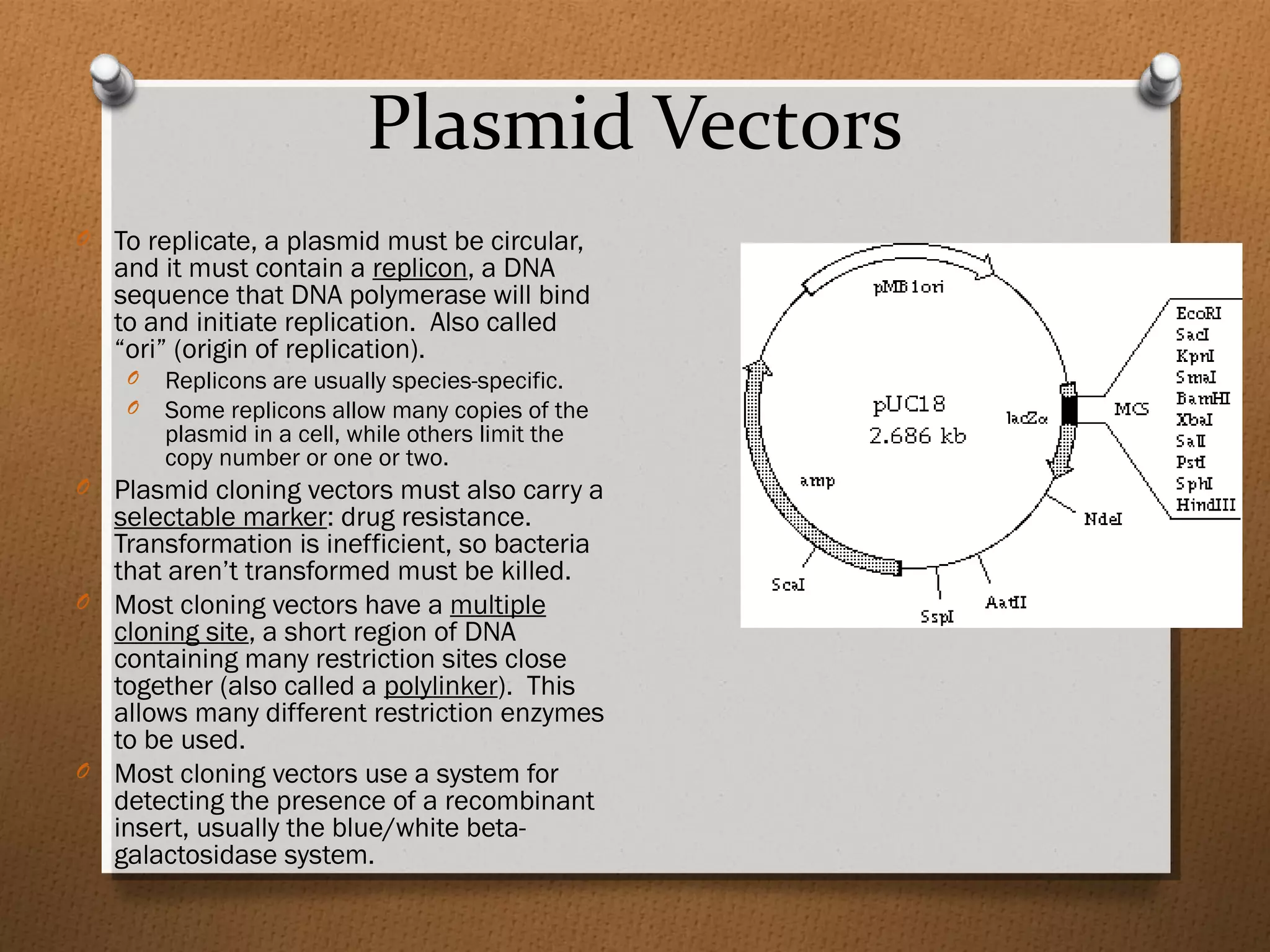
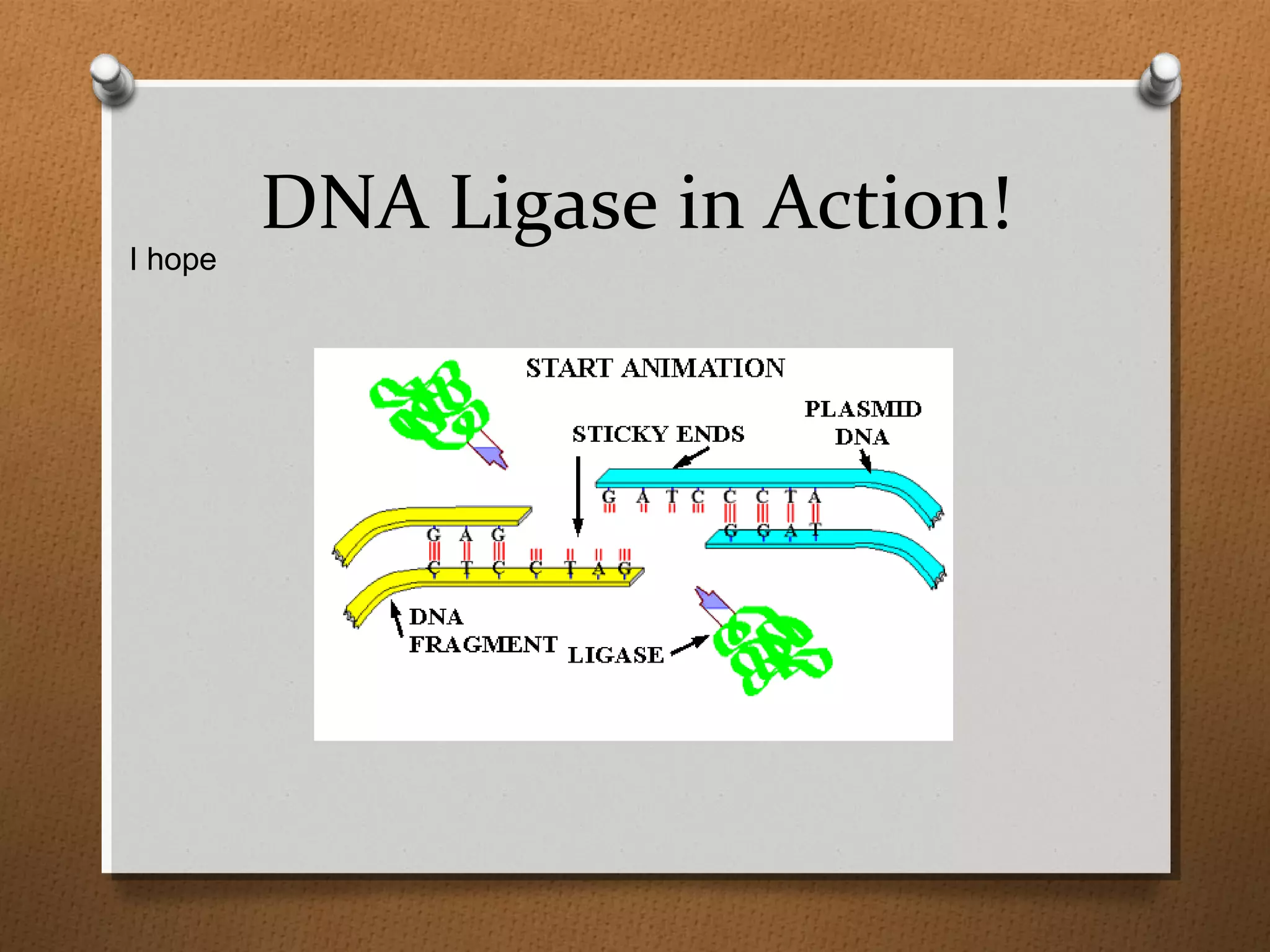
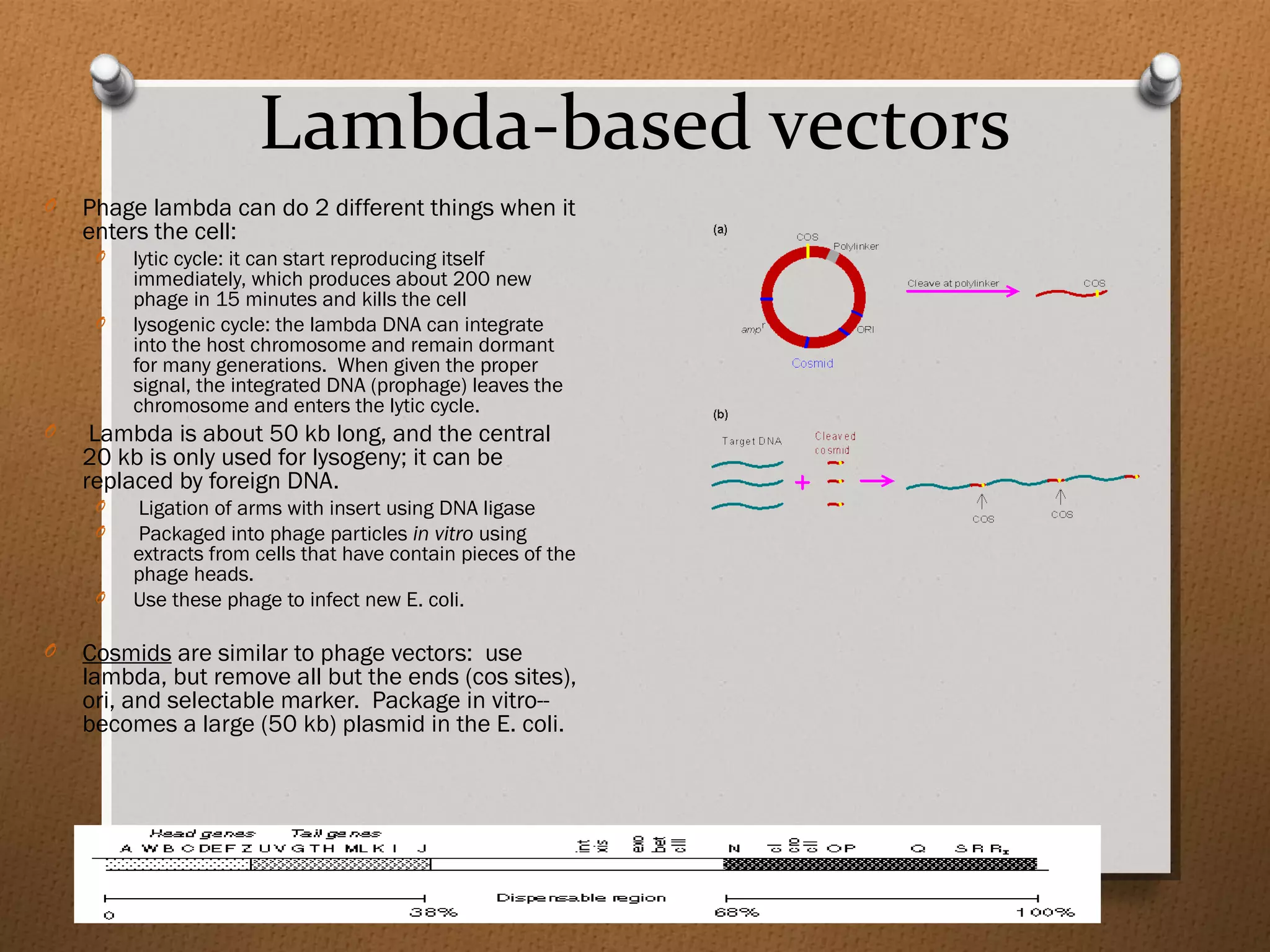
