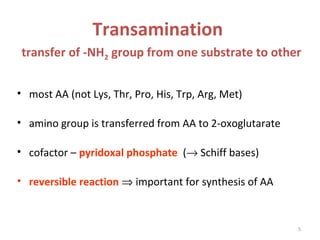
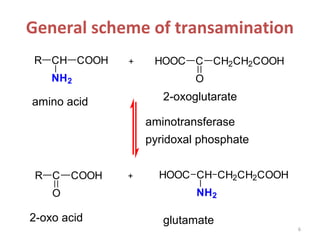
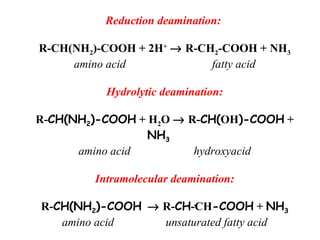
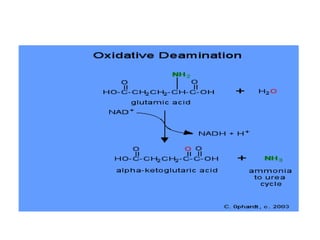
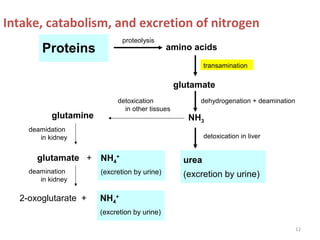
This document discusses transdeamination and deamination processes in the human body. It explains that transdeamination involves transamination followed by oxidative deamination, where the amino group is transported from tissues to the liver as glutamic acid and then deaminated in liver mitochondria. Transamination is the exchange of an amino group from one molecule, like an amino acid, to a keto group on another molecule like a keto acid. Deamination removes the amino group from a molecule, primarily through oxidative deamination of glutamic acid in the liver, converting the amino acid into a keto acid and ammonia. The ammonia is further processed in the urea cycle and excreted.