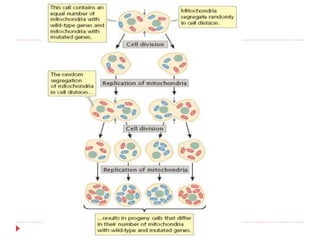
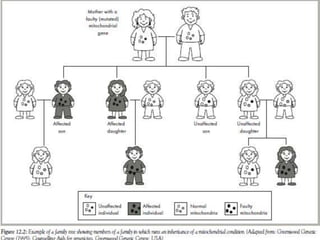
Cytoplasmic inheritance, also known as organellar inheritance, refers to the genetic transmission of traits due to plasmagenes located in the cytoplasm, primarily within mitochondria and chloroplasts. Notably, this type of inheritance is typically maternal, with traits passed from the female parent, as illustrated by C. Correns' work on leaf variegation in Mirabilis jalapa. This inheritance can manifest as either plastid (chloroplast) or mitochondrial inheritance, with the latter often leading to maternal inheritance of faulty mitochondrial genes affecting offspring energy production.