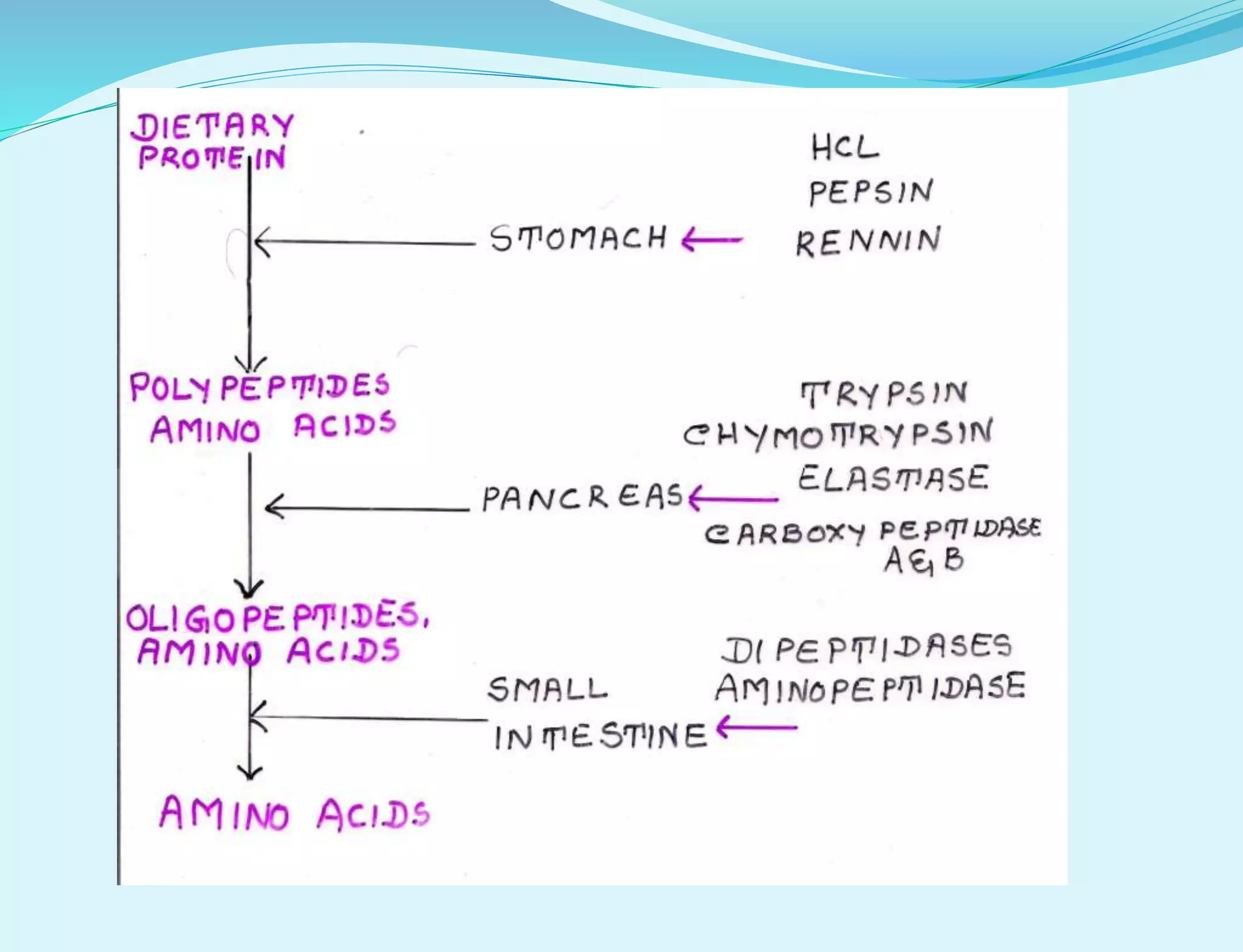
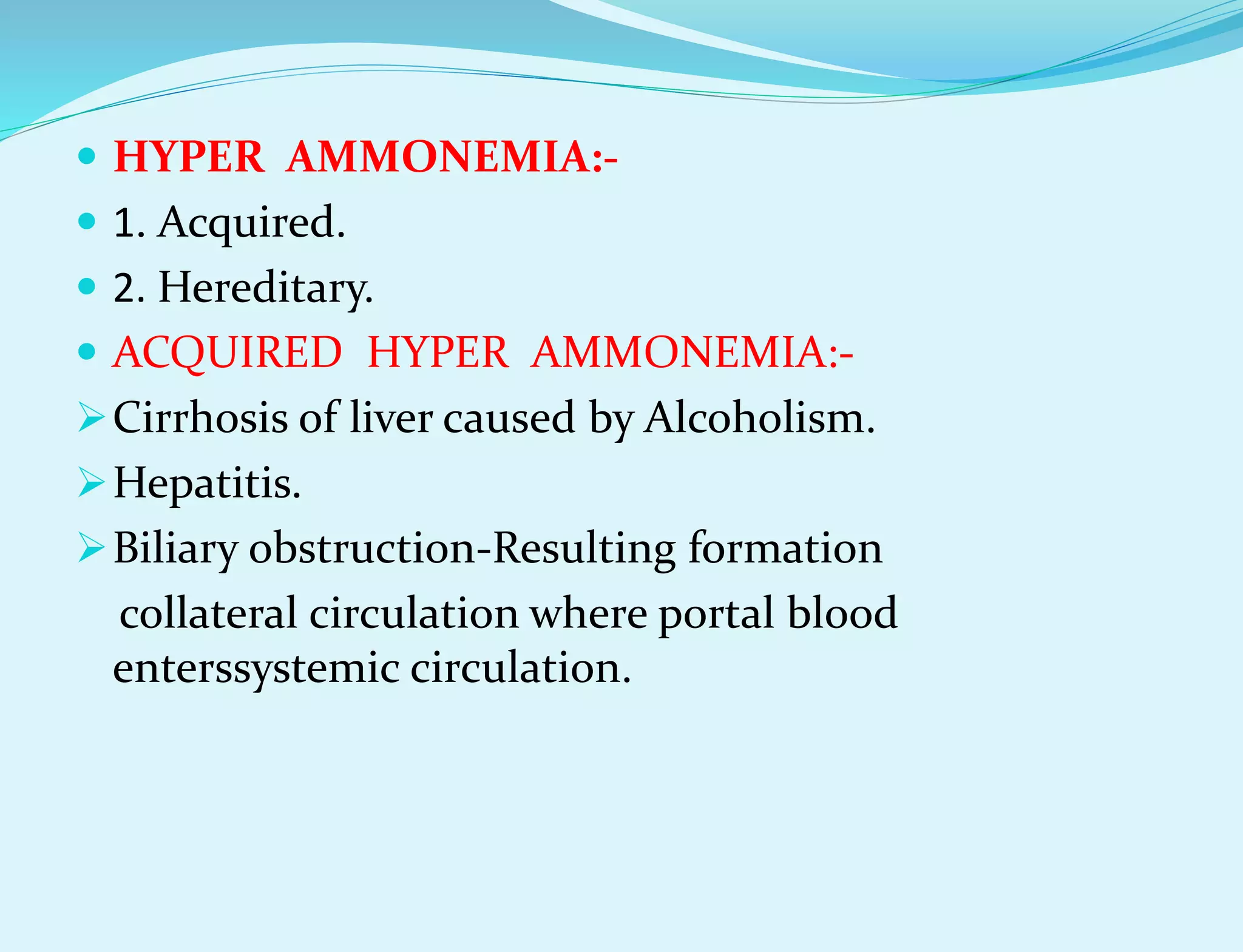
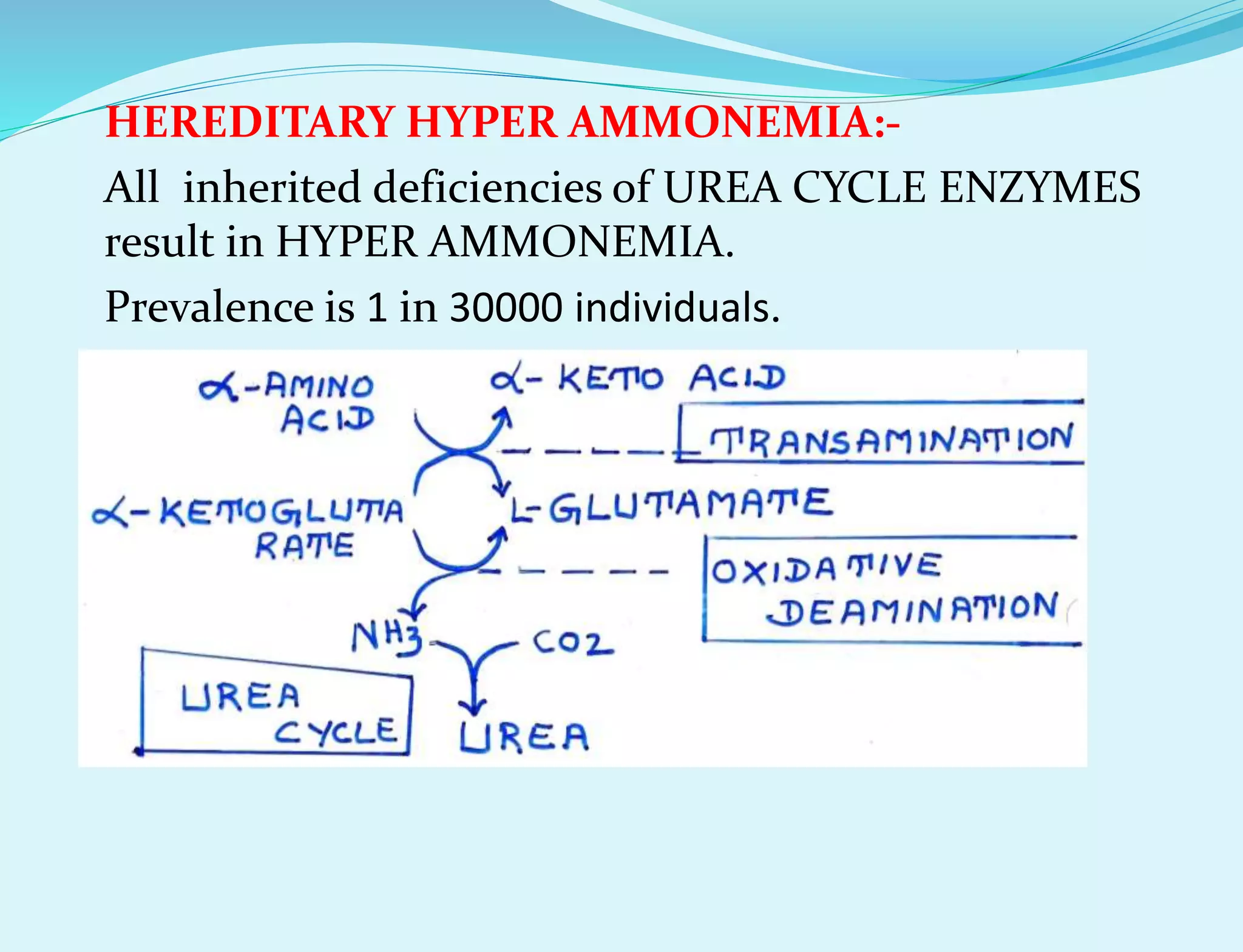
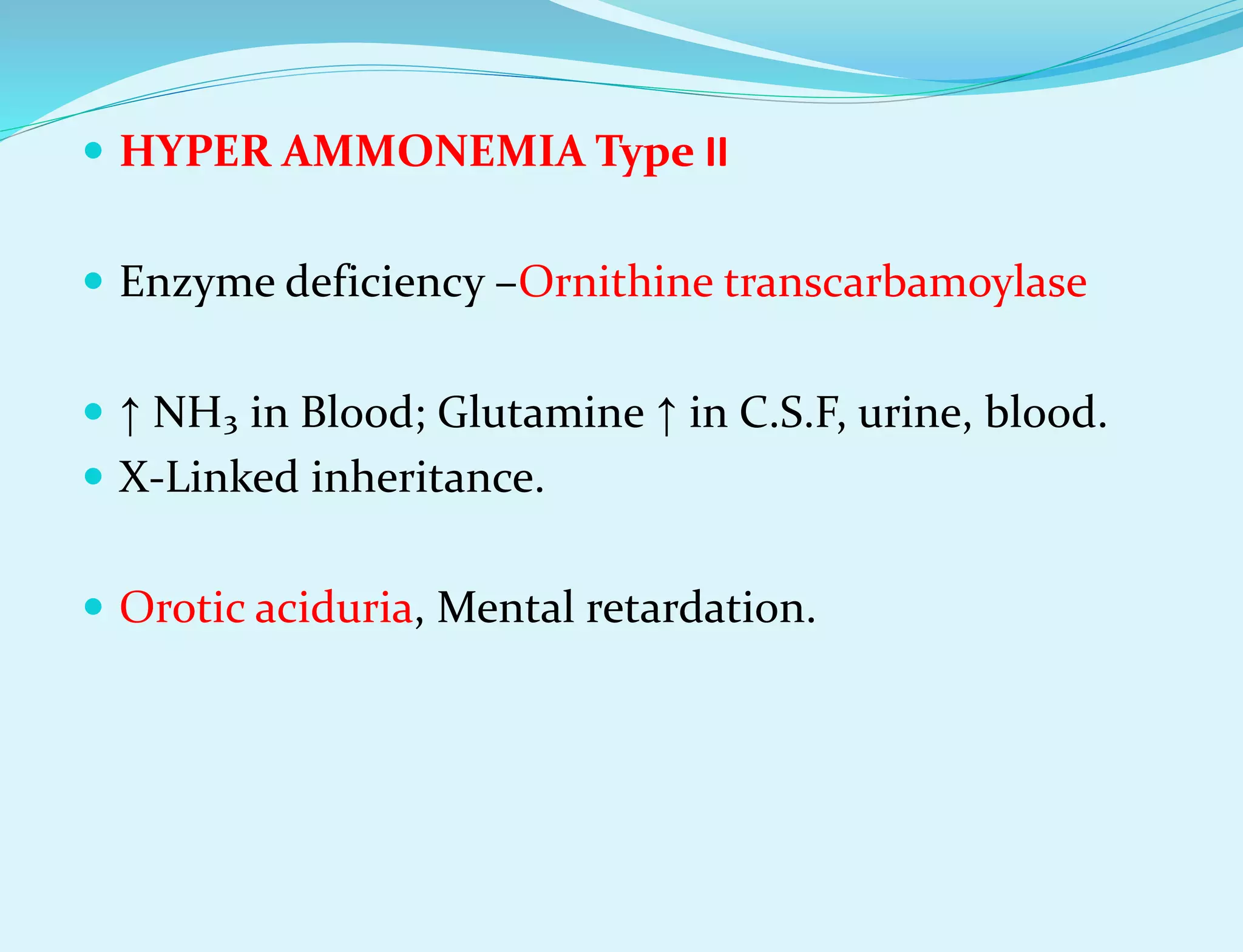
This document provides information about protein metabolism. It discusses that proteins undergo constant breakdown and resynthesis through protein turnover. The amino acids released are utilized for synthesis of new proteins, nucleic acids, and other biomolecules. Excess amino acids are converted to urea which is excreted in urine. The urea cycle occurring in the liver is the major route for ammonia detoxification. Deficiencies of urea cycle enzymes can cause hyperammonemia.