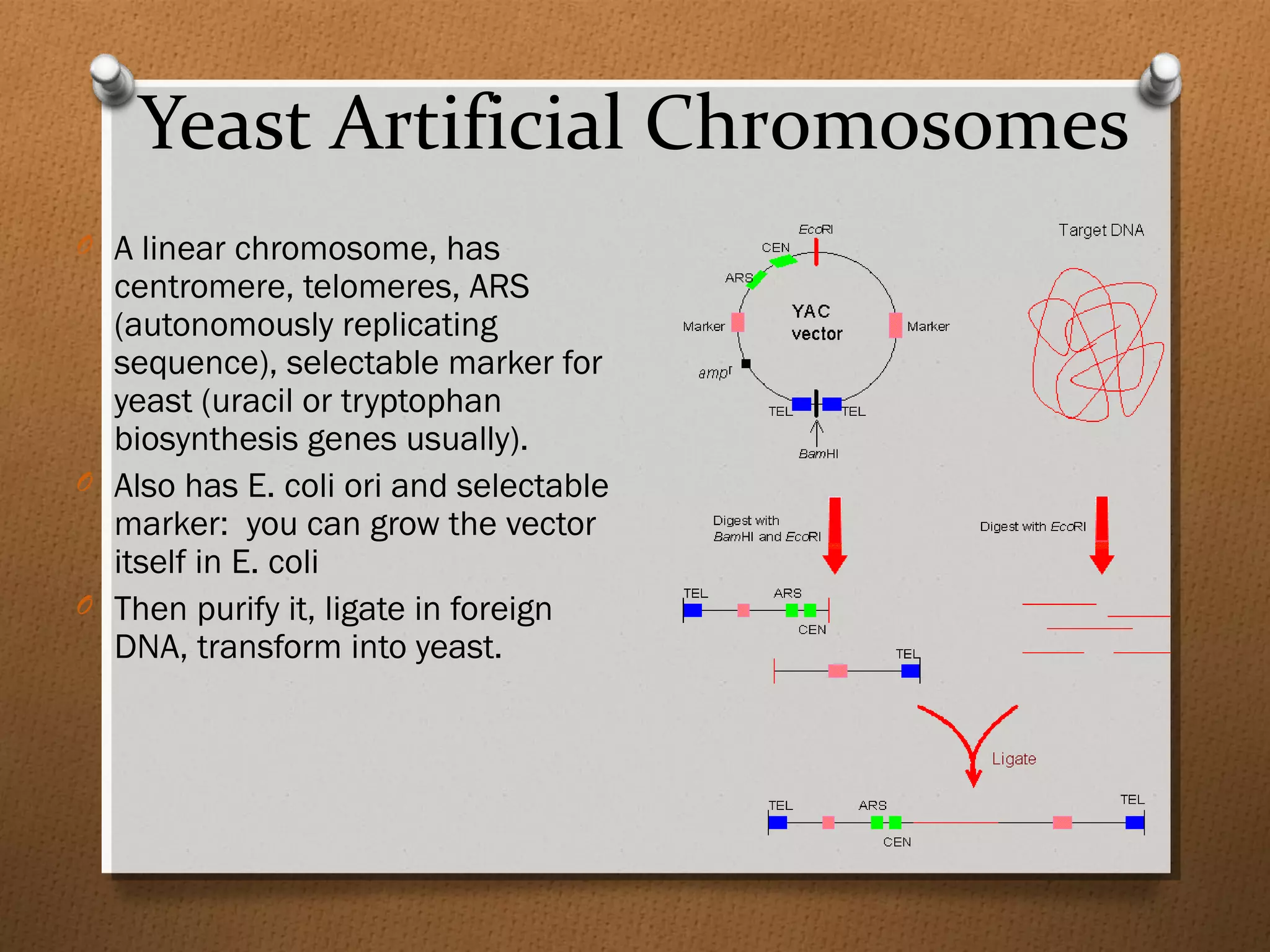
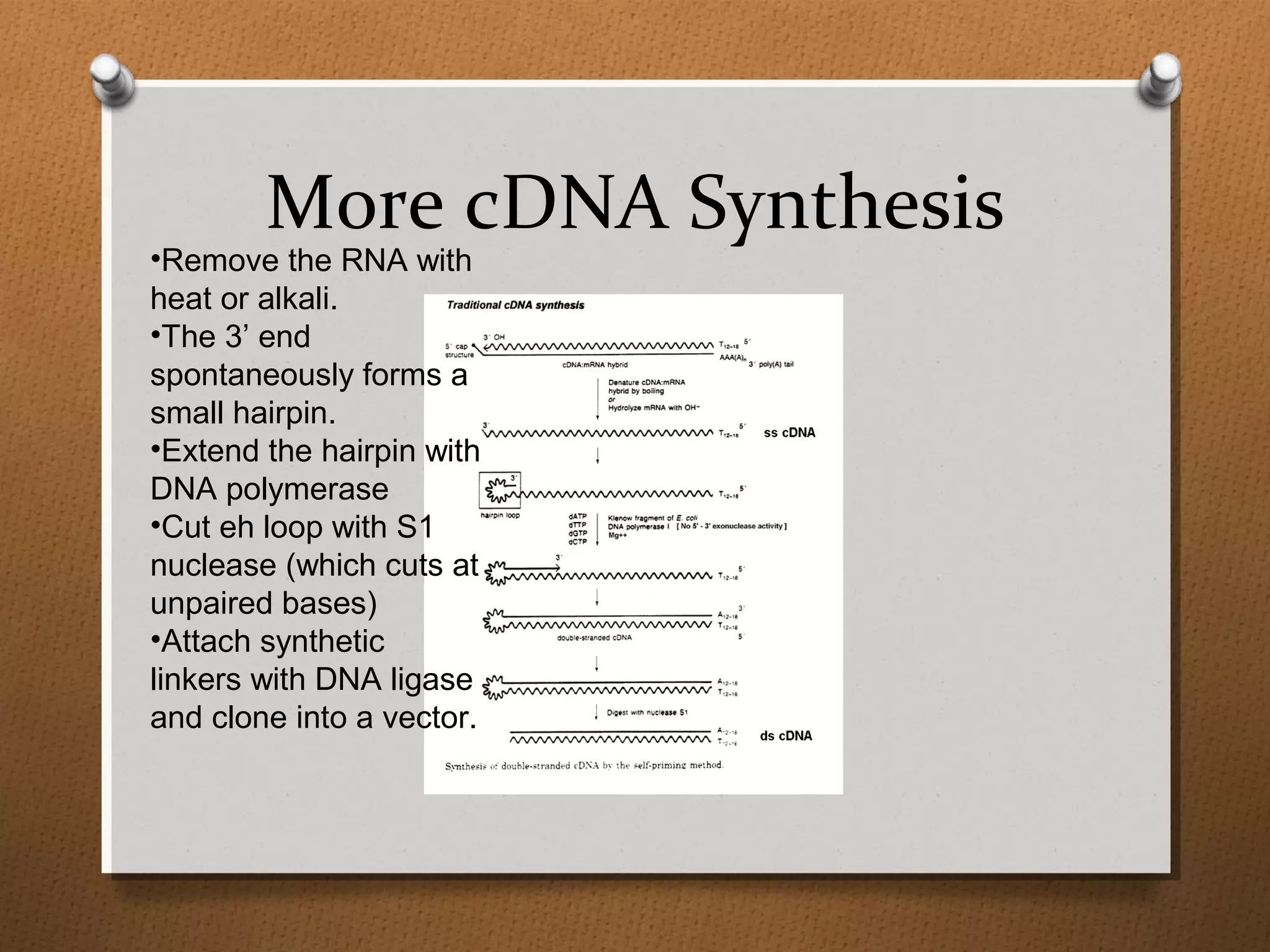
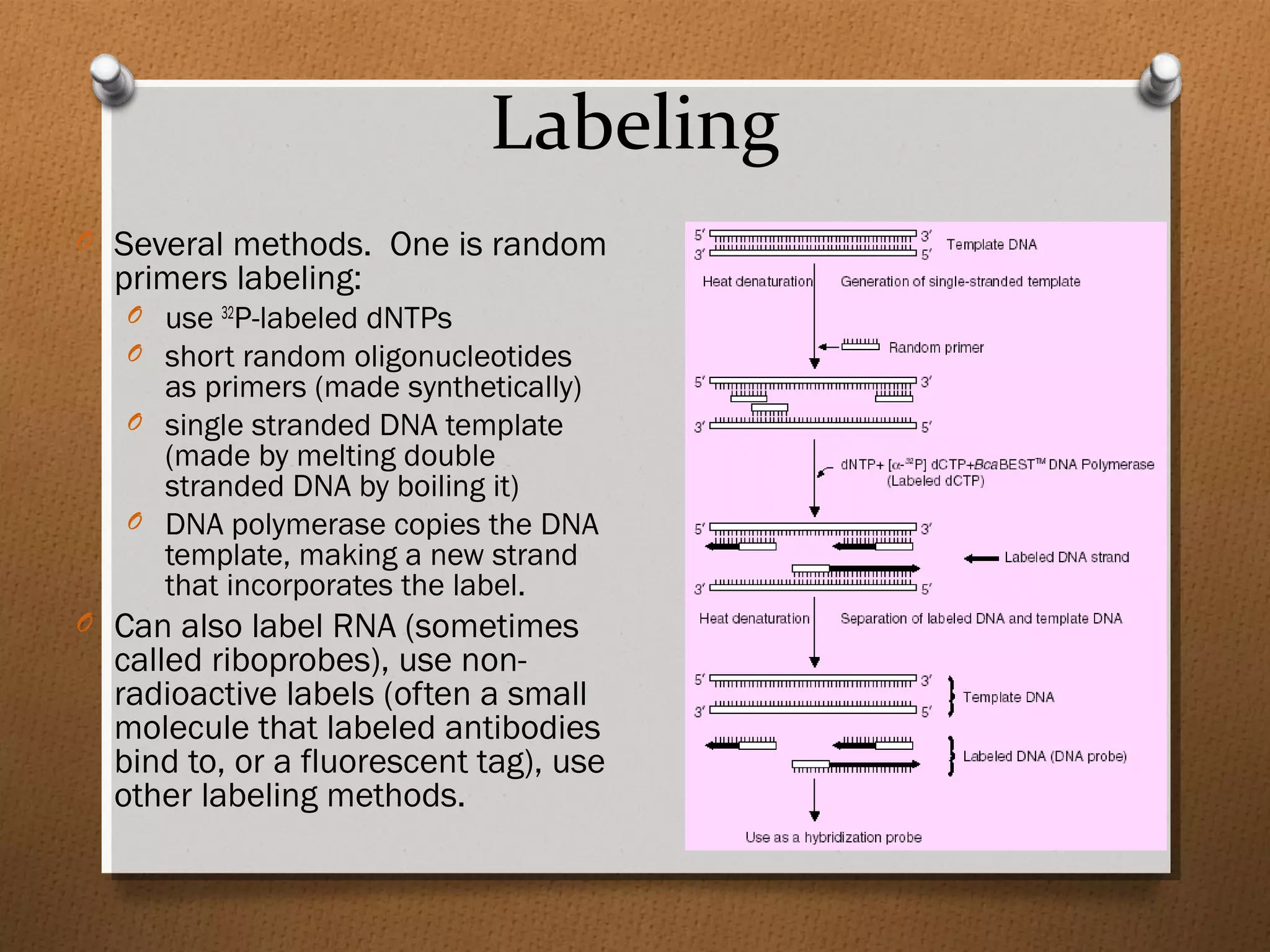
