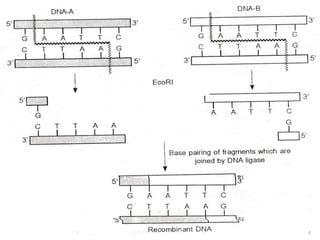
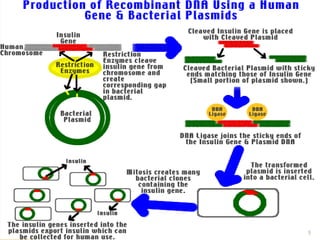
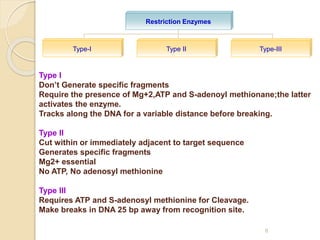
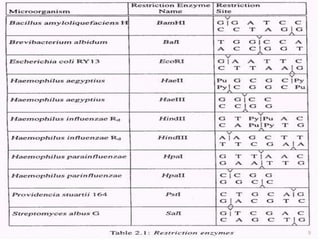
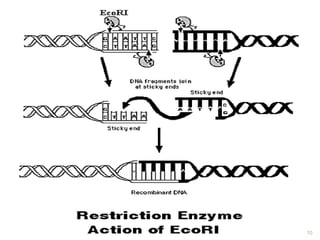
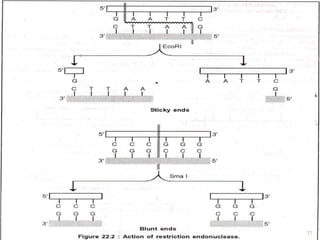
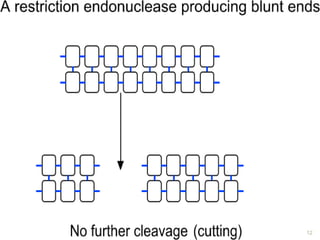
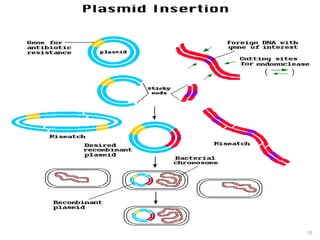
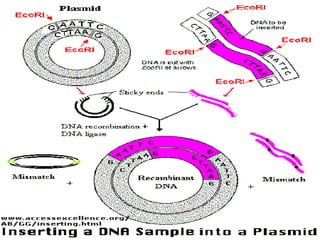
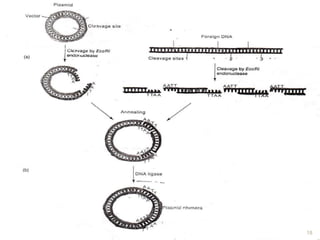
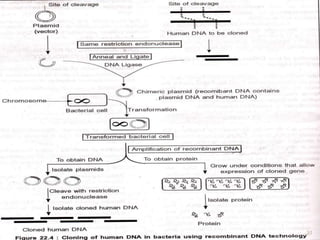
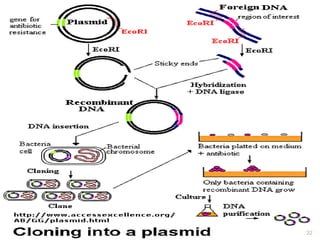
This document provides an overview of recombinant DNA technology. It discusses the basic principles, which involve generating DNA fragments, inserting a selected fragment into a cloning vector, introducing the vector into host cells, and multiplying the recombinant molecules. Key steps include using restriction enzymes to cut DNA at specific sites, ligases to join fragments, and various vectors like plasmids and bacteria to clone the DNA. The document also outlines several applications of rDNA technology, such as producing proteins, diagnosing diseases, and developing genetically engineered plants.