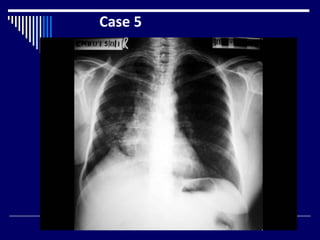
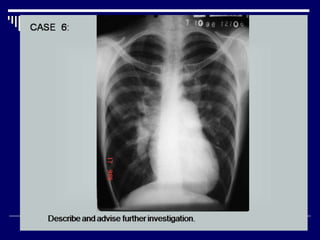
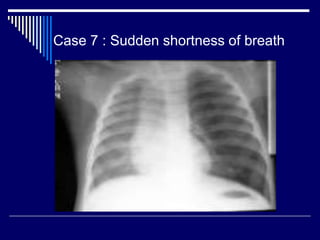
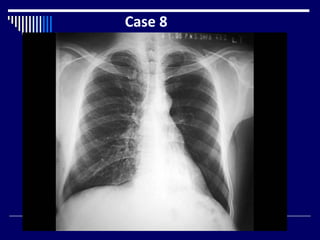
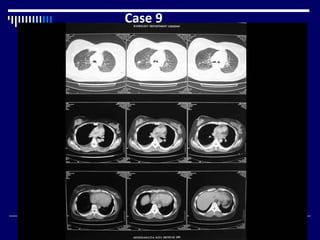
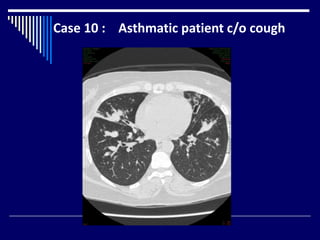
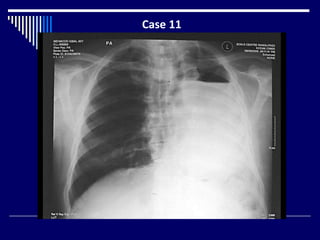
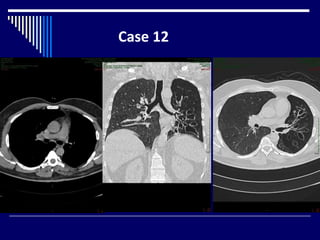
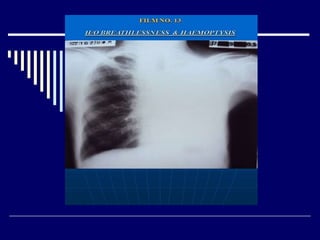
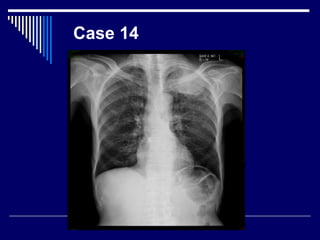
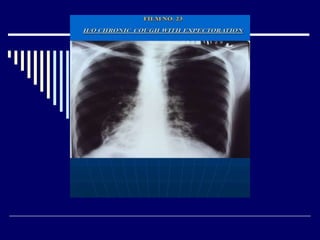
The document contains findings from 14 radiology cases summarized in 3 sentences or less:
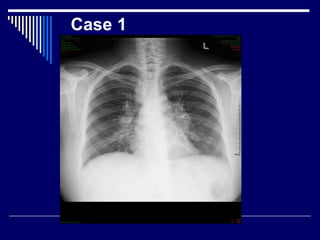
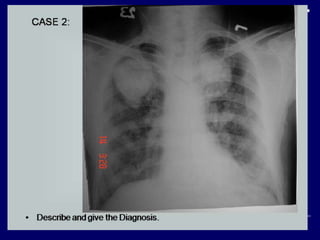
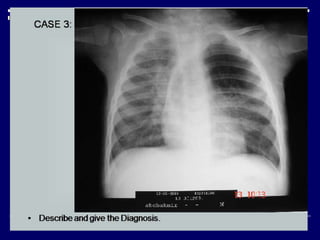
Case 1 describes bilateral symmetrical bulky hila and a diagnosis of sarcoidosis stage 1. Case 2 finds large rounded nodules with calcification, a diagnosis of pneumoconiosis with progressive massive fibrosis. Case 3 finds left upper lobe hyperinflation and herniation in a young child, diagnosed as congenital lobar emphysema.