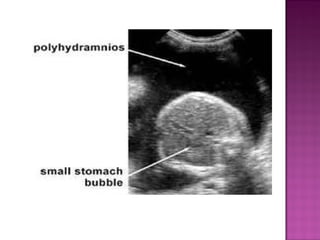
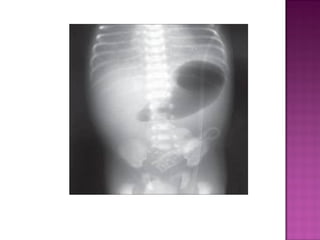
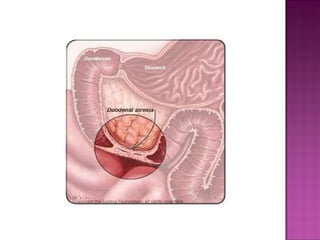
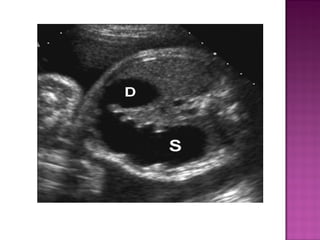
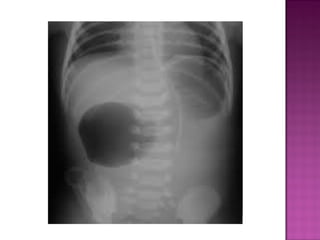
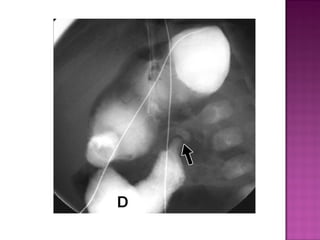
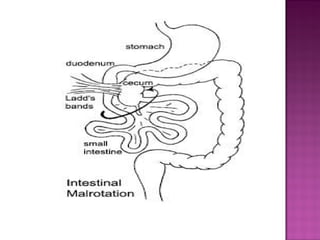
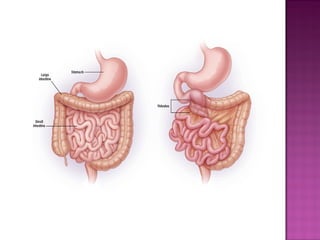
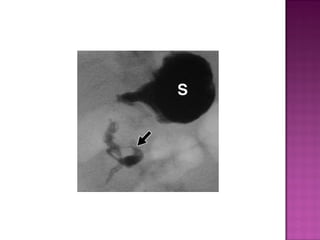
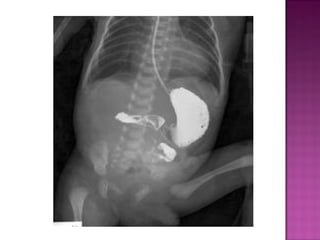
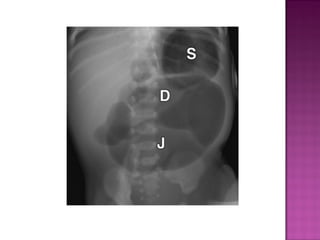
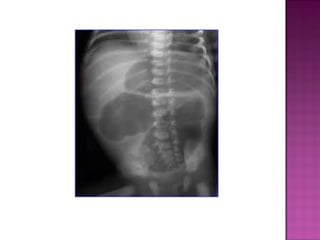
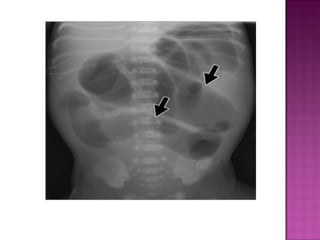
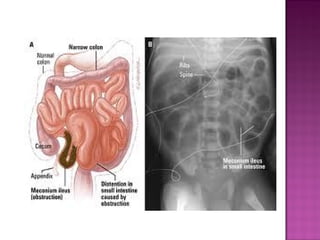
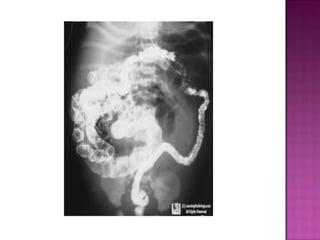
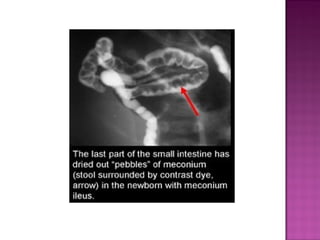
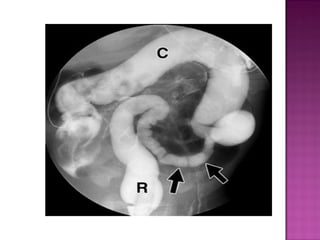
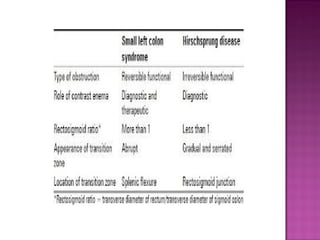
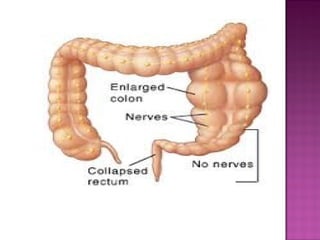
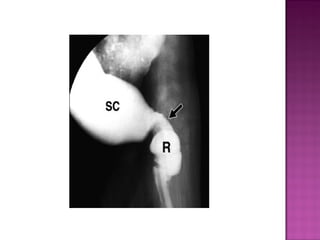
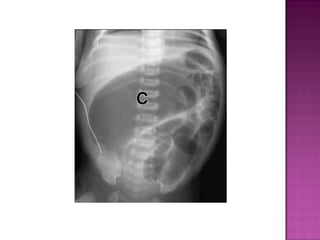
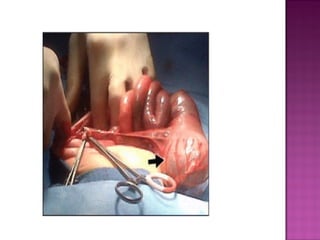
This document discusses various types of intestinal obstructions in neonates. It describes high intestinal obstructions, which occur proximal to the ileum such as gastric, duodenal or jejunal obstructions. It also describes low intestinal obstructions, which occur distal to the ileum and in the colon. Specific causes of obstruction discussed include duodenal atresia, intestinal malrotation, necrotizing enterocolitis, meconium ileus and Hirschsprung's disease. Diagnosis involves abdominal x-rays and contrast studies to identify the location and cause of obstruction.