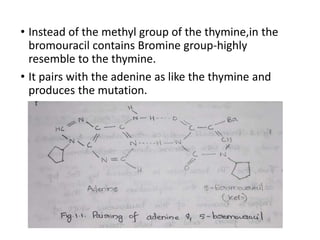
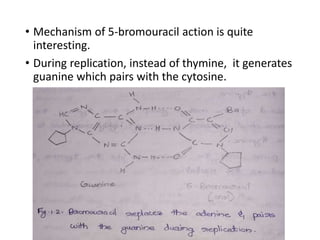
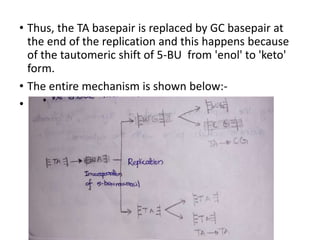
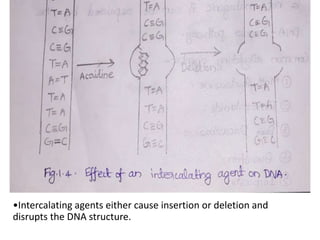
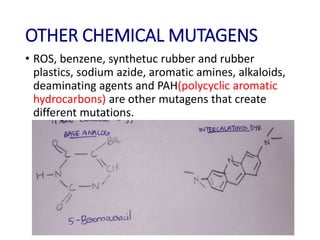
This document discusses different types of chemical mutagens that can cause mutations in DNA. It describes four main categories of mutagens: 1) base analogs like bromouracil and aminopurine that are incorporated into DNA instead of normal bases, 2) alkylating agents like mustard gas and ethylnitrosourea that add alkyl groups to DNA, 3) intercalating agents like ethidium bromide that insert between DNA bases, and 4) metal ions like nickel and chromium that can directly damage DNA or produce reactive oxygen species. It provides examples of common mutagens for each category and explains their mechanisms of inducing mutations.