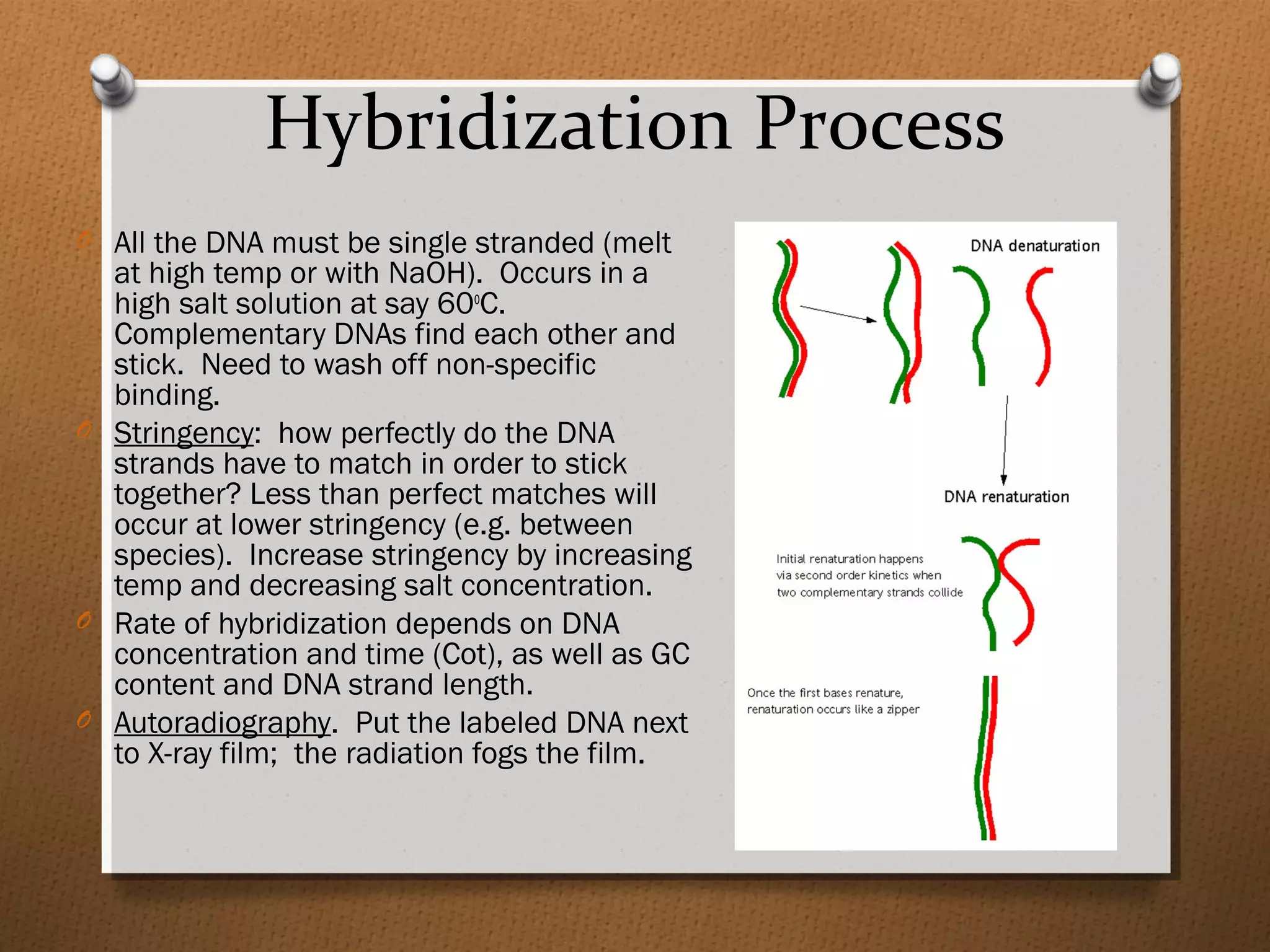
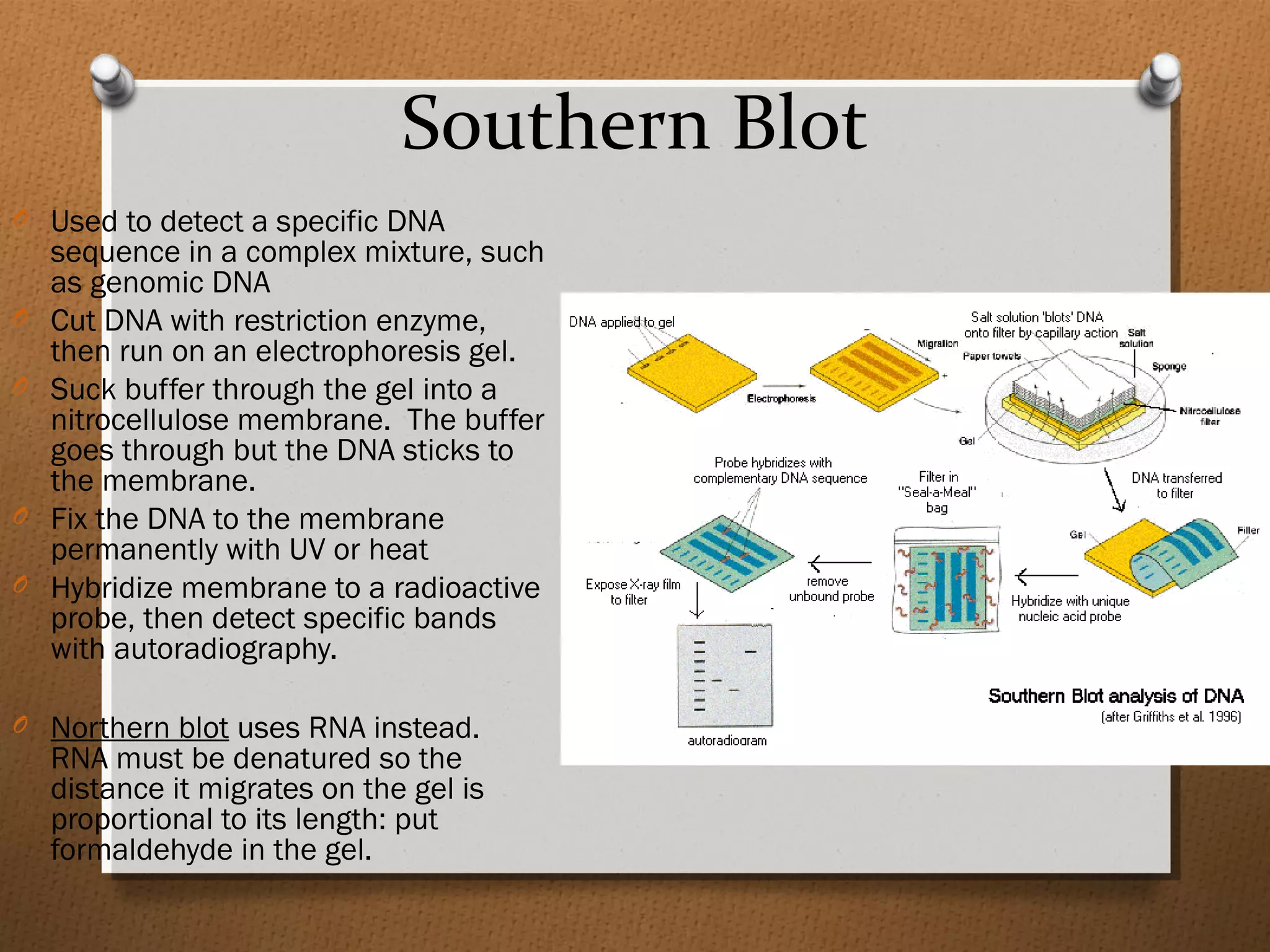
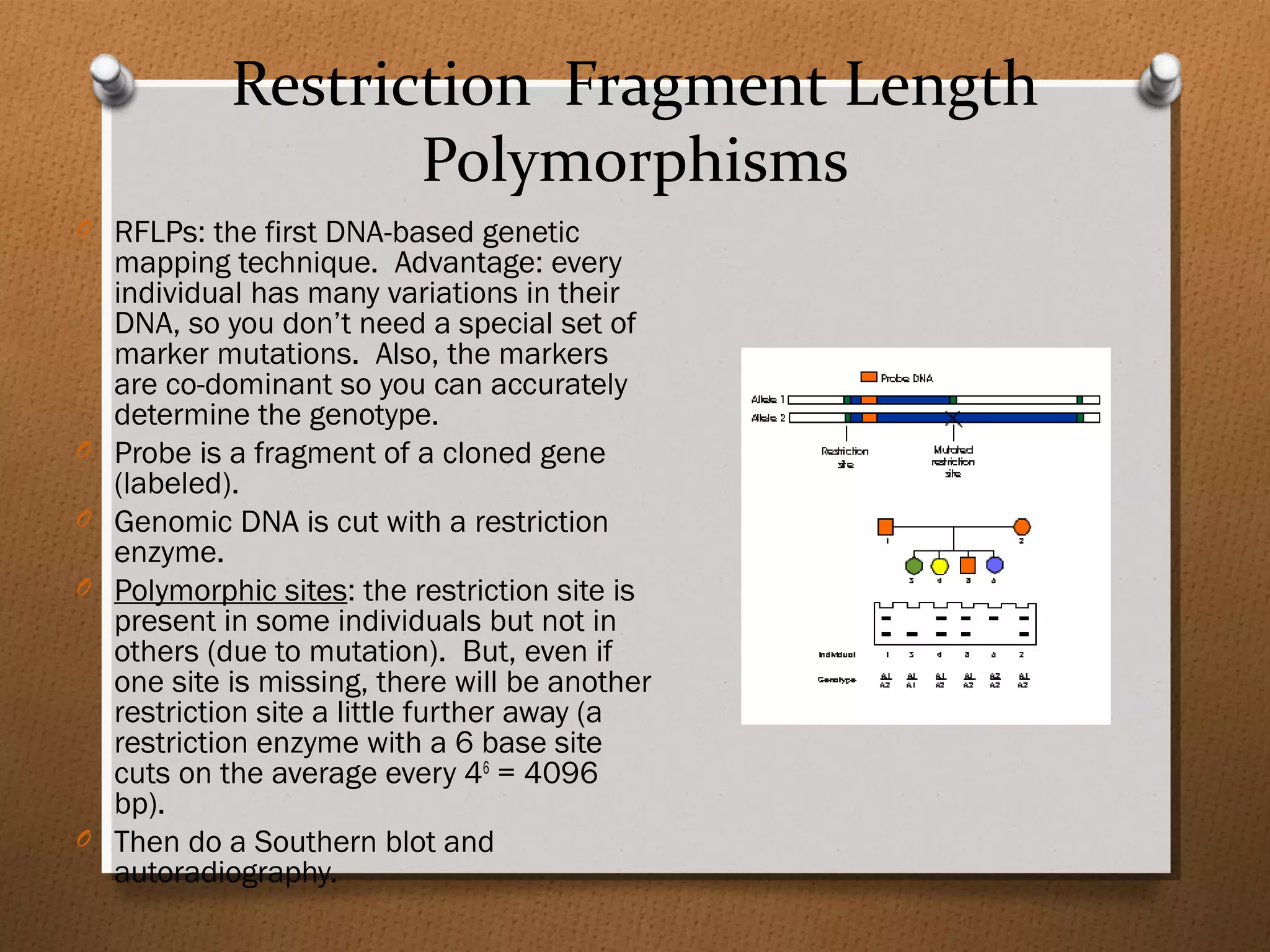
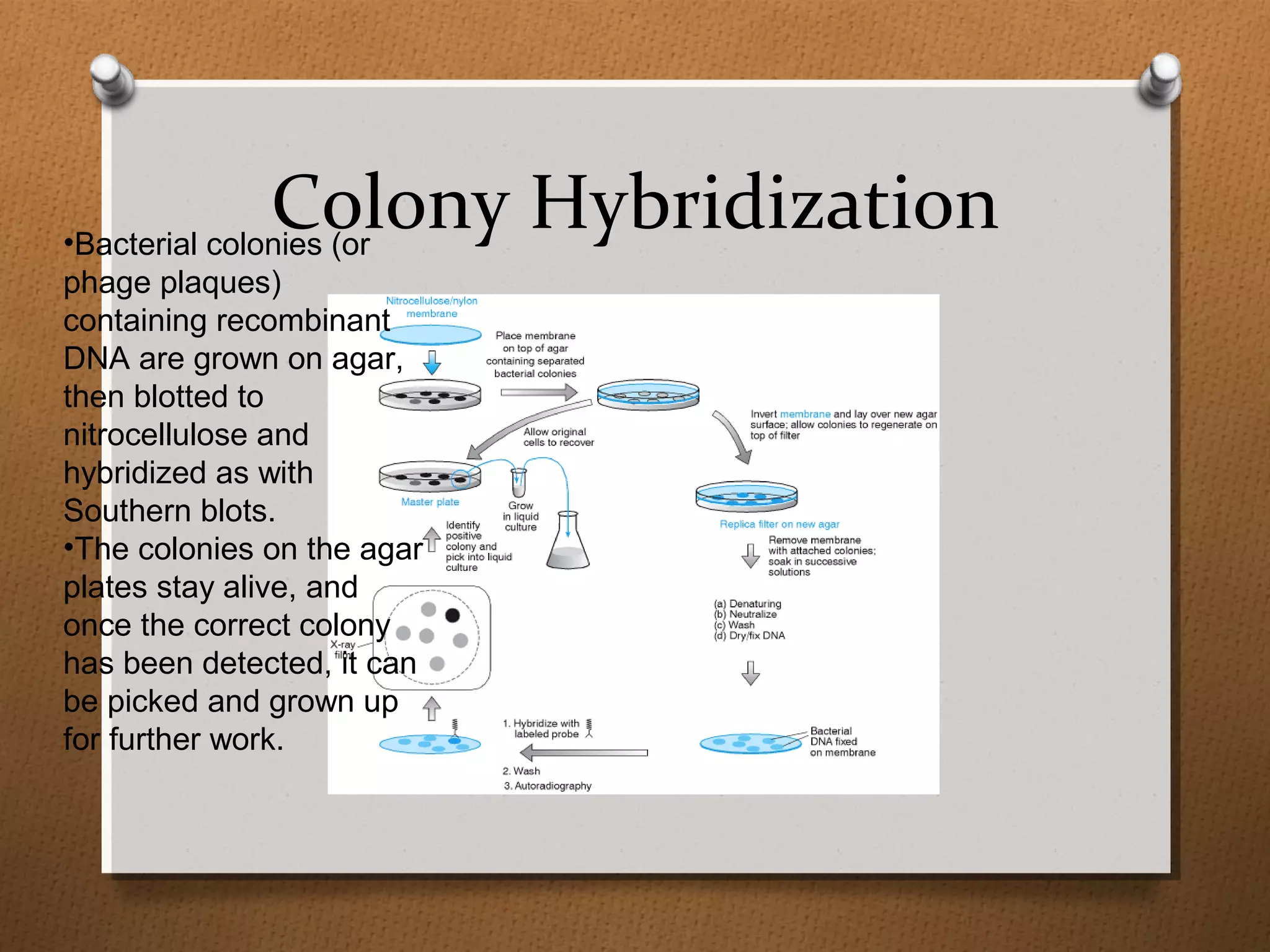
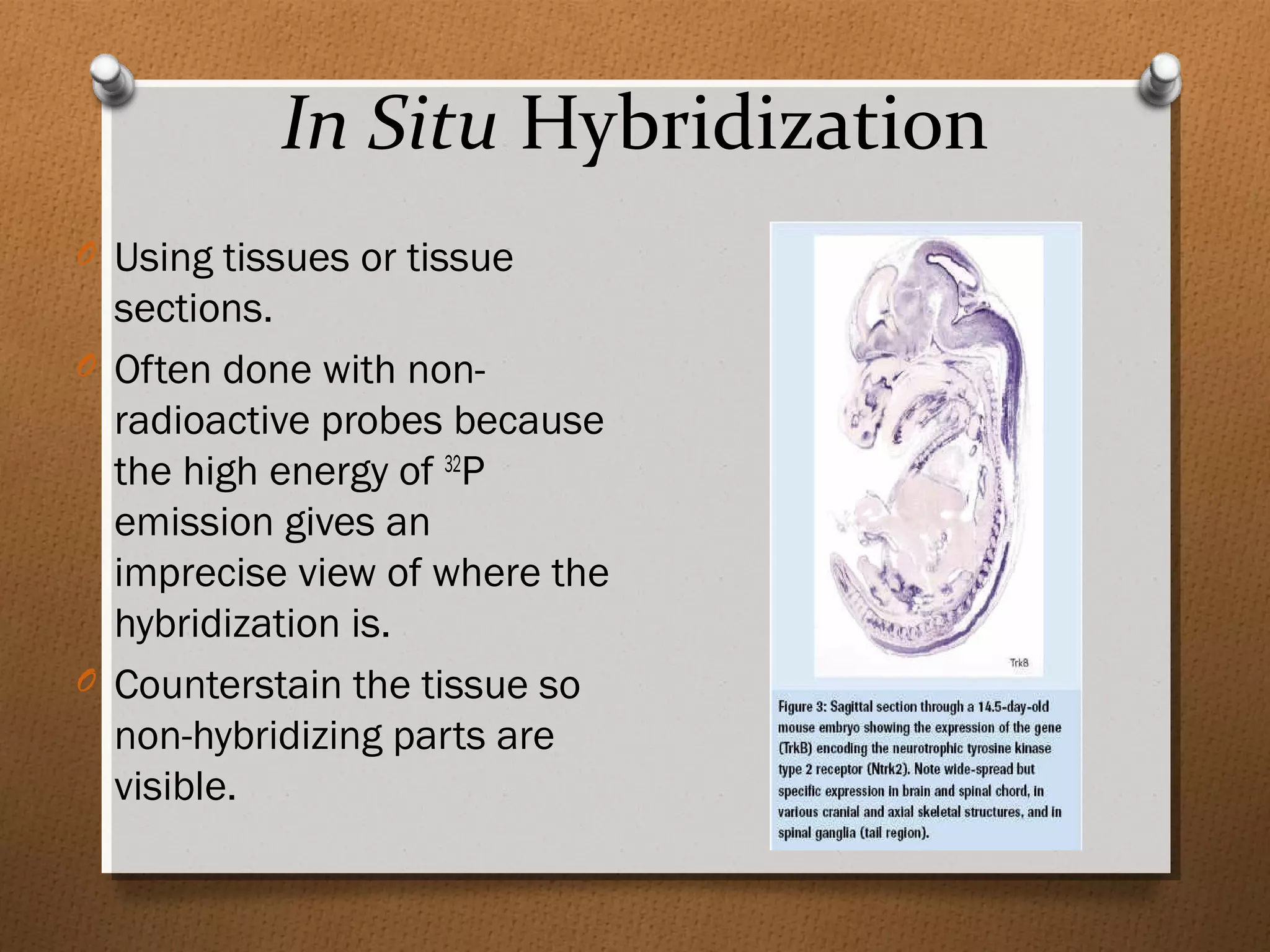
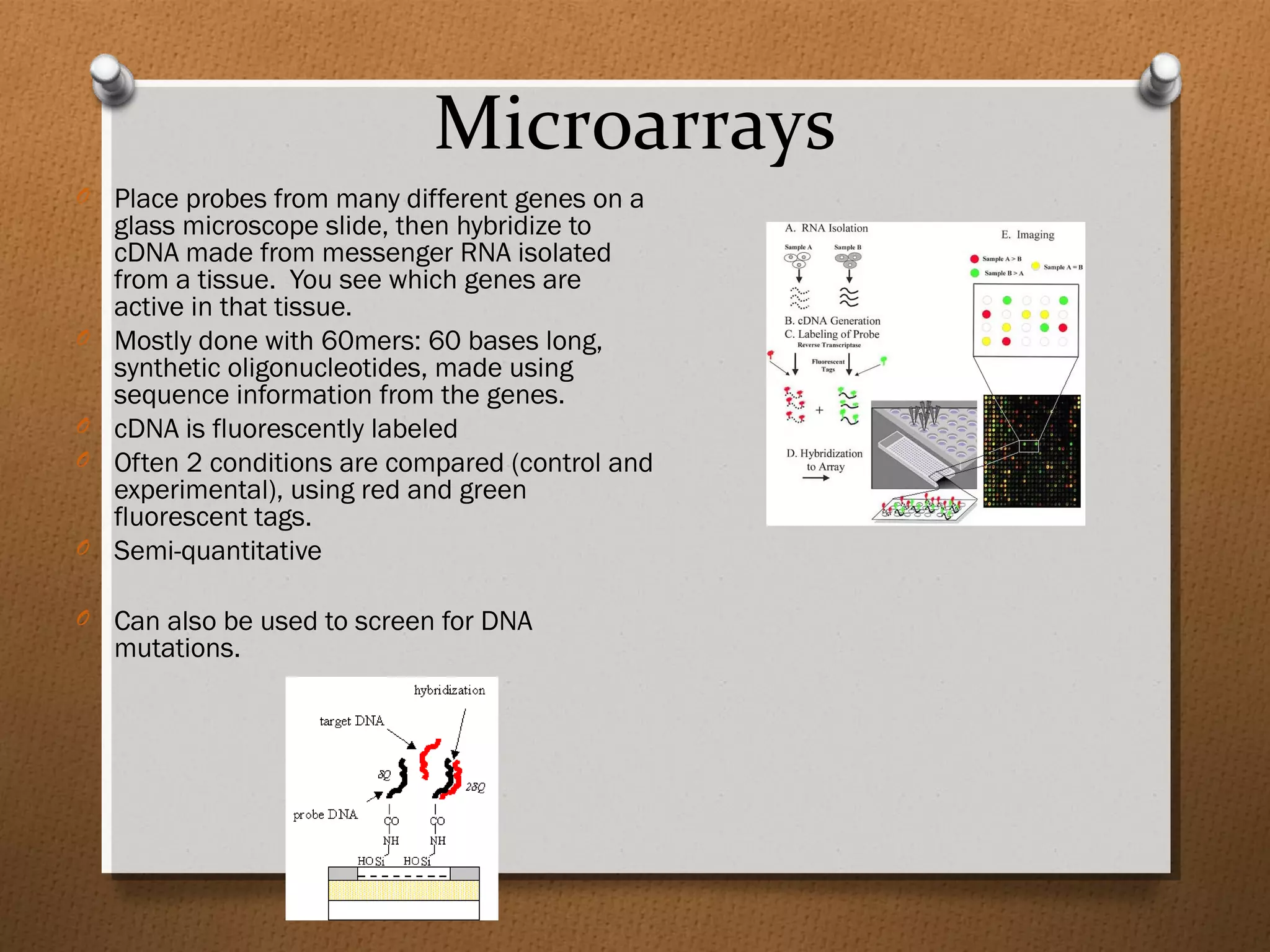
Recombinant DNA technology allows scientists to isolate and amplify specific genes from an organism's genome. There are three main approaches: polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to make copies of a gene region; cell-based molecular cloning using bacterial plasmids and restriction enzymes; and hybridization techniques using labeled probes to detect complementary DNA sequences. PCR is a powerful method that uses the enzyme DNA polymerase to exponentially amplify a targeted DNA region defined by primer sequences.